
Research identifies a potential developmental link related to autism
A study suggests a potential link to autism development
Many people experience an urgent need to use the bathroom shortly after eating, sometimes within minutes of finishing a meal. While this can feel alarming or inconvenient, doctors explain that it is often linked to a natural digestive response. However, in some cases, it may also point to an underlying digestive issue that shouldn’t be ignored.
Understanding why this happens can help you decide when it’s normal — and when it may be time to pay closer attention to your gut health.
In most cases, the sudden urge to poop after eating is caused by a natural bodily mechanism known as the gastrocolic reflex. When food enters the stomach, the stomach stretches. This triggers signals to the colon, telling it to start contracting and moving existing waste forward to make room for new food.
This reflex helps regulate digestion and bowel movements. It does not mean that the food you just ate is passing straight through your system. Instead, it’s your body clearing out what was already there.
For many people, this reflex is mild and barely noticeable. For others, it can feel strong and urgent.
Everyone has a gastrocolic reflex, but its intensity varies. Some individuals have a more sensitive digestive system, which makes the reflex stronger and faster.
People with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) often experience an exaggerated gastrocolic reflex. Their intestines may be more reactive to stretching and nerve signals, leading to cramping, urgency, or loose stools after meals.
Stress and anxiety can also amplify gut activity. Because the brain and digestive system are closely connected, emotional tension can trigger stronger bowel contractions after eating.

Certain factors can make the need to poop after eating more noticeable, including:
Large meals that stretch the stomach more than usual
High-fat or greasy foods
Caffeinated drinks like coffee or energy drinks
Alcohol
Food intolerances, such as lactose or certain carbohydrates
Spicy or heavily processed foods
These triggers don’t always signal a medical problem, but frequent reactions may indicate food sensitivity or digestive imbalance.

While post-meal bowel movements are often normal, doctors advise paying attention if the pattern is frequent, sudden, or disruptive, especially when combined with other symptoms.
You should consider medical advice if you experience:
Diarrhea after most meals
Abdominal pain, cramping, or bloating
Urgent bowel movements that are hard to control
Unexplained weight loss
Symptoms that persist for several weeks
In these cases, the issue may be related to IBS, food intolerance, malabsorption, inflammation, or another gastrointestinal condition that needs evaluation.

If needing to poop immediately after eating interferes with daily life, several strategies may help:
Eat smaller, more frequent meals instead of large ones
Identify and limit trigger foods
Reduce fatty, fried, and highly processed foods
Manage stress through relaxation techniques
Keep a food and symptom diary to spot patterns
These steps can often reduce the intensity of the gastrocolic reflex and improve digestive comfort.
Needing to poop shortly after eating is usually caused by the gastrocolic reflex — a normal part of digestion. For most people, it’s harmless. However, if the urge is strong, frequent, or accompanied by pain or diarrhea, it may be your body signaling a deeper digestive issue.
Listening to your symptoms and seeking medical guidance when needed can help protect your gut health and prevent long-term problems.

A study suggests a potential link to autism development

Fa.tty liver explained: Causes, symptoms and effective treatment options
Doctors Issue Warning: These 4 Morning Symptoms May Signal Lung Cancer Is Advancing

Doctors identify the blo.od type linked to the lowest can.cer risk

An overlooked vegetable packed with nutrients and remarkably high in calcium
This natural drink may help ease mucus, cough and sinus discomfort
How to get rid of phlegm and mucus in your chest and throat

Eating walnuts regularly can bring a wide range of health benefits

You don’t need to believe in magic drinks to enjoy beet juice.


These foods were found to benefit not only cardiovascular health but also provide clear advantages for the nervous system and cognitive function.
A single rushed movement after waking up can trigger a stroke.
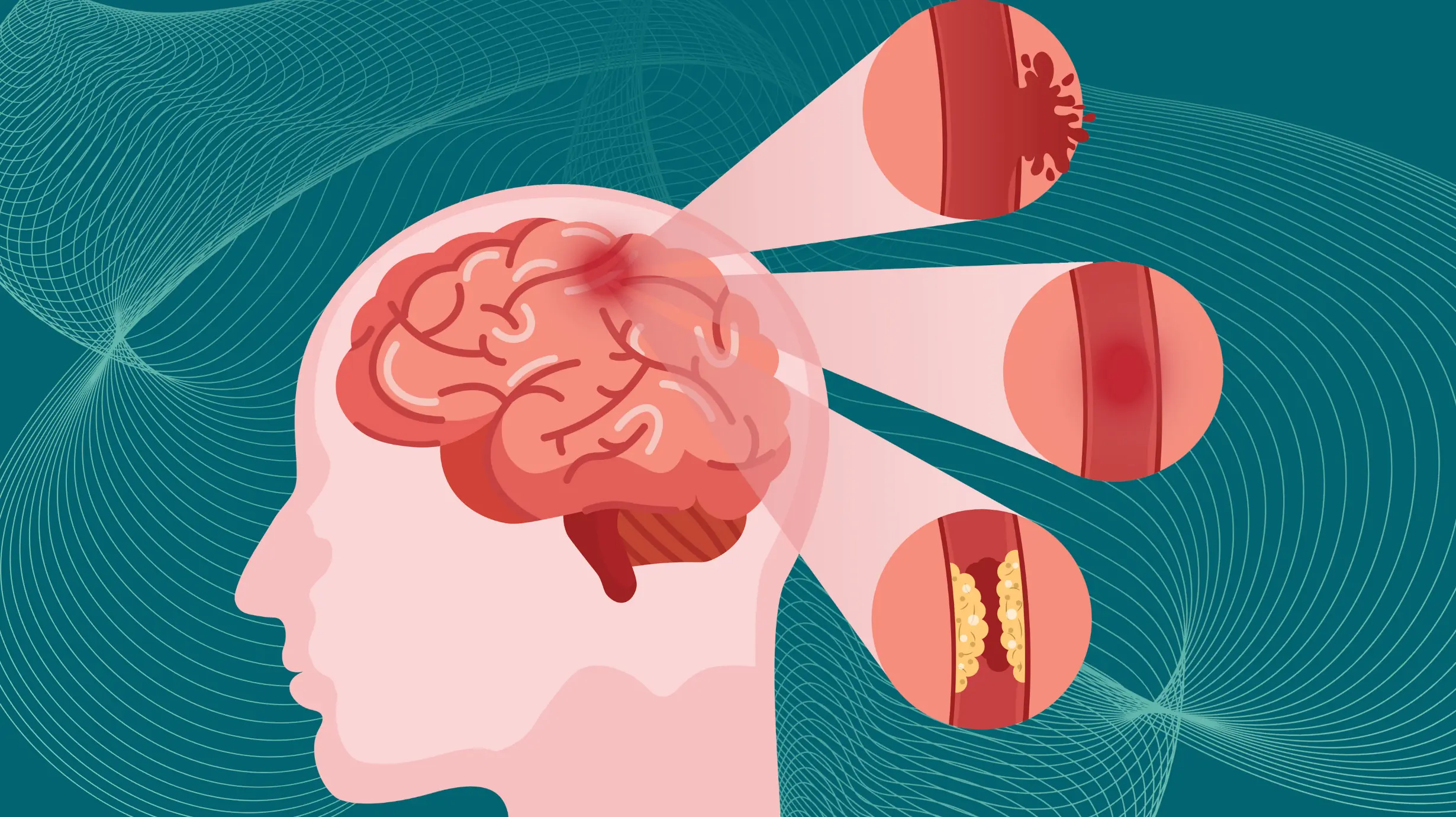
Preventing Stroke At Any Age: 3 “Don’ts” After Meals — And 4 “Don’t” Before Bed

Nighttime leg cramps may signal dehydration or hidden health issues.
Say Goodbye to Swelling …
Understanding Mucus in the Throat: Causes You Might Not Expect

Here are 3 dishes you should add to your daily menu
Some unhealthy habits during intimacy may be a hidden cause of cervical can.cer in women

3 fruits that fight liver fat, regulate sugar and cholesterol

A study suggests a potential link to autism development

Fa.tty liver explained: Causes, symptoms and effective treatment options

Doctors Issue Warning: These 4 Morning Symptoms May Signal Lung Cancer Is Advancing

Doctors identify the blo.od type linked to the lowest can.cer risk

An overlooked vegetable packed with nutrients and remarkably high in calcium

This natural drink may help ease mucus, cough and sinus discomfort

How to get rid of phlegm and mucus in your chest and throat

A creamy, healthy burrito that’s quick to make and impossible to resist.

Eating walnuts regularly can bring a wide range of health benefits

You don’t need to believe in magic drinks to enjoy beet juice.

After a period of use, showerheads often get clogged due to mineral deposits sticking inside, causing uneven water flow.

Here’s a surprisingly simple household trick to sharpen your old, dull scissors without any special tools.


These foods were found to benefit not only cardiovascular health but also provide clear advantages for the nervous system and cognitive function.

A single rushed movement after waking up can trigger a stroke.
Your sleeping posture may reveal more about your future than you think.

Preventing Stroke At Any Age: 3 “Don’ts” After Meals — And 4 “Don’t” Before Bed

Certain everyday phrases may quietly signal emotional or physical infidelity.

Nighttime leg cramps may signal dehydration or hidden health issues.