
Swollen legs and edema are symptoms of what disease?
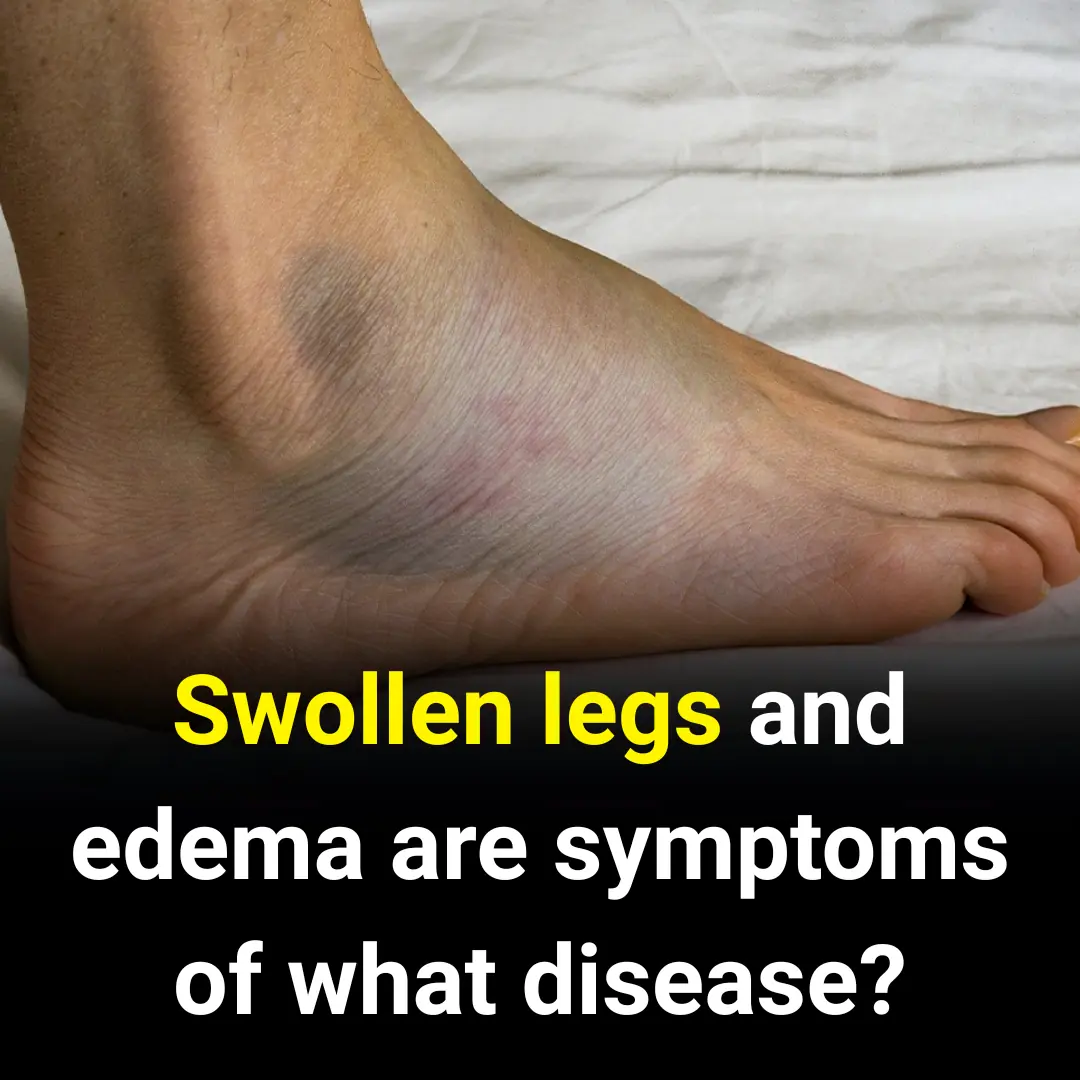
Swelling in the feet, ankles, or lower legs is often caused by fluid buildup or the body’s response to injury or infection.
Edema is a condition where excess fluid is retained in body tissues, causing swelling—commonly in the feet, ankles, and lower legs. It may be due to injury or inflammation. Swelling can make walking difficult, so identifying the cause is important for timely treatment.
Here are some common causes of swelling and edema in the legs:
-
Pregnancy
-
Swelling in the legs is common during pregnancy due to factors like natural fluid retention, increased pressure on veins from an expanding uterus, and hormonal changes.
-
Pregnant women often experience more swelling in the evening, especially after long walks. Swelling in the feet and ankles usually starts from the fifth month of pregnancy and resolves after childbirth.
-
Sudden or severe swelling in the ankles, hands, or face could be a sign of preeclampsia, a serious condition marked by high blood pressure and protein in the urine, usually occurring after the 20th week.
-
To prevent swelling: avoid standing for long periods, elevate your feet when sitting, wear comfortable shoes (avoid high heels), wear compression socks or stockings, and sleep on your left side.
-
If the swelling is painful, see a doctor to check blood pressure and rule out preeclampsia or other conditions.
-
-
Bursitis
-
Bursitis occurs when the fluid-filled sacs around joints become inflamed, causing pain and swelling.
-
It is common among older adults and people who overuse joints, such as athletes or those with physically demanding jobs.
-
It can occur in any joint with a bursa, but is most common in the legs, knees, and ankles.
-
Treatment includes pain relievers, ice packs, and rest. More serious cases may require corticosteroids or antibiotics if infection is present.
-
-
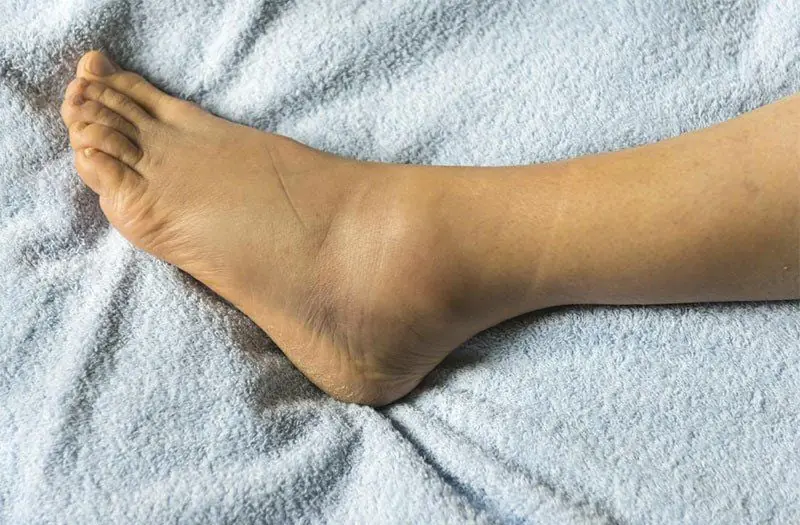
Chronic venous insufficiency
-
This condition occurs when vein valves are damaged from prolonged standing or sitting, affecting blood flow from the legs to the heart.
-
It leads to blood pooling in leg veins and causes swelling.
-
Prevention includes: avoiding long periods of standing/sitting, doing foot and ankle exercises, elevating the legs, walking regularly, maintaining a healthy weight, and wearing compression stockings.
-
-
Diabetes
-
Diabetes affects blood sugar control, which can lead to poor circulation and fluid buildup in the lower legs.
-
Chronic circulation problems may also damage foot nerves, causing injuries and swelling.
-
To reduce swelling: wear compression socks, exercise regularly, elevate legs while sleeping, lose weight, reduce salt intake, and soak feet in Epsom salt (under doctor supervision).
-
-
Gout
-
Caused by uric acid buildup in the blood, gout leads to swelling in affected joints—especially the big toe.
-
Flare-ups typically last 3 to 10 days.
-
Treatment includes NSAIDs or corticosteroids to prevent flare-ups. Apple cider vinegar and tart cherry juice may help relieve symptoms, but consult a doctor for severe cases.
-
-
Kidney disease
-
Poor kidney function can cause excess salt buildup in the blood.
-
The body retains fluid, leading to swelling in the feet and ankles.
-
Other symptoms may include: trouble concentrating, loss of appetite, fatigue, sleep issues, muscle cramps, dry itchy skin, frequent urination, nausea, and vomiting.
-
Treatment may involve diuretics, blood pressure medications, cholesterol-lowering drugs, calcium and vitamin D supplements.
-
-
Injury
-
Swelling in the feet, ankles, or lower legs may result from inflammation due to acute or chronic injury.
-
Blood rushes to the injured area, causing swelling.
-
Common injuries include sprains, fractures, or tendon tears.
-
Use ice packs (up to 20 minutes at a time), compression bandages, elevate the leg (especially at night).
-
Depending on severity, doctors may prescribe painkillers, braces, or surgery.
-
-
Lymphedema
-
Caused by damage or removal of lymph nodes (often during cancer treatment), leading to fluid retention and swelling in the feet and ankles.
-
Other symptoms: tight or heavy feeling, limited mobility, aches, and recurring infections.
-
Though not curable, it can be managed by reducing pain and swelling. Severe cases may require surgery. Light exercises, elevation, and massage are often recommended.
-
-
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
-
An autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks the lining of the joints.
-
Fluid builds up around joints, causing swelling and potential permanent damage.
-
Symptoms also include joint pain, stiffness, fatigue, fever, and anemia.
-
Treatment may involve corticosteroids, NSAIDs, and physical therapy.
-
News in the same category


Some vegetables flagged for possible can.cer risks are still commonly eaten, raising health concerns.

When the body sends out these 4 signals, your cervical spine may be “crying for help”: Don’t wait until paralysis to regret it

Red Clover: 15 Amazing Benefits and How to Use This Healing Herb

Senna Alata: The Powerful Candle Bush Offering 30 Remarkable Health Benefits and Simple DIY Remedies

Boiled Bay Leaves and Cloves: A Powerful Natural Elixir for Better Health

Eating leftovers from the fridge, 50-year-old man d.i.e.s: 5 foods you should never keep overnight, if left over, throw it away

Juniper: An ancient healing plant with powerful modern benefits
Red-Brown Speckles on Palms and Fingers: Harmless Marks or a Health Warning?
9 Early Signs of Diabetes You Shouldn't Ignore

Eggs and health: 6 types of eggs you should avoid to protect your body

10 powerful foods that can help lower your risk of str.oke
White Spots Around the Eyes: What Are They Really Telling You About Your Health?

This fruit is known as the “poor man’s ginseng”: cheap, available year-round, and sold in every Asian market

Don't Eat Sweet Potatoes Until You Know These 13 Important Facts!

5 types of vegetables that help detoxify and lower liver enzymes

5 effective drinks that support rapid blo.od sugar reduction
Muscle pain behind the knee, a dan.gerous symptom that should not be ignored
A Young Couple Both Developed Li.ver Ca.ncer Because of a Type of “Purified Water” Many People Believe Is Clean

10+ Warning Signs You're Eating Too Much Sugar
News Post
Four Conditions That Seem Harmless but Can Be Precursors to Can.cer

The ‘Longevity Drink’ That Keeps an 82-Year-Old Professor Energetic and Youthful

Some vegetables flagged for possible can.cer risks are still commonly eaten, raising health concerns.

Clam and Mushroom Clear Soup

A Rare Blood Moon Will Occur on March 3, 2026

When the body sends out these 4 signals, your cervical spine may be “crying for help”: Don’t wait until paralysis to regret it

Red Clover: 15 Amazing Benefits and How to Use This Healing Herb

Shrimp Rice Porridge (Savory Congee)

Senna Alata: The Powerful Candle Bush Offering 30 Remarkable Health Benefits and Simple DIY Remedies

Boiled Bay Leaves and Cloves: A Powerful Natural Elixir for Better Health

Strawberry Cheesecake Stuffed Cookies

There’s always a reason: Why dogs bark at or chase people?

Eating leftovers from the fridge, 50-year-old man d.i.e.s: 5 foods you should never keep overnight, if left over, throw it away

Juniper: An ancient healing plant with powerful modern benefits

Garlic skins may seem useless, but they can be surprisingly helpful in daily life

Red-Brown Speckles on Palms and Fingers: Harmless Marks or a Health Warning?

Chicken, Avocado & Tomato Bowl

Teriyaki Chicken Healthy Bowl

9 Early Signs of Diabetes You Shouldn't Ignore
