Ectomorph, Mesomorph, or Endomorph? Discover Your True Body Type
Ectomorph, Mesomorph, or Endomorph? Discover Your True Body Type

Bruising occurs when blood becomes trapped under the skin, usually following an impact injury that damages small blood vessels. However, not all bruising has a simple explanation.
Although random or sudden bruising does not necessarily mean a person has a medical condition, it may still be worth discussing with a doctor.
This article will expand on the factors and causes of random bruising and accompanying symptoms. It will also explain bruising during pregnancy and when to see a doctor.
Most bruises are nothing to worry about and will heal within weeks or months. They can vary in color, and skin color may affect the appearance of a bruise.
However, random, sporadic bruising may be a symptom of something less obvious, especially if there are other symptoms. Bruises on the torso, back, or face could be a concern.
Here are some key factors in random bruising:
Unexplained bruising is very common and heals relatively quickly. However, if a bruise persists, changes in size, or looks unusual, there may be an underlying condition or other factors.
The following are some possible causes of random bruising.
Medications such as anticoagulants, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and corticosteroids reduce the blood’s ability to clot. This may result in blood leaking from vessels and accumulating under the skin.
Someone who takes medication and has random bruising should speak to a doctor for advice and to discuss their drug and family medical history.
Underlying bleeding disorders — such as hemophilia, thrombocytopenia, or factor V deficiency — can cause bruising.
Hemophilia is a rare genetic condition in which people lack either clotting factor VIII or IX, resulting in excessive bruising.
People with immune thrombocytopenia have a low platelet count, and bruising
Factor V deficiency is a
Other common symptoms of a bleeding disorder include:
Sepsis is an infection that causes a buildup of toxins in the blood or tissues. People with sepsis may develop a cluster of tiny blood spots, resembling pinpricks in the skin (petechiae) or purple areas (purpura). Without treatment, these may increase, join together, and form larger bruises.
Also known as blood poisoning, sepsis requires immediate emergency treatment.
A poor diet can negatively affect health, and vitamin deficiencies can contribute to random bruising.
Some deficiencies include vitamin C deficiency and vitamin K deficiency.
Vitamin C is versatile and vital to health. It is necessary for collagen production, boosts the immune system, and maintains antioxidant activity. It also eliminates harmful free radicals that can lead to tissue degeneration and random bruising.
The result of extreme vitamin C deficiency is scurvy, which also leads to bleeding gums, fingernail and tooth loss, and heart failure.
Meanwhile, vitamin K deficiency can
However, taking anticoagulants and antibiotics that interfere with vitamin K production may cause deficiencies.
People can prevent vitamin deficiencies by making dietary changes and taking supplements.
When the liver experiences damage, it stops producing the proteins required for blood clotting. Cirrhosis, for example, is the result of continuous long-term damage, and bruising easily is a symptom.
However, it may appear alongside fatigue, appetite loss, abdominal pain, and nausea. A person with kidney disease may also bruise easily due to a loss of skin elasticity.
Medications for treating liver or kidney disease can also hinder the blood clotting process and inhibit platelet function. Ecchymosis, which occurs when blood leaks from a broken capillary into surrounding tissue, is common and requires a preventive treatment plan.
Anyone who suspects liver or kidney disease should consult a doctor.
Cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy and targeted therapy, may also lead to bruising. This is because they lower the amount of platelets in the blood.
Easy bruising and bleeding are common leukemia symptoms. They generally affect the back, legs, and hands. Another indication of possible leukemia is lots of bruises with no indication as to a cause. Bruises that take longer than usual to disappear are another concern.
Bernard-Soulier syndrome is a rare, inherited blood clotting disorder. People with this condition may bruise easily, bleeding from small blood vessels under the skin.
Doctors will check a woman’s platelet levels throughout pregnancy, but bruising could be a symptom of gestational thrombocytopenia, which can lead to a low platelet count.
Always mention any unusual bruising during pregnancy to a doctor or midwife.
It is impossible to completely prevent bruising. Although bruises are usually harmless, they can sometimes indicate a medical condition that requires treatment.
For example, a person should see a doctor if:
Bruises may result from underlying medical conditions, age as the skin becomes thinner, or genetics. Many bruises may also result from knocks against objects and usually fade within a few weeks.
A person should speak with a doctor if they have continuous bruising with no apparent reason, bruises in certain locations such as the torso, or they appear alongside other symptoms such as fatigue and nausea.
Deficiencies that may cause random bruising include vitamin C deficiency and vitamin K deficiency.
Occasional bruising is rarely a cause for concern. However, it is worth talking with a doctor if the discoloration does not heal within a few weeks. There may be a blood clotting issue or another underlying condition that needs treatment.
Taking certain medications and growing older can be the root of the problem. However, further investigation may be necessary if a person experiences other symptoms alongside random bruising.

Ectomorph, Mesomorph, or Endomorph? Discover Your True Body Type

The Hidden Health Risks of Poor Sleep Posture (And How to Correct Them)

7 must-know tips for using cloves effectively
Researchers outline 7 hidden health problems your nails might suggest
For many people, simply hearing the word “colonoscopy” is enough to cause immediate fear or discomfort.

Peanuts, also known as groundnuts, are rich in vitamins and nutrients, often hailed as a "longevity nut" that is highly beneficial for health.
Occasionally noticing foamy urine is usually harmless and not a cause for concern.

Heart disease does not always announce itself with dramatic chest pain during the day. In many cases, the heart sends subtle warning signals at night, when the body is at rest and symptoms become more noticeable.
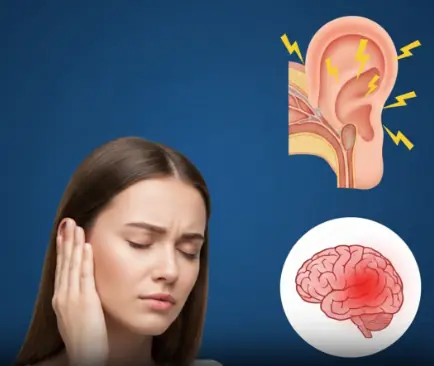
Have you ever noticed a faint hum, buzz, or ringing in your ear — especially when everything around you is silent?

When our skin becomes itchy, we often attribute the discomfort to external factors such as sweat, hygiene products, laundry detergents, or the fabric of our clothing.
tching is a common condition that everyone experiences, and it is usually not a serious sign.

Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) is one of the most studied and respected medicinal plants in modern herbal medicine.

Understanding Persistent Tinnitus and When to Seek Care
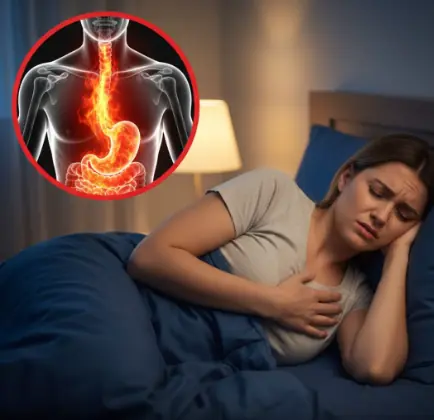
Waking up with a dry mouth may feel like a small inconvenience, but it can actually be your body’s subtle way of raising a warning sign.
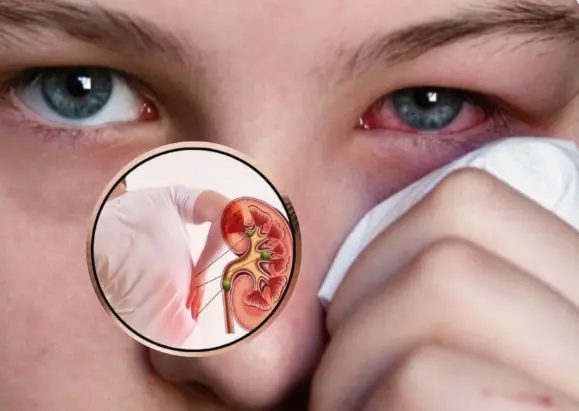
Kidney failure is a serious condition that can lead to lifelong dialysis or other severe health complications if left untreated.
Pain on the right side: This is what it could mean
Thyroid patients: check this list before your next meal.
A lump in the neck can be harmless or a sign of something serious

Doctors say this simple daily habit can help your health after 50 👇

Stone breaker: A traditional plant remedy strengthened by modern findings

Ectomorph, Mesomorph, or Endomorph? Discover Your True Body Type

The Hidden Health Risks of Poor Sleep Posture (And How to Correct Them)

7 must-know tips for using cloves effectively

Researchers outline 7 hidden health problems your nails might suggest

For many people, simply hearing the word “colonoscopy” is enough to cause immediate fear or discomfort.

Peanuts, also known as groundnuts, are rich in vitamins and nutrients, often hailed as a "longevity nut" that is highly beneficial for health.

Occasionally noticing foamy urine is usually harmless and not a cause for concern.

Heart disease does not always announce itself with dramatic chest pain during the day. In many cases, the heart sends subtle warning signals at night, when the body is at rest and symptoms become more noticeable.

Have you ever noticed a faint hum, buzz, or ringing in your ear — especially when everything around you is silent?

When our skin becomes itchy, we often attribute the discomfort to external factors such as sweat, hygiene products, laundry detergents, or the fabric of our clothing.

tching is a common condition that everyone experiences, and it is usually not a serious sign.

Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) is one of the most studied and respected medicinal plants in modern herbal medicine.

Understanding Persistent Tinnitus and When to Seek Care

Waking up with a dry mouth may feel like a small inconvenience, but it can actually be your body’s subtle way of raising a warning sign.

Kidney failure is a serious condition that can lead to lifelong dialysis or other severe health complications if left untreated.

Before you spend hours defrosting your freezer, read this.

Pain on the right side: This is what it could mean

Thyroid patients: check this list before your next meal.

A lump in the neck can be harmless or a sign of something serious

Doctors say this simple daily habit can help your health after 50 👇