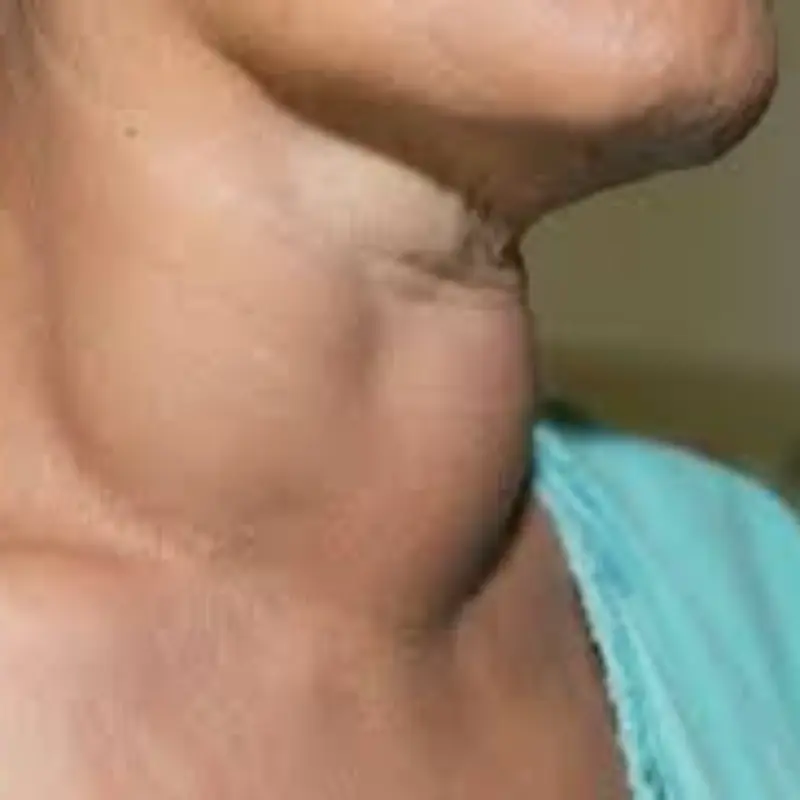
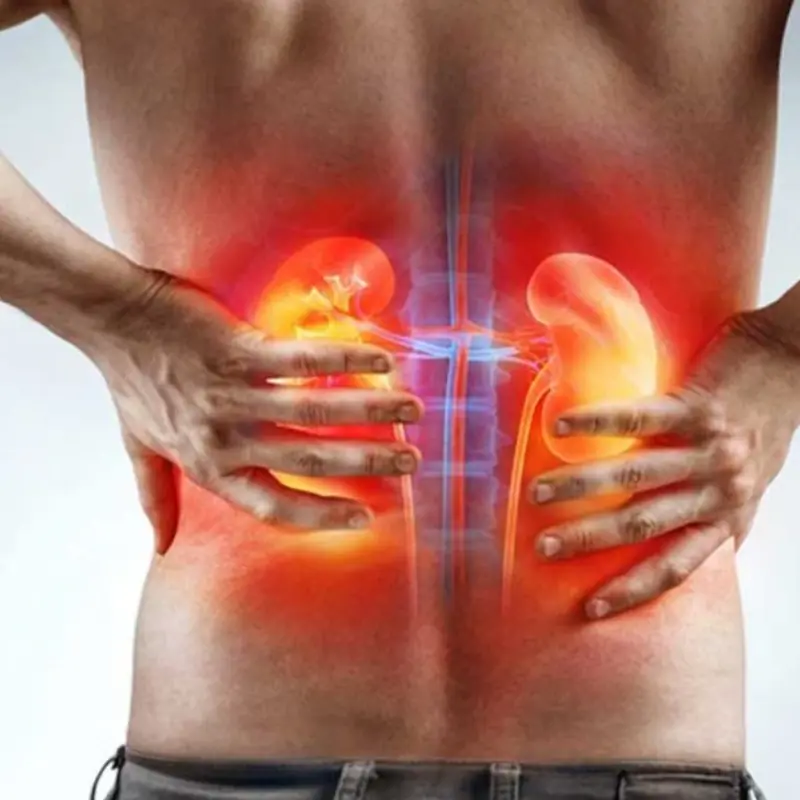
1. Swelling (Edema)
- What Happens: Swelling occurs in the legs, feet, hands, or face due to fluid retention.
- Why It Happens: The kidneys fail to remove excess fluid and sodium, leading to edema.
- What to Do: Seek medical advice if swelling persists or worsens.
2. Persistent Fatigue
- What Happens: Extreme tiredness and weakness are common.
- Why It Happens: Failing kidneys can lead to anemia (low red blood cell count), as they produce less erythropoietin, a hormone that stimulates red blood cell production.
- What to Do: Check for accompanying symptoms like pale skin or shortness of breath.
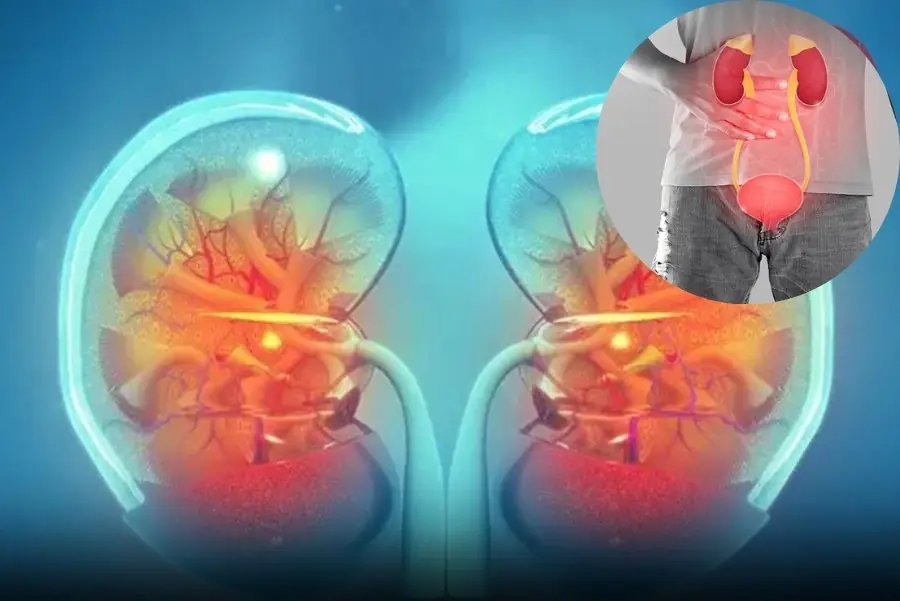
3. Changes in Urination
- What Happens: Increased or decreased urination, foamy urine, or dark-colored urine.
- Why It Happens: Kidneys regulate fluid balance, and damage can disrupt this process.
- What to Do: Monitor urine changes and consult a doctor if abnormalities persist.
4. High Blood Pressure
- What Happens: Elevated blood pressure may indicate kidney issues.
- Why It Happens: Kidneys regulate blood pressure through sodium and water balance. Impairment can lead to hypertension, worsening kidney damage.
- What to Do: Manage blood pressure and undergo regular monitoring.
5. Shortness of Breath
- What Happens: Difficulty breathing, especially after minimal activity.
- Why It Happens: Fluid buildup in the lungs (pulmonary edema) or anemia caused by kidney failure can lead to this symptom.
- What to Do: Immediate medical attention is required if shortness of breath is severe.
6. Nausea and Vomiting
- What Happens: Feeling sick or vomiting, especially in the mornings.
- Why It Happens: Waste and toxins build up in the bloodstream due to reduced kidney function, leading to uremia.
- What to Do: Seek treatment if nausea is frequent or accompanied by other symptoms.
7. Itchy Skin
- What Happens: Persistent, severe itching.
- Why It Happens: Toxins and waste products accumulating in the blood can cause itching. Phosphorus imbalances in advanced kidney disease may also contribute.
- What to Do: Discuss with a healthcare provider, as this could indicate chronic kidney disease.
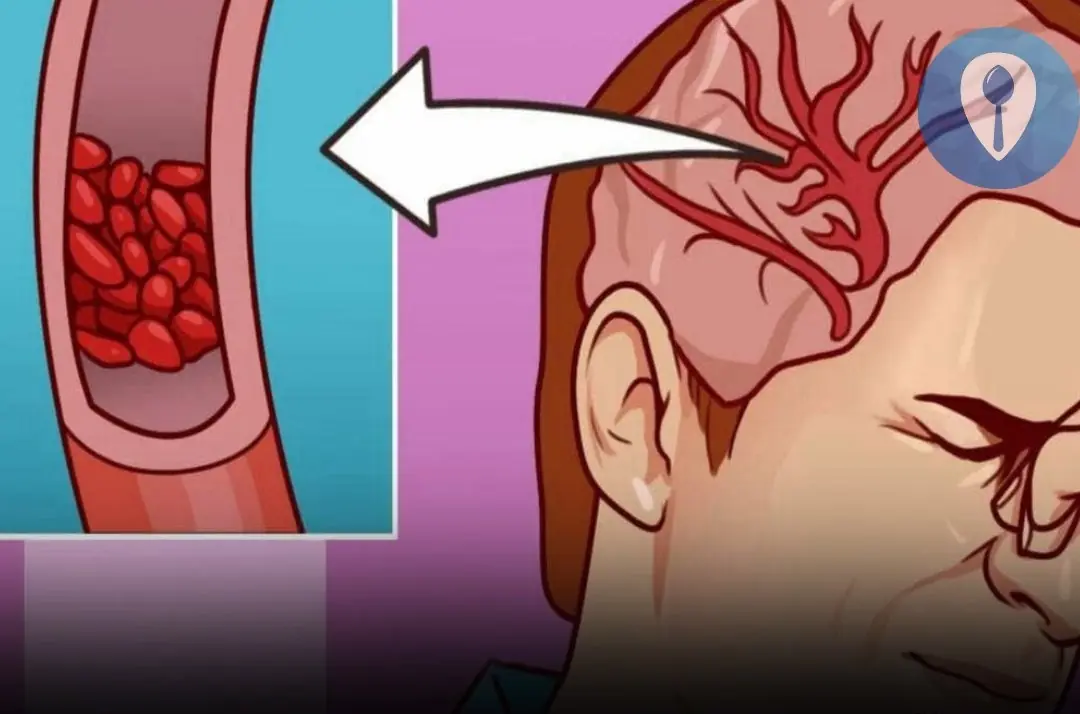
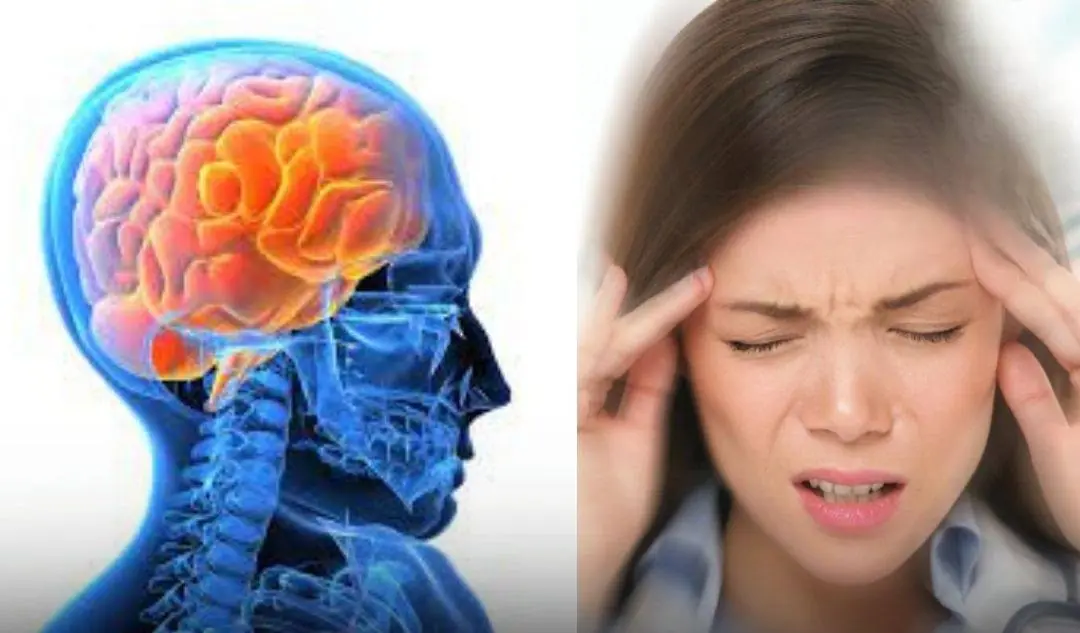
8. Difficulty Concentrating or Dizziness
- What Happens: Mental fog, confusion, or dizziness.
- Why It Happens: Anemia and toxin buildup can reduce oxygen delivery to the brain, causing cognitive issues.
- What to Do: Address symptoms early to prevent further complications.
Why These Signs Are Critical
Ignoring these symptoms can lead to:
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) progression.
- Life-threatening complications, including kidney failure.
- The need for dialysis or a kidney transplant in severe cases.
Preventing Kidney Failure
- Maintain Blood Pressure and Blood Sugar:
- Manage diabetes and hypertension, as they are leading causes of kidney disease.
- Stay Hydrated:
- Drink sufficient water, but avoid overhydration if kidney function is impaired.
- Eat a Kidney-Friendly Diet:
- Limit sodium, phosphorus, and protein intake.
- Avoid Overuse of Painkillers:
- NSAIDs and other over-the-counter medications can damage kidneys with prolonged use.
- Regular Check-Ups:
- Monitor kidney function, especially if you have risk factors like diabetes, high blood pressure, or a family history of kidney disease.