
Genetic Reality: Doctors Warn That If Parents Have These 6 Diseases, Their Children May Inherit a Higher Risk
Genetic Reality: Doctors Warn That If Parents Have These 6 Diseases, Their Children May Inherit a Higher Risk
Modern genetic studies confirm what many families have suspected for generations: certain diseases run strongly in families, and children of affected parents may carry a significantly higher risk of developing the same conditions.
Doctors emphasize that genes are not destiny, but understanding hereditary risk is critical for prevention, early screening, and lifestyle modification.
Below are six diseases with the strongest known hereditary links, according to medical researchers.
1. Cardiovascular Disease
If one or both parents have hypertension, coronary artery disease, or stroke, their children have a two- to threefold higher risk.
Inherited factors include:
-
Arterial stiffness
-
Abnormal cholesterol metabolism
-
Predisposition to high blood pressure
Combined with lifestyle habits (stress, salty food, smoking), the risk becomes even higher.
2. Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is one of the most strongly hereditary metabolic diseases.
Risk statistics show:
-
If one parent has diabetes → child’s risk increases 40%
-
If both parents have diabetes → risk rises up to 70–80%
Genes affecting insulin resistance and fat metabolism contribute to this risk.
3. Certain Cancers
Cancer is not fully determined by genes, but some types have clear hereditary patterns, including:
-
Breast cancer (especially BRCA1/BRCA2 mutations)
-
Ovarian cancer
-
Colorectal cancer
-
Prostate cancer
If close relatives had cancer at a young age, genetic testing and earlier screening are strongly recommended.
4. Mental Health Disorders
Psychiatric conditions often have a strong genetic component.
The risk increases significantly for children when parents have:
-
Depression
-
Bipolar disorder
-
Anxiety disorders
-
Schizophrenia
Genetic susceptibility combined with environmental triggers explains why these illnesses can appear across generations.
5. Obesity
Genes play a large role in:
-
Metabolism
-
Appetite regulation
-
Fat storage
-
Response to exercise
Studies show children of obese parents are three times more likely to become overweight, especially without early lifestyle intervention.
6. Allergies and Autoimmune Diseases
Conditions such as:
-
Asthma
-
Atopic dermatitis
-
Allergic rhinitis
-
Psoriasis
-
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
…are all more common in families with similar diagnoses.
Immune system “overreactivity” can be passed from parent to child.
**Are Children Destined to Get These Diseases?
Doctors Say: Absolutely Not**
Genetics account for 30–50% of risk.
The remaining percentage depends on:
-
Diet
-
Weight
-
Stress
-
Environmental exposures
-
Physical activity
-
Sleep quality
This means hereditary risk can be significantly reduced with the right lifestyle choices.
How to Protect Yourself if You Have Family Risk
Doctors recommend:
1. Get screened earlier than the general population
For example:
-
Colonoscopy earlier for families with colon cancer
-
Diabetes screening every 6–12 months
-
Yearly cardiovascular checkups
2. Maintain a healthy weight
Especially for families with diabetes or hypertension.
3. Avoid smoking and limit alcohol
These greatly amplify genetic risks.
4. Prioritize anti-inflammatory, whole-food diets
Plenty of vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and omega-3 sources.
5. Manage stress and sleep well
Stress can “activate” inherited vulnerabilities.
Conclusion
Heredity can be harsh, but knowledge is power.
When parents carry genes linked to chronic diseases, their children inherit higher risk — but not the disease itself.
With early screening, preventive care, and evidence-based lifestyle habits, individuals can outsmart their genes and maintain long-term health.
News in the same category

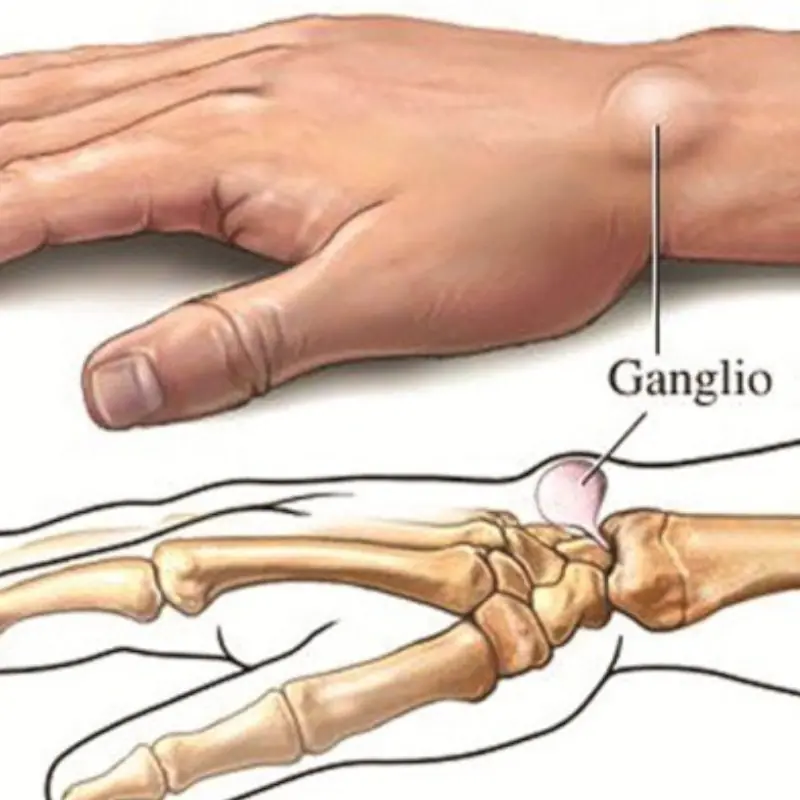
Notice This Lump on Your Wrist? It May Be Caused by a Daily Habit
Husbands With These Habits May Put Their Wives at Higher Risk of Can:cer — Stop Them Now Before They Harm the Whole Family

THE BODY KNOWS WHEN DE.A.TH IS NEAR AND IT ALL BEGINS WITH THE NOSE
A Husband and Wife Were Both Diagnosed With Li.ver Can.cer
5 skin signs that could be warning you about kid.ney problems
Cracked heels are not always caused by dry skin: Be aware of these conditions

4 parts of the chicken contain many parasites, but many people don't know that
6 early signs of stomach ca.nc.er to watch out for

The Amazing Benefits of Dates That Many People Still Don’t Know
Four symptoms that start in your leg could be a sign of 'dea:dly' cance.r

7 Fruits That Become More Beneficial to Health When Steamed
Stop drinking these 5 types of water immediately - The truth about vascular health
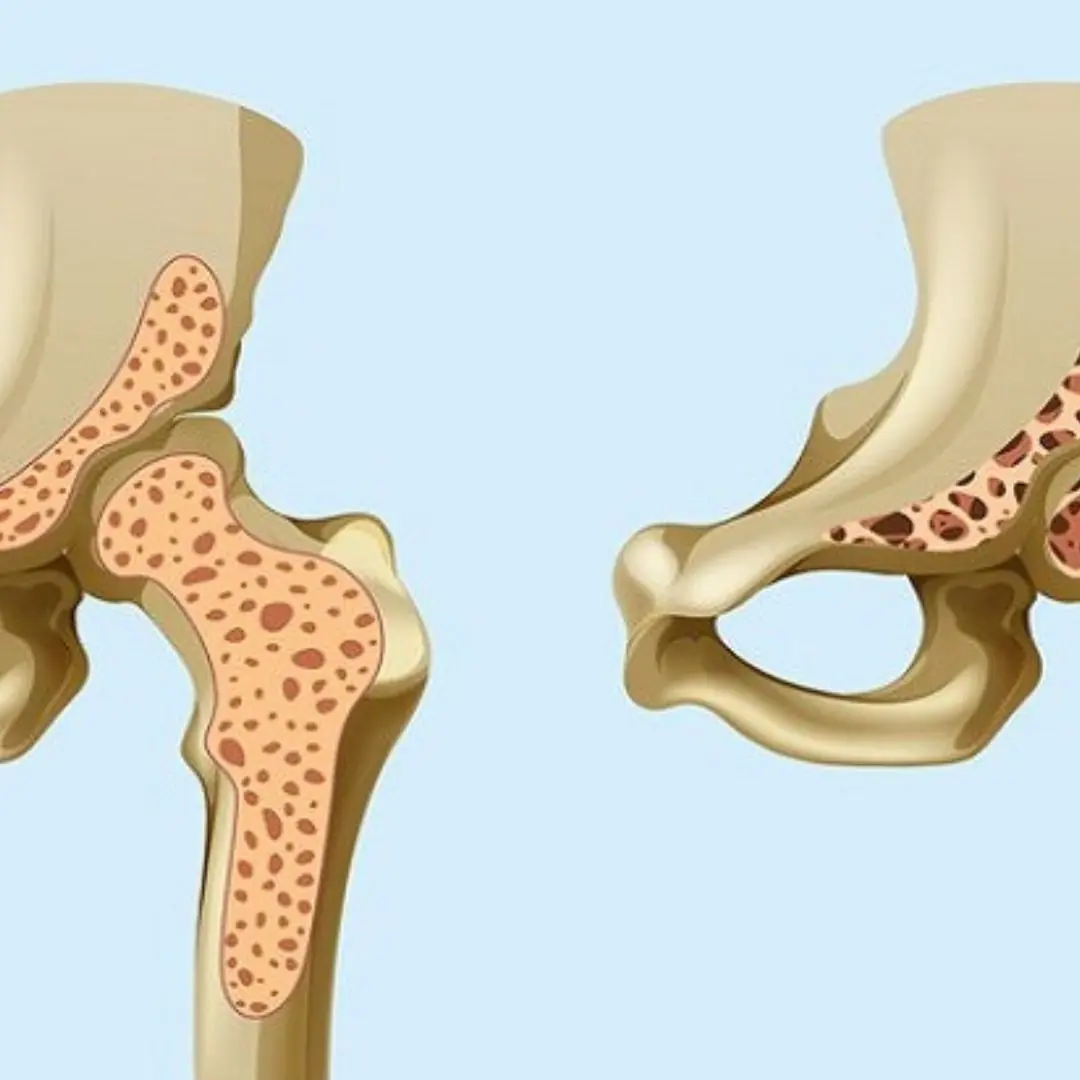
Drinking These Too Often Can Quietly Weaken Your Bones — 3 Hidden Calcium Thieves

How to spot mini-str.oke symptoms before a major str.oke happens
Suffering from Hand Arthritis? Don’t Miss These 6 Beneficial Foods
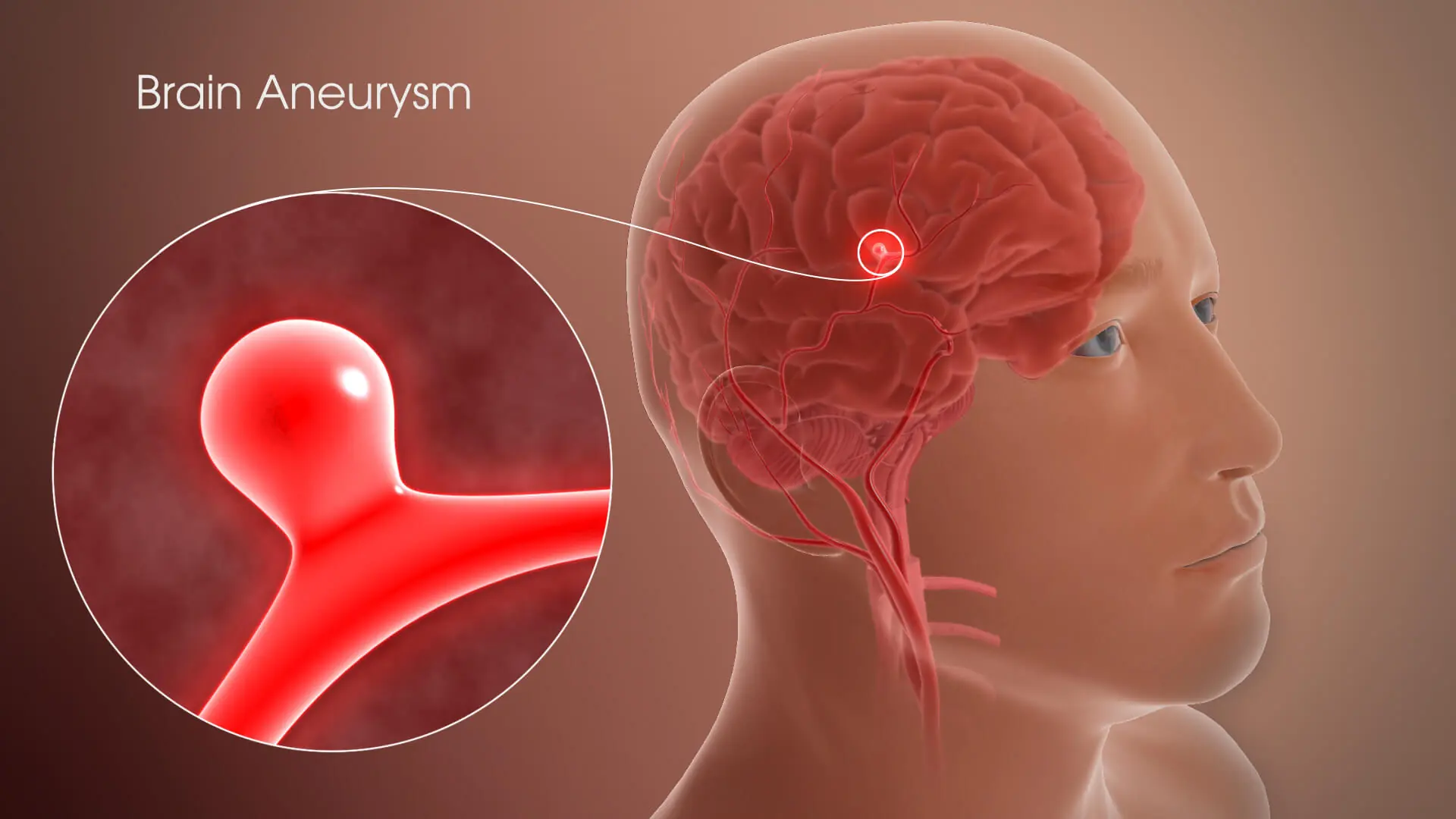
Many People Miss These 12 Brain Aneurysm Signs — Don’t Let It Happen to You
Doctors shocked after a 52-year-old man’s d.e.a.th — this habit was the cause

If Your Parent Shows These 3 Signs, They May Be Nearing the End of Life. Prepare Yourself for What’s to Come
News Post

Surprising Nutrition Insight: 4 Sprouted Foods That Become Even Healthier — Not Toxic

Doctors Warn: 4 Nighttime Signs Showing Your Liver Is Weakening — Don’t Ignore Them

Doctors Warn: Going to Bed Too Early May Be Harmful for Seniors — People Over 65 Should Sleep at This Recommended Time

Experts Warn: 4 Fruits Most Commonly Sprayed With Pesticides — Shoppers Should Avoid Buying Them Hastily

Cream Cheese–Stuffed Salmon Medallions (Pan-Seared)

Notice This Lump on Your Wrist? It May Be Caused by a Daily Habit

Husbands With These Habits May Put Their Wives at Higher Risk of Can:cer — Stop Them Now Before They Harm the Whole Family

Healthy Protein Bowl with Shrimp, Chicken, Soft-Boiled Eggs & Vegetables

THE BODY KNOWS WHEN DE.A.TH IS NEAR AND IT ALL BEGINS WITH THE NOSE

Glazed Beef Steak with Mashed Potatoes, Fresh Salad & Cornbread

A Husband and Wife Were Both Diagnosed With Li.ver Can.cer

Classic Homemade Beef Stew with Potatoes & Carrots

5 skin signs that could be warning you about kid.ney problems

Strawberry Hot Chocolate
The finger you cut first might say more about you than you think

Savory Tuscan Chicken Bake Delight

Cracked heels are not always caused by dry skin: Be aware of these conditions

4 parts of the chicken contain many parasites, but many people don't know that
