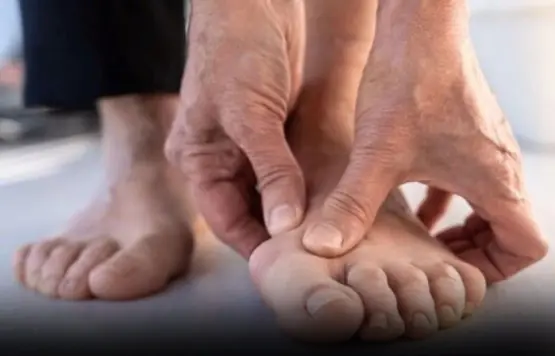
Pay Attention: 6 Foot Signs Linked to Serious Conditions
Diabetic neuropathy complications are one of the most common chronic complications of diabetes and also a major cause of diabetic foot disease.
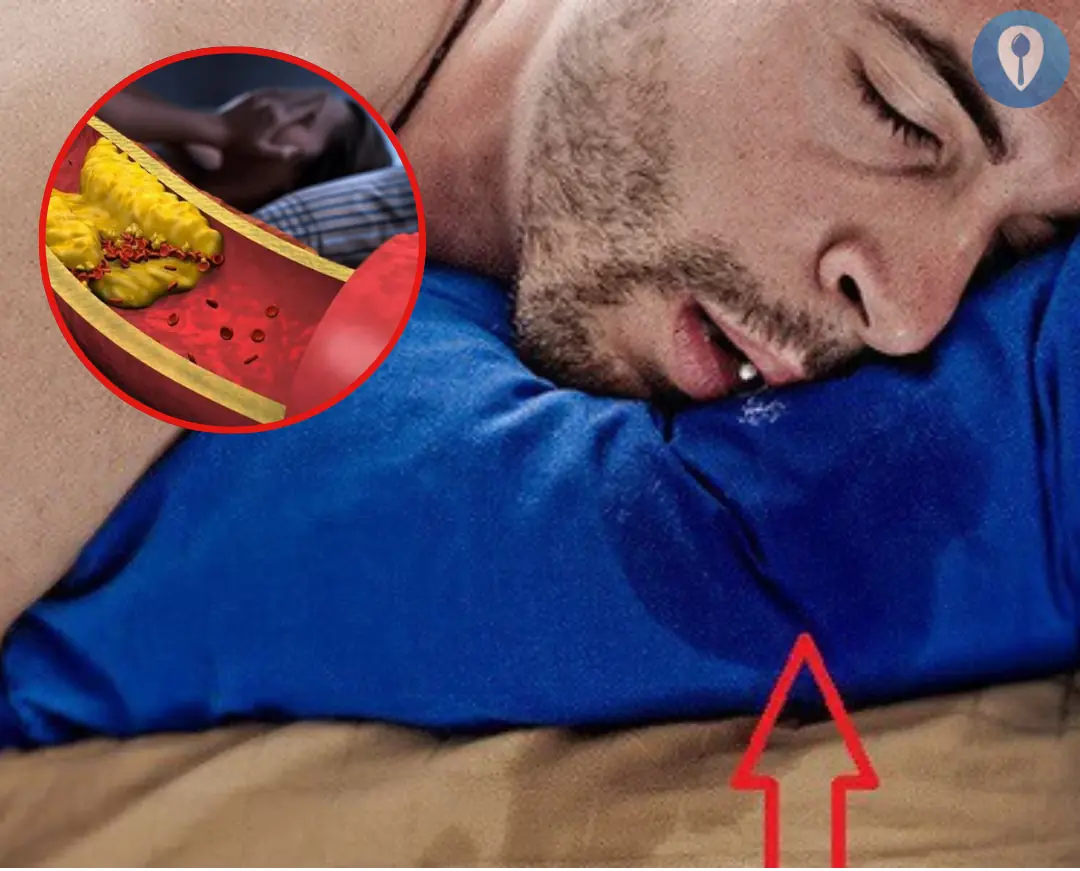
Excessive Saliva Production in the Mouth: A Warning Sign of Health Issues You Shouldn’t Ignore
Introduction: Understanding Excessive Saliva Production
Saliva is an essential fluid produced by the salivary glands that plays a vital role in maintaining oral health. It helps with the digestion of food, cleanses the mouth, and protects the teeth from decay. However, in some individuals, excessive saliva production can occur, which can be a sign of underlying health issues. This condition is referred to as "hypersalivation" or "sialorrhea." It may be temporary or chronic, and it can interfere with normal daily activities, leading to discomfort and embarrassment.
In this article, we will explore the causes, potential health implications, and treatment options for excessive saliva production.
What Is Excessive Saliva Production?
Excessive saliva production refers to the condition in which a person produces more saliva than necessary to maintain oral health. While everyone produces saliva naturally, certain conditions can lead to an overproduction of saliva, causing it to accumulate in the mouth. This may result in drooling, difficulty swallowing, and even a noticeable excess of saliva on the pillow while sleeping.
There are two main types of hypersalivation:
Causes of Excessive Saliva Production
Several factors can contribute to excessive saliva production. Some of the most common causes include:
Neurological Disorders:
Medications: Some medications, such as antipsychotics, anticonvulsants, and tranquilizers, can increase saliva production as a side effect. These drugs may interfere with normal nerve function and lead to an overproduction of saliva.
Infections: Oral infections, such as those caused by viruses or bacteria, can lead to inflammation of the salivary glands and increased saliva production. Conditions like mumps, which causes swelling of the salivary glands, are well-known examples.
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): GERD is a chronic digestive condition in which stomach acid frequently flows backward into the esophagus. This can stimulate the salivary glands to produce more saliva to neutralize the acid and protect the esophagus.
Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can cause an increase in saliva production. This is especially common during the first trimester and is often referred to as "pregnancy-related sialorrhea."
Allergies: Allergic reactions, especially those involving the respiratory system, can lead to increased mucus production, which may mimic or exacerbate saliva production. Conditions such as hay fever or allergic rhinitis can cause symptoms that affect the salivary glands.
Toxic Exposure: In rare cases, exposure to certain toxins or poisons, such as heavy metals, can affect the salivary glands, resulting in excessive saliva production.
Symptoms of Excessive Saliva Production
Excessive saliva production may present itself in a variety of ways. Some of the common symptoms include:
Health Implications of Excessive Saliva Production
While excessive saliva production might seem harmless, it can lead to several health complications if not addressed. Some of the potential issues include:
Chronic Drooling: Prolonged drooling can cause embarrassment and social anxiety, especially in public or professional settings. It may also lead to skin irritation around the mouth and chin.
Infection Risks: Constant exposure to excess saliva can increase the risk of developing oral infections, such as gingivitis or periodontitis. Bacteria in the saliva may lead to inflammation of the gums and teeth, causing discomfort and potential tooth loss.
Dehydration: If the body produces too much saliva, it may result in excessive swallowing and a higher frequency of urination. This could lead to dehydration if the individual is unable to maintain proper fluid balance.
Sleep Disruptions: Excessive drooling during sleep can result in disturbed rest. This can affect the quality of sleep, leading to fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating during the day.
Treatment Options for Excessive Saliva Production
Treatment for excessive saliva production depends on the underlying cause. Some common treatment options include:
Medications: Anticholinergic medications, which reduce saliva production, may be prescribed to manage hypersalivation. However, these drugs may have side effects, including dry mouth and blurred vision.
Botox Injections: Botulinum toxin (Botox) injections can be used to temporarily block the signals that stimulate the salivary glands, reducing excessive saliva production. This treatment is especially useful for individuals with neurological conditions like Parkinson’s disease.
Speech and Swallowing Therapy: For individuals with neurological disorders, speech and swallowing therapy can help improve coordination of the muscles involved in swallowing and reduce the need to produce excess saliva.
Dental Care: Proper oral hygiene practices, such as regular brushing, flossing, and mouth rinsing, can help manage the symptoms of excessive saliva production and prevent complications like tooth decay and gum disease.
Surgical Options: In severe cases, surgical intervention may be required to remove or reposition the salivary glands to reduce the amount of saliva produced.
Conclusion: Don’t Ignore the Signs
Excessive saliva production can be a warning sign of underlying health problems. If you or someone you know experiences this condition, it is important not to ignore the symptoms. Early intervention and proper diagnosis can help manage the issue and improve quality of life. Always consult a healthcare provider to determine the cause and best treatment options tailored to the individual’s needs.
Remember, while excessive saliva production may seem like a minor inconvenience, it could be a symptom of something more serious. Don’t hesitate to seek medical advice if you notice any of the symptoms mentioned above.

Diabetic neuropathy complications are one of the most common chronic complications of diabetes and also a major cause of diabetic foot disease.
Bathing is a habit that helps clean the body and relax, but we should not always bathe immediately.

The Myth About Fruits Feeding Cancer Cells: A Critical Look at the Claims
Some unhealthy habits during intimacy may be a hidden cause of cervical cancer in women.
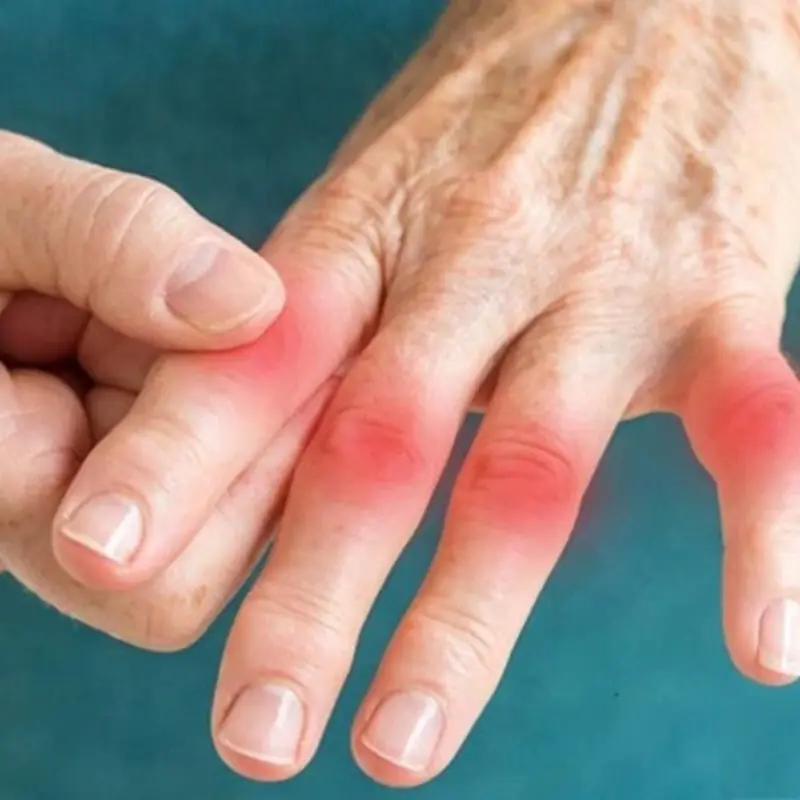
A hidden disease may grow silently — and one habit worsens it.
Garlic has long become an indispensable spice in the family kitchen.
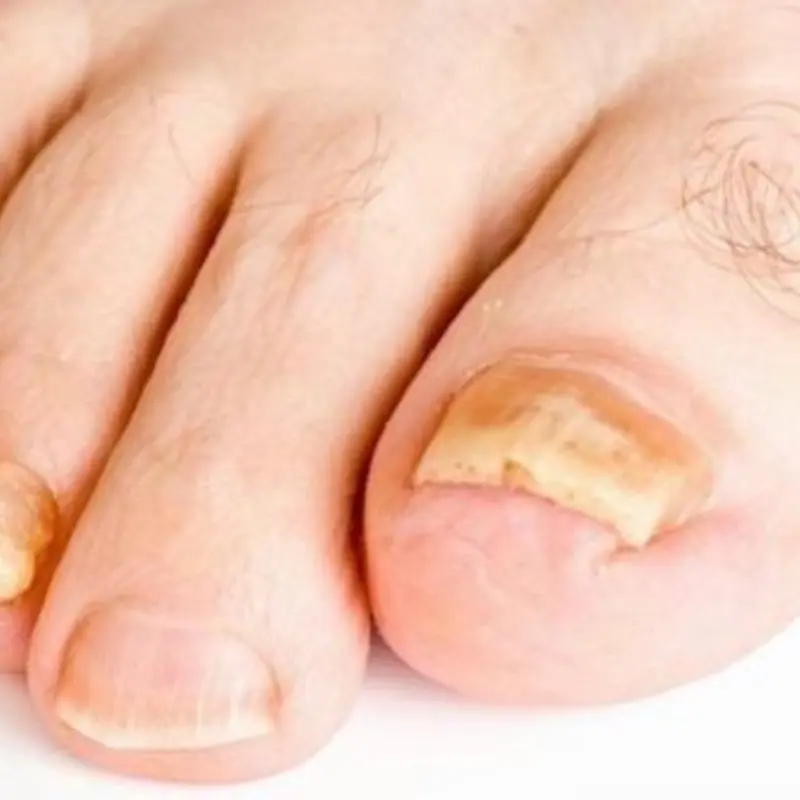
Two small changes in your feet may reveal serious hidden health risks.
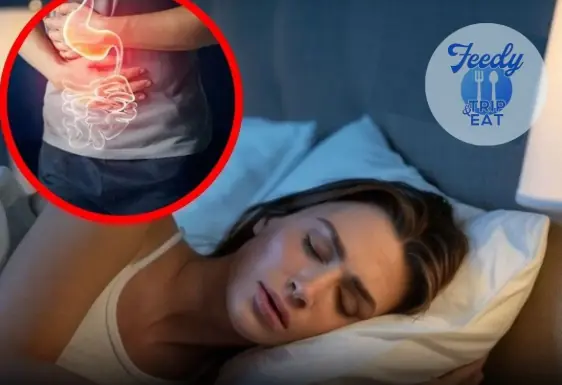
Despite having a full night’s rest, many people still get up feeling sleepy and lacking energy.
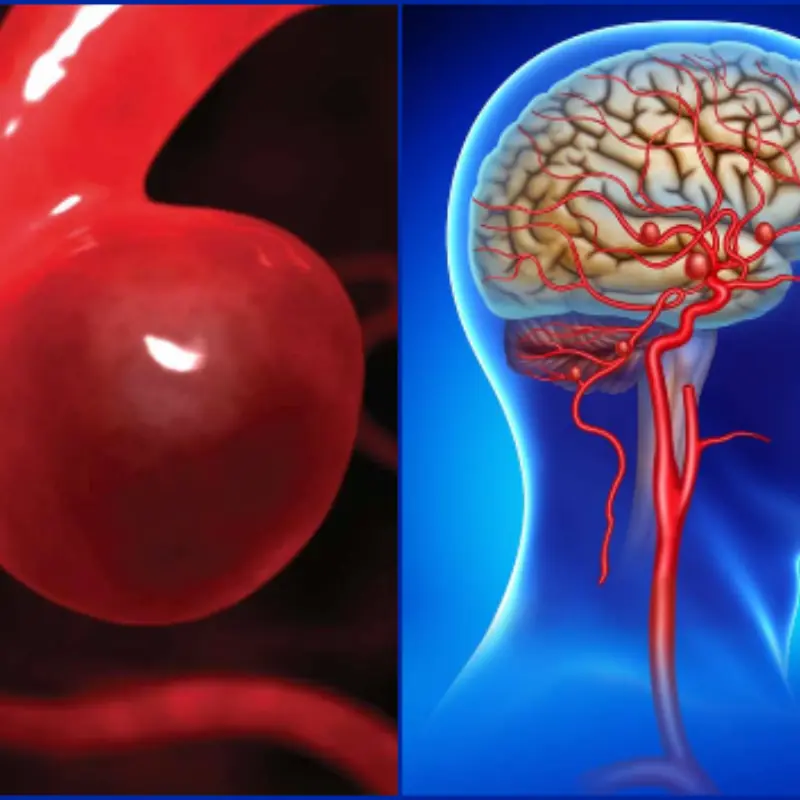
Hidden aneurysm signs can appear suddenly and turn life-threatening.
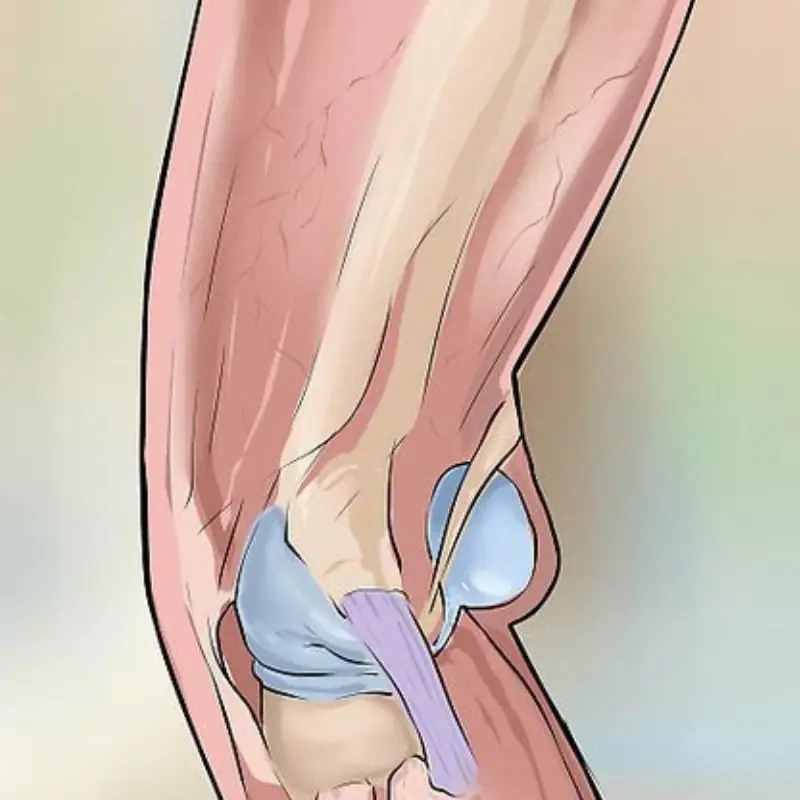
Pain behind the knee may signal hidden health risks—don’t ignore it.

Pay attention to these signs!
Almost no one knows about it, and it's more useful than you think
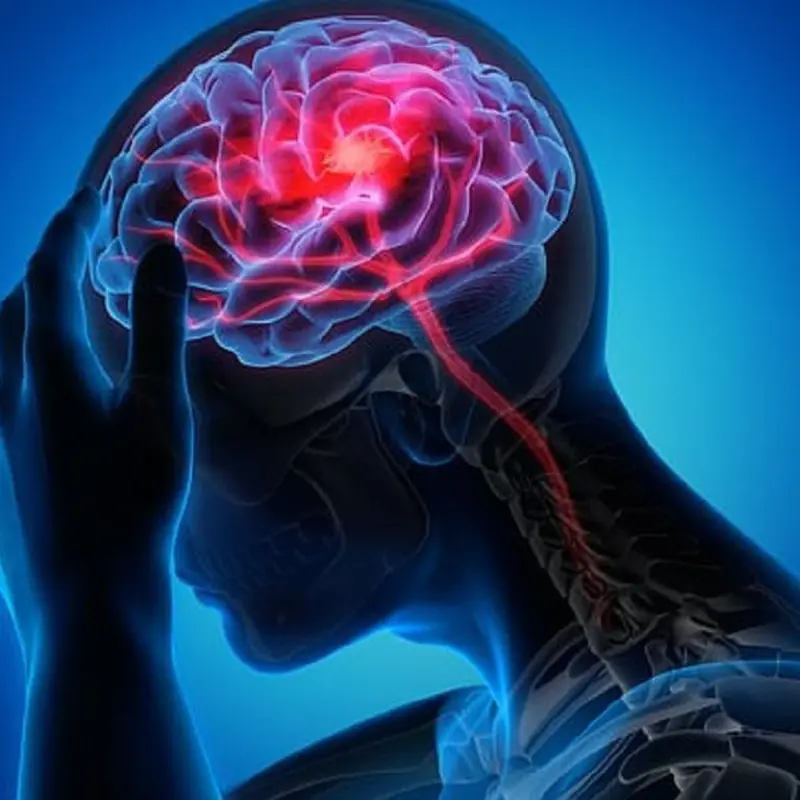
9 subtle warning signs of brain clots that may appear before a stroke
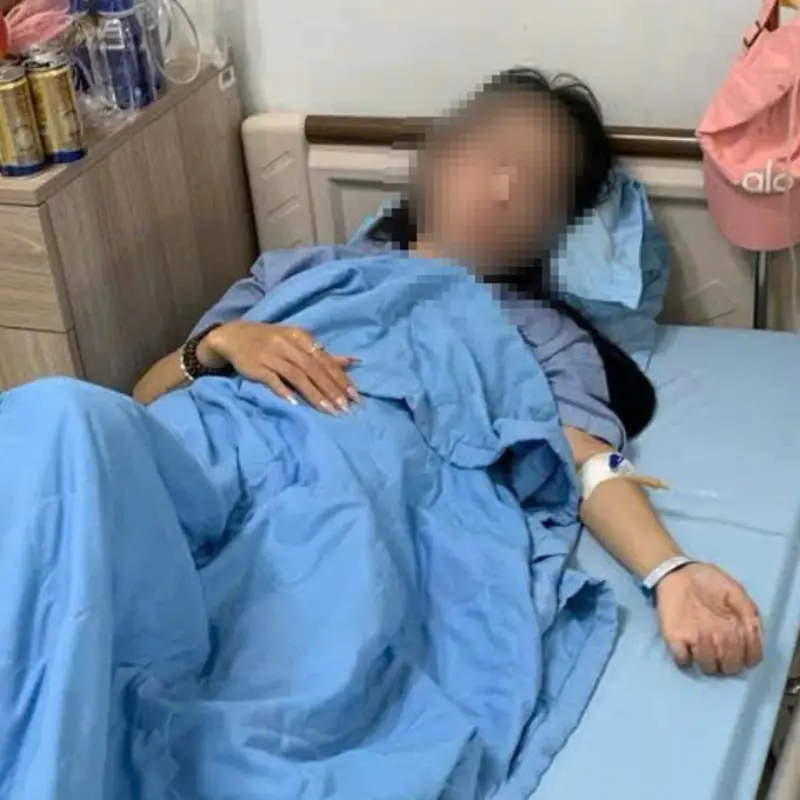
Doctors warn after woman develops sudden kidney failure post-dinner.
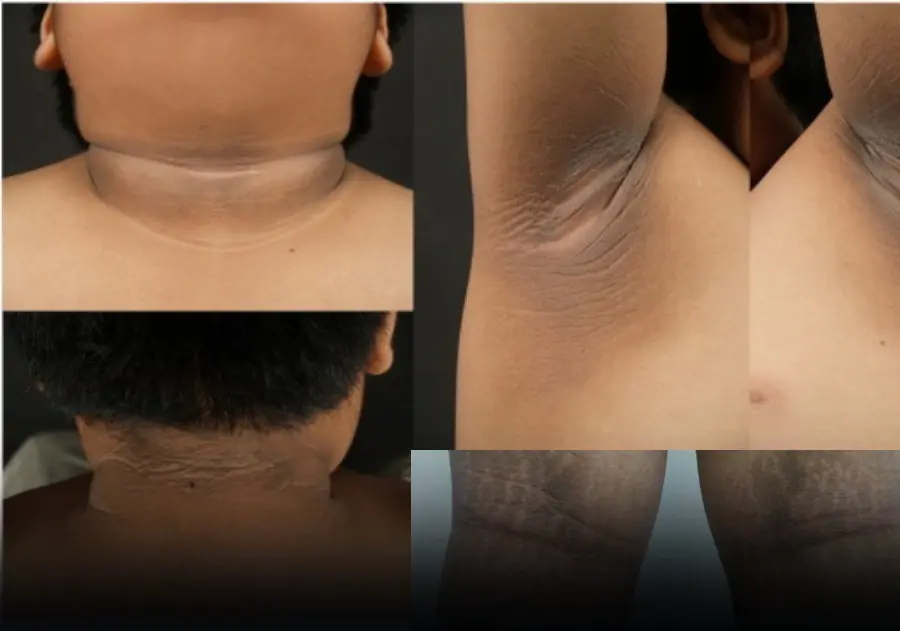
It commonly occurs in healthy people, but in some cases it can be a sign of an underlying disease.

Why You Should Drink Water on an Empty Stomach Immediately After Waking Up
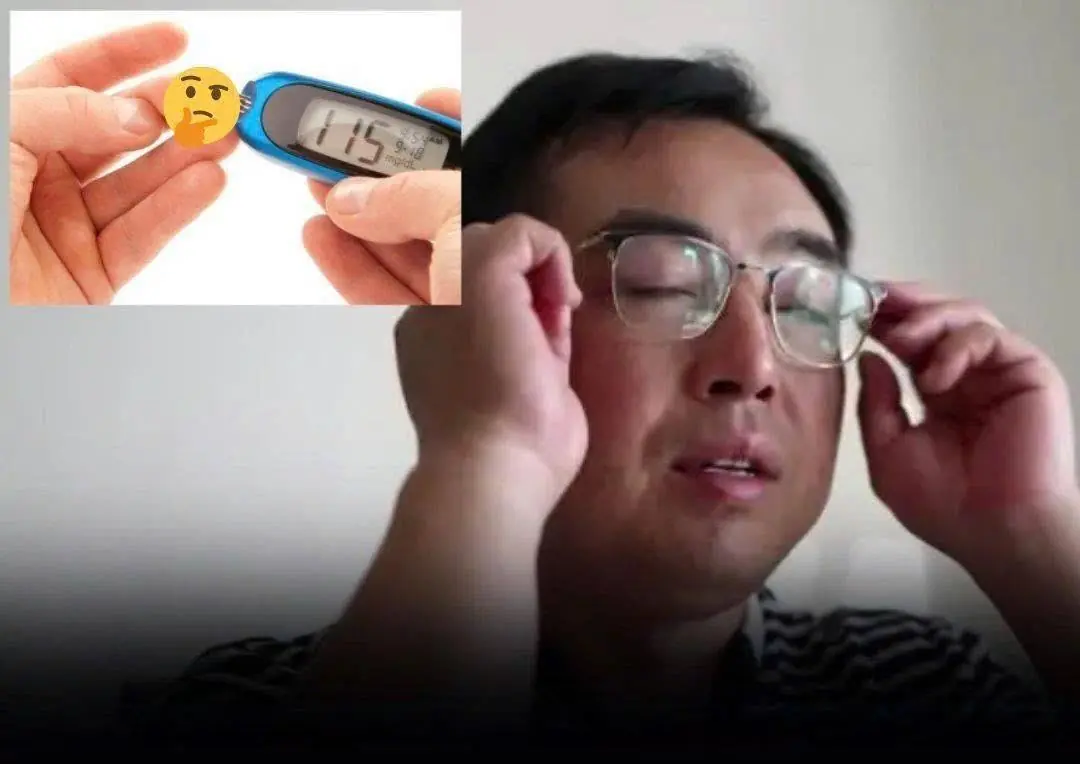
Your eyes can reveal more than you think — even hidden signs of diabetes that often go unnoticed
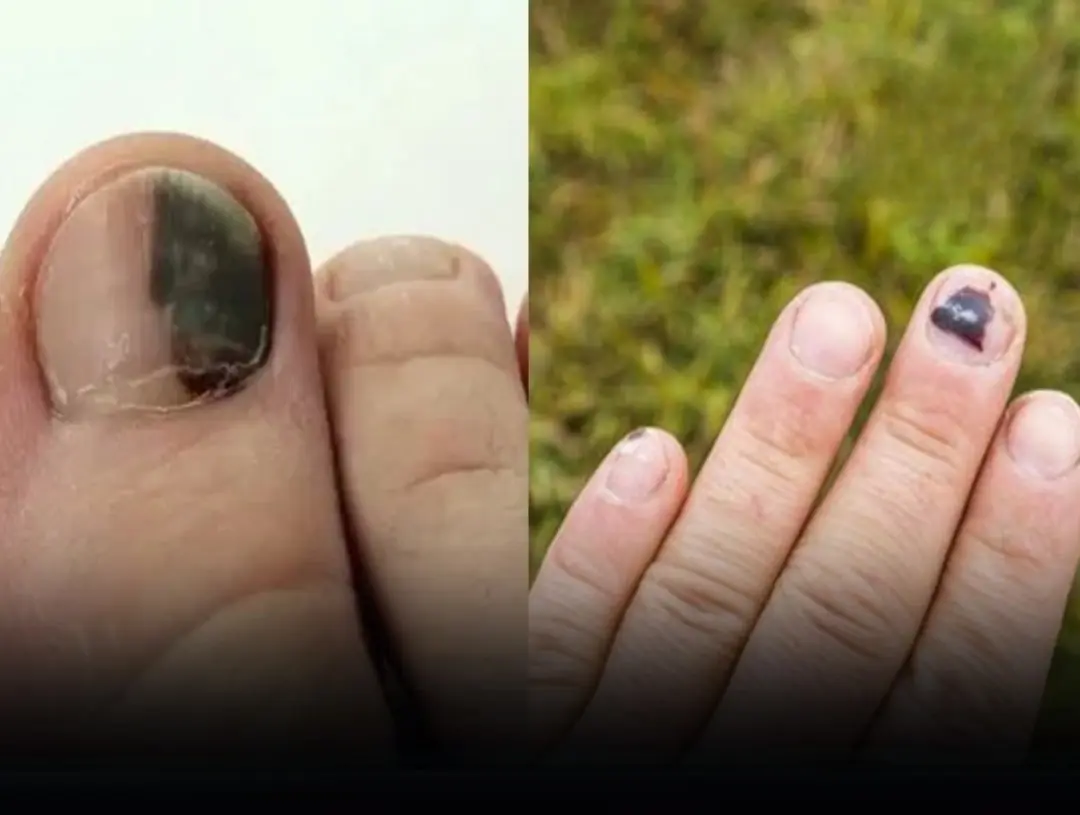
3 Subtle Limb Changes You Should Never Ignore
One spoon a day — and these 8 surprising benefits will transform your body
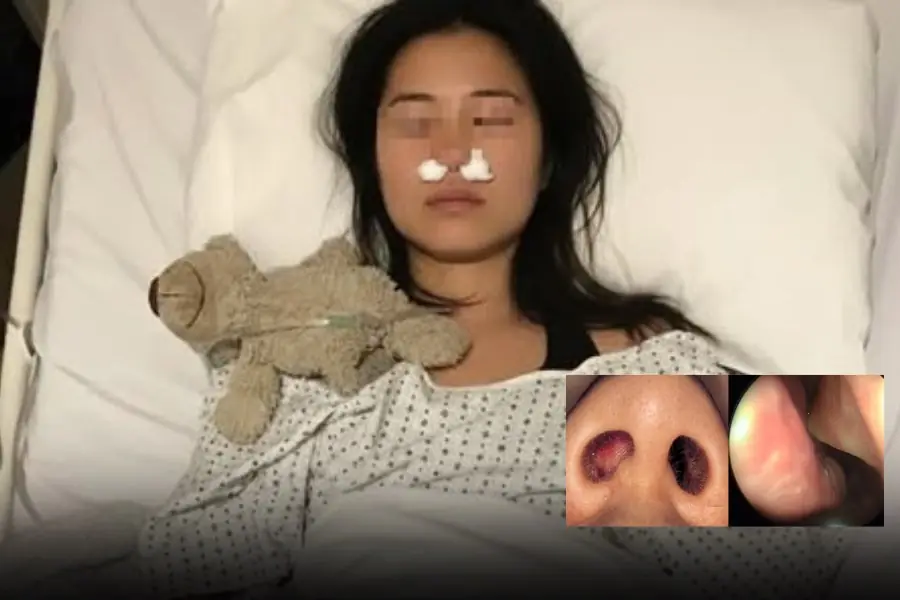
She grew a cluster of fungi in her nose — all because of a habit nearly everyone does daily

Diabetic neuropathy complications are one of the most common chronic complications of diabetes and also a major cause of diabetic foot disease.

Bathing is a habit that helps clean the body and relax, but we should not always bathe immediately.

The Myth About Fruits Feeding Cancer Cells: A Critical Look at the Claims

Some unhealthy habits during intimacy may be a hidden cause of cervical cancer in women.

A hidden disease may grow silently — and one habit worsens it.

Garlic has long become an indispensable spice in the family kitchen.

Two small changes in your feet may reveal serious hidden health risks.

Despite having a full night’s rest, many people still get up feeling sleepy and lacking energy.

Hidden aneurysm signs can appear suddenly and turn life-threatening.

Pain behind the knee may signal hidden health risks—don’t ignore it.

He Ordered in German to Humiliate the Waitress—But She Spoke Seven Languages

My Husband Started Taking Our Dog on Three-Hour “Walks” Every Night—Until I Checked Daisy’s GPS Colla

Pay attention to these signs!

I Let Them Think I Was a Freeloader—Until Thanksgiving Changed Everything

Twelve Julys of “The Islands”—And the Phone Call That Changed Everything

Almost no one knows about it, and it's more useful than you think

A millionaire’s unexpected discovery: how love, truth, and a child’s laughter changed everything

9 subtle warning signs of brain clots that may appear before a stroke

Penthouse Illusions: The Swipe That Ended Their Fantasy

Doctors warn after woman develops sudden kidney failure post-dinner.