In Japan, it’s praised as the most powerful anti-can.cer food, but Vietnamese have enjoyed it for centuries
Why Sweet Potatoes Are Considered a Powerful Health Food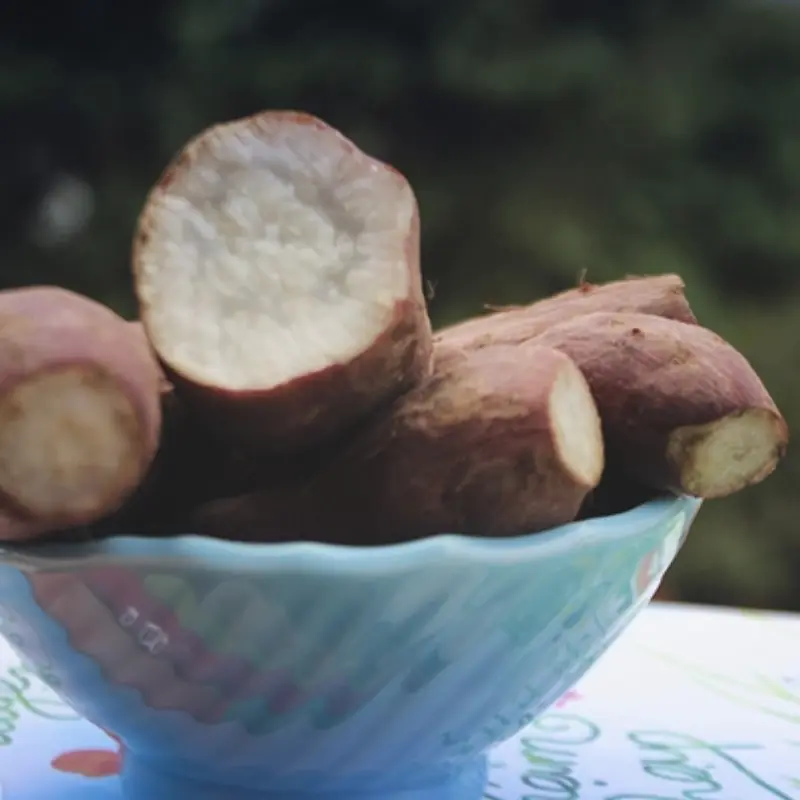
Sweet potatoes (especially orange and purple varieties) are packed with natural compounds that help protect the body from inflammation and oxidative stress—two processes closely linked to many chronic diseases, including cancer.
They are rich in:
-
Beta-carotene (Vitamin A precursor)
-
Anthocyanins (in purple sweet potatoes)
-
Dietary fiber
-
Vitamin C, potassium, and antioxidants
-
Resistant starch (when cooled after cooking)
These nutrients don’t “cure cancer,” but they may support the body’s natural defenses and reduce risk factors.
1. Powerful Antioxidants That Fight Cell Damage
One of the biggest reasons sweet potatoes get attention is their high antioxidant content. Antioxidants help neutralize free radicals—unstable molecules that can damage DNA and cells over time.
-
Orange sweet potatoes are high in beta-carotene, which supports immune health and protects cells.
-
Purple sweet potatoes contain anthocyanins, known for their strong antioxidant activity.
A diet rich in colorful fruits and vegetables is consistently linked to lower inflammation and better long-term health, which may play a role in cancer prevention.
2. Fiber Supports Gut Health (And Your Immune System)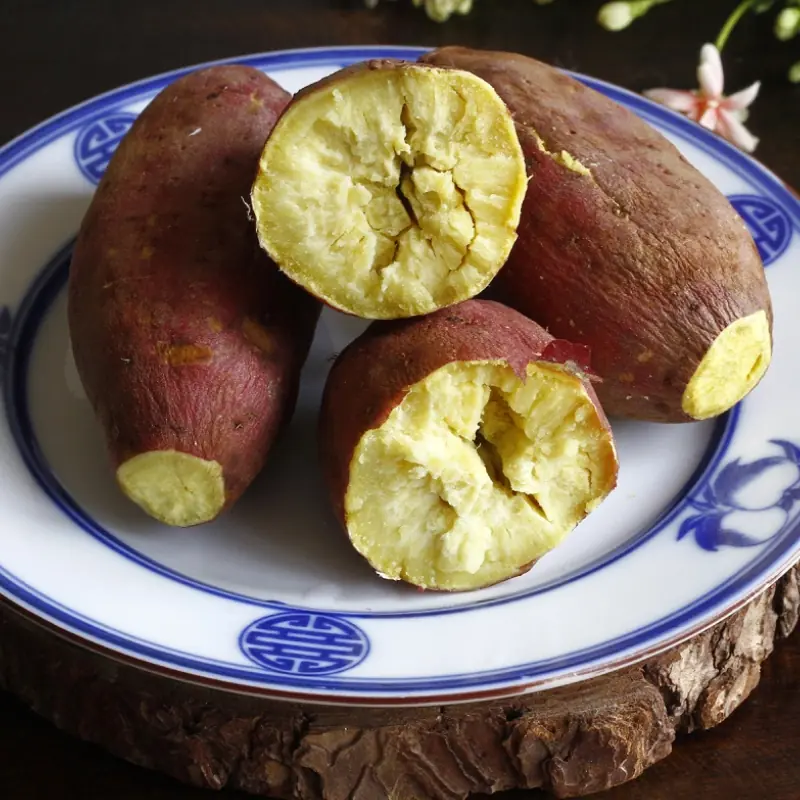
Sweet potatoes are an excellent source of fiber, which supports digestion and helps maintain a healthy gut microbiome. This matters more than many people realize because your gut is deeply connected to immunity and inflammation.
Fiber also helps:
-
Promote regular bowel movements
-
Reduce constipation
-
Support “good” gut bacteria
-
Control blood sugar spikes
-
Lower cholesterol
A healthy digestive system helps the body eliminate waste efficiently—another reason fiber is often emphasized in cancer prevention diets.
3. Resistant Starch May Improve Metabolic Health
Here’s a surprising fact: sweet potatoes can become even healthier after cooling.
When cooked sweet potatoes are cooled (like leftovers stored in the fridge), some of the starch converts into resistant starch, which behaves like fiber in the body. Resistant starch may help:
-
Improve insulin sensitivity
-
Support gut bacteria
-
Reduce inflammation
-
Keep you full longer
Better blood sugar control is important because long-term insulin imbalance is associated with higher risk of many chronic diseases.
4. Nutrient Dense Yet Naturally Light
Compared to many refined carbs, sweet potatoes provide more nutrition per bite. They’re naturally sweet, satisfying, and loaded with vitamins and minerals—especially potassium, which supports blood pressure and heart health.
This is one reason sweet potatoes are popular in Japan, where many people prioritize balanced meals and long-term wellness.
How to Eat Sweet Potatoes for Maximum Benefits
To enjoy sweet potatoes as part of a healthy lifestyle, focus on simple cooking methods:
✅ Best choices:
-
Steamed
-
Boiled
-
Roasted
-
Baked
-
Air-fried (light oil)
⚠️ Limit:
-
Deep-fried sweet potatoes
-
Sweet potato desserts loaded with sugar or condensed milk
Pro tip: Pair sweet potatoes with protein (eggs, fish, tofu) and healthy fats (nuts, avocado) for better blood sugar balance.
Who Should Be Careful With Sweet Potatoes?
Sweet potatoes are healthy for most people, but moderation matters if you:
-
Have diabetes (watch portion size)
-
Are on a low-carb diet
-
Have kidney issues (potassium restriction)
-
Tend to overeat starchy foods
Eating too much can raise blood sugar—even if it’s a “healthy” carb.
News in the same category


Yawning is considered a very normal physiological reaction

3 Painful Areas on Your Body That Could Be Early Signs of Can.cer — Don’t Ignore Them, or It Might Spread
Just because it’s in the fridge doesn’t mean it’s in a safe deposit box!

Stop Them Now Before They Harm The Whole Family

Group 1 Carcinogens: Foods Scientifically Proven to Increase Cancer Risk

Not Tooth Decay: Two Oral Signs That Could Be Your Body’s Cry for Help

The Drink Linked to Can.cer Risk: One Glass a Day May Raise the Danger by 90%
Kidney Failure Is Increasing Among Young People: A Dangerous Habit Many Ignore

Rising Dea.ths from Diabetes: Doctors Warn — It’s Better to Go Hungry Than to Eat These 7 Vegetables
Smart women take advantage of their peri.od to do these 4 things
Pancreatic Cancer: 10 Key Signs That May Help with Early Detection

Things to keep in mind when eating jellyfish to avoid food poisoning

Eating a boiled egg every morning: The surprising effects on your body

7 Health Problems Linked to Not Drinking Enough Water
3 pain areas on the body that could signal early-stage can:cer: don't delay, or it could spread

6 Surprising Reasons Women Should Eat Dates More Often

Two vegetables considered “natural remedies” for headaches—eat them and sleep soundly through the night
The 4 earliest warning signs the body sends as a “cry for help” for cerv.ical can.cer—sadly, many women overlook them
News Post

Don’t Drink Water Immediately After Waking Up: Doctors Reveal 5 Important Things to Do First

Don’t overlook this: frequent drooling during sleep could signal more than you think

Yawning is considered a very normal physiological reaction

3 Painful Areas on Your Body That Could Be Early Signs of Can.cer — Don’t Ignore Them, or It Might Spread

Just because it’s in the fridge doesn’t mean it’s in a safe deposit box!

A 106-Year-Old Woman Reveals a Zero-Cost Secret to Longevity — And It’s Not Exercise or Dieting

Stop Them Now Before They Harm The Whole Family

Group 1 Carcinogens: Foods Scientifically Proven to Increase Cancer Risk

Crispy Sweet & Spicy Cauliflower Bites

Oversalted your dish? Don’t dilute it with water—add this one ingredient to balance the flavor fast.

Spicy Grilled Chicken Skewers (Paprika & Garlic Style)

Not Tooth Decay: Two Oral Signs That Could Be Your Body’s Cry for Help

The Drink Linked to Can.cer Risk: One Glass a Day May Raise the Danger by 90%

Kidney Failure Is Increasing Among Young People: A Dangerous Habit Many Ignore

Rising Dea.ths from Diabetes: Doctors Warn — It’s Better to Go Hungry Than to Eat These 7 Vegetables
Butcher’s Honest Advice: When Buying Pork, It’s Best to Avoid These Three Types — Only the Uninformed Like Them
Shrimp, Mango & Avocado Bowl

Smart women take advantage of their peri.od to do these 4 things
