Don’t overlook this: frequent drooling during sleep could signal more than you think
Drooling While Sleeping Often: What It Could Mean for Your Health
Drooling during sleep is something many people experience at least occasionally. After a deep night’s rest, waking up to a damp pillow can feel embarrassing—but in most cases, it is completely harmless. However, the image above highlights an important point: frequent or excessive drooling while sleeping can sometimes be a sign of an underlying health issue, especially when it happens regularly and is accompanied by other symptoms.
This article is not meant to alarm. Drooling alone does not mean disease. But when it becomes persistent, it may be the body’s way of signaling that something needs attention.

Why Do People Drool While Sleeping?
Saliva production continues even during sleep. Normally, swallowing reflexes keep saliva from escaping the mouth. Drooling happens when:
-
Sleeping position allows saliva to flow out
-
Mouth remains open during sleep
-
Swallowing reflex is reduced in deep sleep
Occasional drooling—especially when sleeping on one’s side—is considered normal. Concern arises when drooling is frequent, excessive, or new.
When Drooling Becomes a Pattern
You may want to pay attention if drooling:
-
Happens almost every night
-
Soaks pillows regularly
-
Appears suddenly without lifestyle changes
-
Comes with snoring, choking, numbness, or facial weakness
In these cases, drooling may be associated with one or more health conditions.
1. Sleep Apnea
One of the most common medical causes of nighttime drooling is obstructive sleep apnea.
How it’s connected:
-
Mouth breathing increases saliva leakage
-
Reduced swallowing during breathing pauses
-
Often accompanied by loud snoring and daytime fatigue
Untreated sleep apnea increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, and high blood pressure, making early evaluation important.
2. Nasal or Sinus Problems
Chronic nasal congestion forces people to breathe through the mouth while sleeping.
Possible causes include:
-
Allergic rhinitis
-
Chronic sinusitis
-
Deviated nasal septum
When nasal airflow is blocked, saliva escapes more easily during sleep.
3. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Acid reflux can increase saliva production as the body attempts to neutralize stomach acid.
Signs that drooling may be linked to GERD:
-
Heartburn
-
Sour taste in the mouth
-
Chronic cough
-
Worsening drooling when lying flat
Managing reflux often reduces drooling significantly.
4. Neurological Conditions
Certain neurological disorders can affect muscle control and swallowing reflexes.
Conditions sometimes associated with drooling include:
-
Parkinson’s disease
-
Stroke recovery
-
Bell’s palsy
-
Multiple sclerosis
In these cases, drooling is often accompanied by speech changes, facial weakness, or difficulty swallowing.
5. Oral and Dental Issues
Problems inside the mouth can also contribute to excessive drooling.
Examples include:
-
Gum disease
-
Mouth infections
-
Poorly fitting dental appliances
-
Inflammation of the salivary glands
Oral discomfort may cause the mouth to remain open during sleep, increasing saliva leakage.
6. Medication Side Effects
Some medications stimulate saliva production or reduce muscle tone during sleep.
Common examples:
-
Certain sedatives
-
Antidepressants
-
Antipsychotics
-
Medications affecting the nervous system
If drooling begins after starting a new medication, it should be discussed with a healthcare provider.

What Drooling Does Not Automatically Mean
It is important to clarify:
-
Drooling does not automatically indicate serious illness
-
Many healthy people drool occasionally
-
Stress, deep sleep, and sleep position are common causes
Medical evaluation is recommended only when drooling is persistent, worsening, or accompanied by other symptoms.
When to Consider Seeing a Doctor
Seek medical advice if drooling:
-
Appears suddenly and frequently
-
Is paired with snoring, choking, or breathing pauses
-
Occurs with facial numbness, weakness, or speech problems
-
Affects quality of life or sleep
Early evaluation helps rule out serious conditions—or identify treatable ones early.
Simple Steps That May Help
Before assuming a medical cause, small adjustments can reduce drooling:
-
Change sleep position (elevate head, avoid stomach sleeping)
-
Treat nasal congestion
-
Improve sleep hygiene
-
Manage acid reflux
-
Review medications with a doctor
Often, simple changes make a noticeable difference.
A Calm but Important Reminder
Drooling while sleeping is usually harmless. But when the body repeats a signal consistently, it deserves attention—not fear.
Health awareness is about noticing patterns, not jumping to conclusions.
If drooling feels excessive, new, or unusual, checking in with a healthcare professional is a responsible step—not an overreaction.
Sometimes, the body’s quiet habits are simply asking to be listened to.
News in the same category

Warning Signs That Cancer Is Growing in Your Body
The Back of Your Hand May Reveal Longevity Secrets: 4 Signs Everyone Should Check

More Than 90% of iPhone Users Don’t Know the Purpose of the Tiny Hole Next to the Camera

Doctors recommend a vegetable that supports the heart, fights aging, has 7x more calcium than bone broth, and is easy to find at the market.
The Biggest Cause of Liver Cancer Identified: Doctors Point to a Common but Overlooked Culprit
These 3 types of pai.n may indicate lung can.cer. Don’t overlook them
“Red Alert” for the Kidneys: Warning Signs You Should Never Ignore

See these 4 garlic bulbs? Don’t buy them… don’t even accept them for free.

Hormonal imbalance in women is a common condition that, if left untreated, can affect various bodily functions.

Yawning is considered a very normal physiological reaction

3 Painful Areas on Your Body That Could Be Early Signs of Can.cer — Don’t Ignore Them, or It Might Spread

In Japan, it’s praised as the most powerful anti-can.cer food, but Vietnamese have enjoyed it for centuries
Just because it’s in the fridge doesn’t mean it’s in a safe deposit box!

Stop Them Now Before They Harm The Whole Family

Group 1 Carcinogens: Foods Scientifically Proven to Increase Cancer Risk

Not Tooth Decay: Two Oral Signs That Could Be Your Body’s Cry for Help

The Drink Linked to Can.cer Risk: One Glass a Day May Raise the Danger by 90%
Kidney Failure Is Increasing Among Young People: A Dangerous Habit Many Ignore
News Post

Drinking Coffee at the Right Time May Support Heart Health, Experts Say

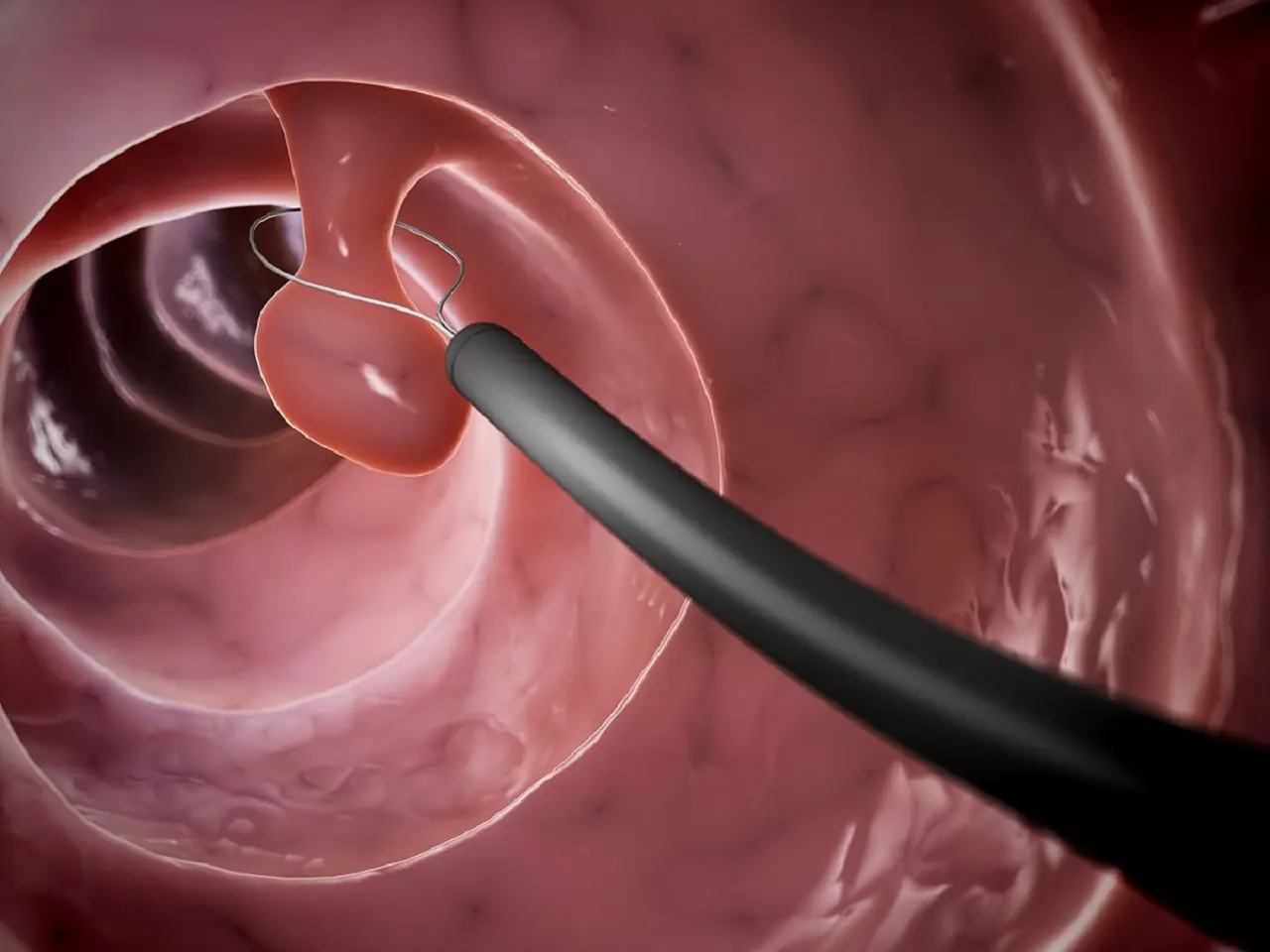
Early detection of colon polyps: The key to effective cancer prevention
For those who are in the habit of poking the leg out of the bed sheet when sleeping

Warning Signs That Cancer Is Growing in Your Body

Health Warning: 4 Types of Electric Kettles You Should Stop Using Immediately

The Back of Your Hand May Reveal Longevity Secrets: 4 Signs Everyone Should Check

More Than 90% of iPhone Users Don’t Know the Purpose of the Tiny Hole Next to the Camera

Doctors recommend a vegetable that supports the heart, fights aging, has 7x more calcium than bone broth, and is easy to find at the market.

The Biggest Cause of Liver Cancer Identified: Doctors Point to a Common but Overlooked Culprit

These 3 types of pai.n may indicate lung can.cer. Don’t overlook them

This type of "poiso,nous sandal" can cause early puberty in children, but many parents still buy it for their children to wear!

“Red Alert” for the Kidneys: Warning Signs You Should Never Ignore

See these 4 garlic bulbs? Don’t buy them… don’t even accept them for free.

Hormonal imbalance in women is a common condition that, if left untreated, can affect various bodily functions.

With this leaf in hand, you don't have to worry about diarrhea or health problems will improve

Don’t Drink Water Immediately After Waking Up: Doctors Reveal 5 Important Things to Do First

Yawning is considered a very normal physiological reaction

3 Painful Areas on Your Body That Could Be Early Signs of Can.cer — Don’t Ignore Them, or It Might Spread
