
Why do dogs often chase strangers
When a dog barks aggressively or even tries to bite one person but completely ignores another, it’s not luck, and it’s not coincidence. There is always a reason behind the reaction. Understanding these triggers helps prevent dangerous situations and teaches us how to interact with dogs safely and respectfully.
1. Dogs react to body language more than anything else
Dogs communicate primarily through body language, and they read human posture far faster than we realize.
A person who runs suddenly, moves too fast, or appears tense can instantly trigger a dog’s instinct. Running, in particular, activates a predator–prey response in many dogs. To them, fast movement can look like a threat or something worth chasing.
People who walk calmly, avoid sudden gestures, and keep a relaxed posture are less likely to attract aggressive barking.
2. Fear has a smell — literally
It might sound surprising, but dogs can detect changes in human scent caused by fear. When someone is scared, the body releases stress hormones like adrenaline and cortisol. Dogs, with their incredibly sensitive noses, can smell these changes instantly.
A frightened person may unintentionally signal to the dog that something is wrong, making the dog more alert or defensive.
Conversely, a calm person sends signals of safety, and the dog feels less threatened.
3. Past experiences shape a dog’s reaction
Dogs remember.
If a dog has had a negative experience with a certain type of person — for example, someone wearing a hood, carrying a stick, running fast, or even a certain gender — it may generalize that fear or distrust.
A dog that has been scared or mistreated may react strongly when it sees someone who reminds it of a past threat.
Meanwhile, another person who moves differently or behaves calmly may not trigger that memory.
4. Dogs sense confidence and uncertainty
Confident energy makes a dog feel stable. Uncertain or anxious energy can make the dog distrustful.
People who approach a dog timidly, stare directly into its eyes, or extend a hand too quickly might unintentionally challenge or frighten the dog.
Dogs prefer clear, predictable behavior. When someone acts in a way the dog doesn’t understand, barking becomes a defensive tool.
5. Territorial instinct is powerful
Some dogs are not aggressive in general — they are simply protective of their space.
If a person enters a dog’s perceived territory (a home, yard, or even a familiar route), the dog may bark loudly or chase to warn them away.
Another person walking calmly on the sidewalk may be completely ignored because they don’t pose a territorial threat.
6. Clothing, scent, and unusual appearance also matter
Dogs notice details that humans often overlook. A large hat, sunglasses, a mask, a heavy backpack, or even the smell of another animal can confuse or alarm a dog.
Some dogs are also sensitive to strong perfumes or odors like alcohol or smoke.
To a dog, small unfamiliar details can create uncertainty, leading to defensive barking.
7. Human behavior can escalate or calm the situation
Looking directly into a dog’s eyes, raising your voice, bending forward, or turning your back quickly can all increase the dog’s tension.
People who stay still, avoid staring, and keep their hands low and relaxed usually appear less threatening.
The dog senses stability and responds in a calmer way.
The bottom line:
Dogs don’t bark or bite randomly. Their reactions are influenced by body language, fear signals, confidence levels, past experiences, scents, and territorial instincts.
Once we understand these triggers, we can avoid risky behavior, interact with dogs more safely, and reduce unnecessary fear on both sides.
A dog’s behavior is communication. When we learn to read it, everything becomes clearer.
News in the same category

5 bad habits that increase the risk of str.oke at night

The Silent Mystery of Seat 11A: From the Most Hated Spot to a “Lucky Charm” That Saved the Only Survivors of Two Air Disasters

Doctor’s note: 4 fruits you should limit due to potential health risks, even if they seem affordable.

How dangerous are scratches on non-stick pans?

Warning: 2 types of cooking oils that are harmful to the heart should be limited

Waking Up Between 3 And 5 AM Could Indicate a Spiritual Awakening

Don’t throw these 4 things when someone passes away

Never leave a charger in an outlet without your phone: I'll expose the three major reasons

The Sho.cking Truth Behind Your Ankle Bracelet And What It Reveals About You - It’s More Than Just Jewelry

Red wax keeps appearing on my daughter-in-law’s door lock, even after she removes it. She’s been living alone ever since my son died. Is this a warning?

6 unexpected effects of perilla leaves

The “Black List” of 5 Household Items: Cheap, Eye-Catching, but Quietly Harmful to Your Family’s Health

The volume button on your mobile phone has 3 useful functions
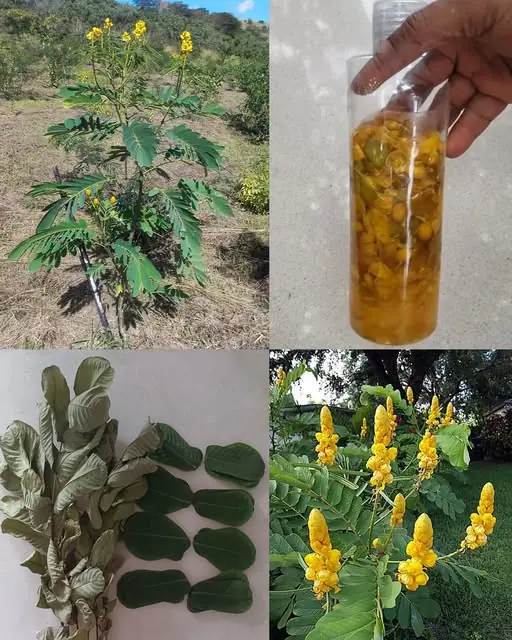

The Powerful Medicinal Benefits and Uses of Senna alata

Eating Too Much Avocado? These Surprising Side Effects Might Sh:ock You

Why Japanese people eat raw fish daily without fearing pa.rasites?

Finger Test for Lung Ca.nc.er: How a Simple Check Could Reveal Your Ca.nc.er Risk
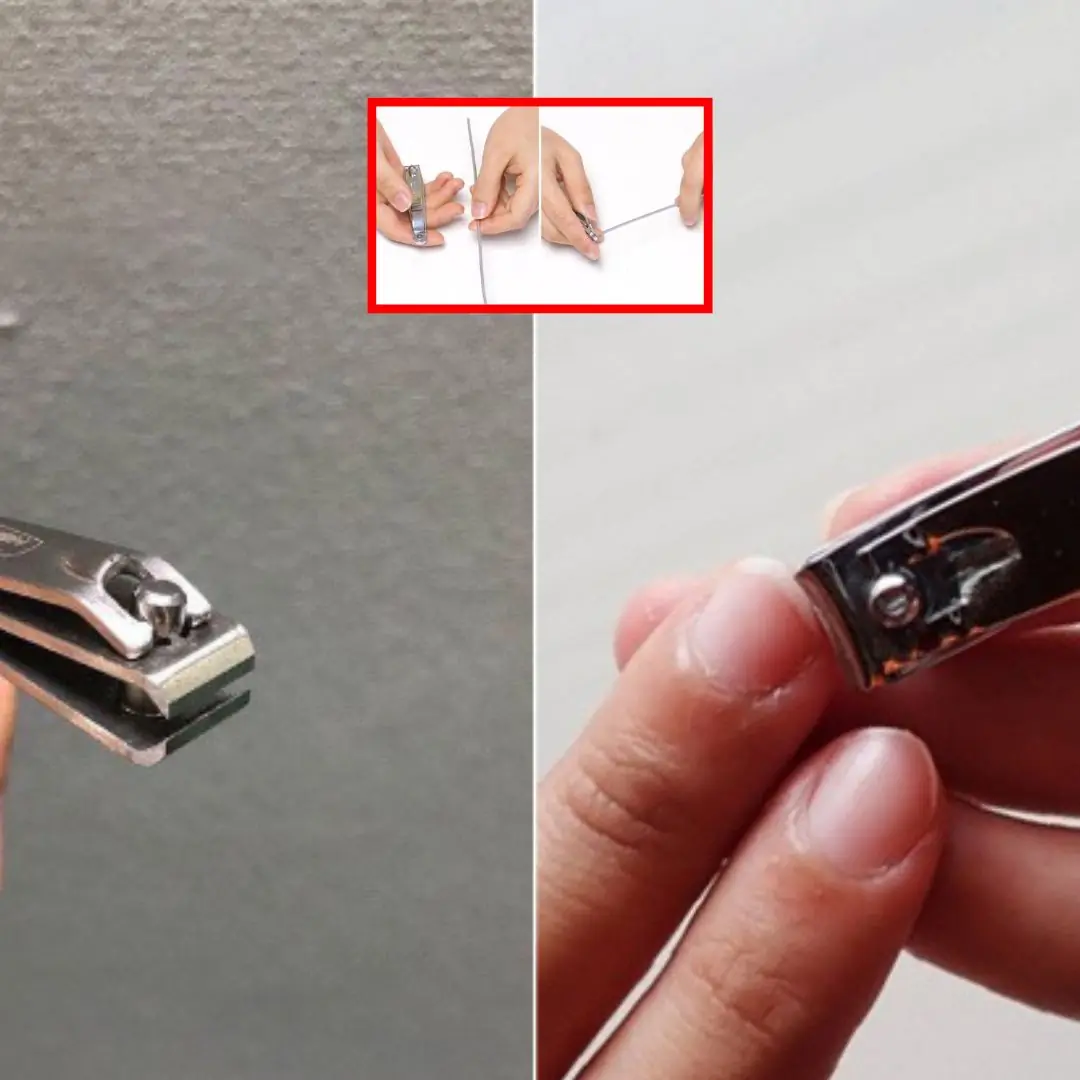

Tiny but mighty: 7 surprising ways to use nail clippers
News Post

When a cat rubs against you, this is what it means

Avoid ginger if you have these 5 health problems..

Pesto Puff Pastry Christmas Trees

6 Plants That Attract Snakes Into Your Home

Roasted Brussels Sprouts & Butternut Squash

How to Store Rice to Prevent Weevils and Mold: Simple Tips to Keep It Fresh

The Age-Defying Herb: How Rosemary Supports Brain Health, Immunity, and Emotional Balance

8 Reasons You May Be Waking Up With a Dry Mouth at Night — What You Need to Know

Cheesy Garlic Butter Corn (Skillet Style)
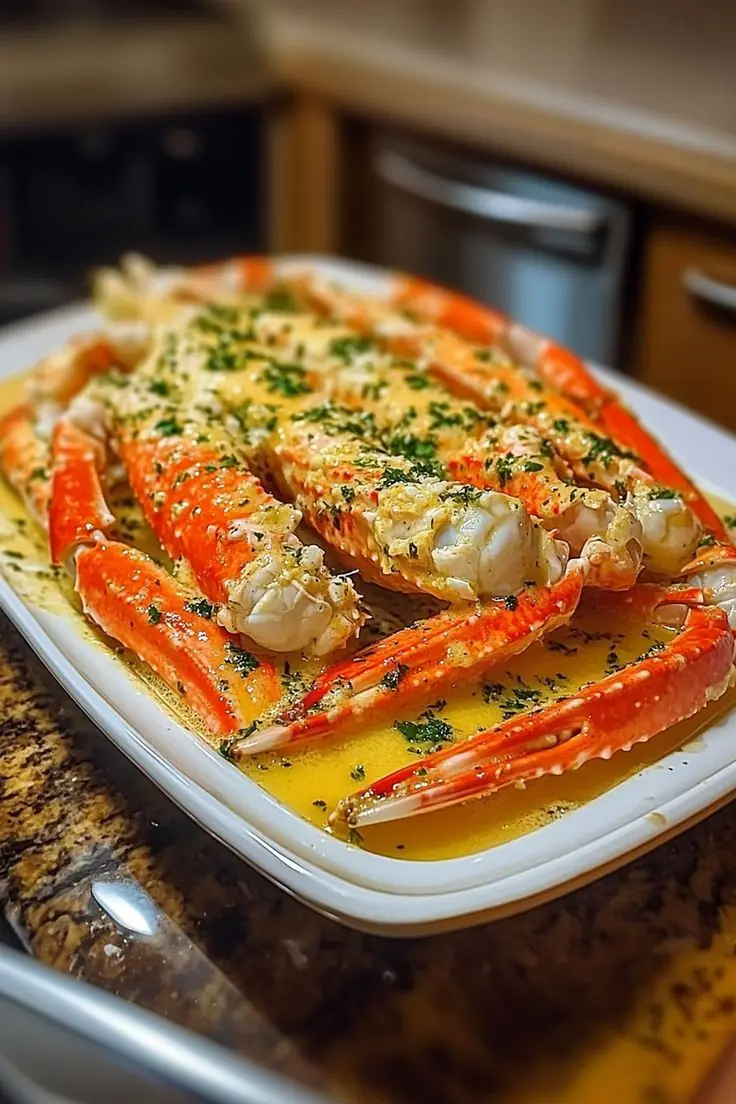

Garlic Butter King Crab Legs
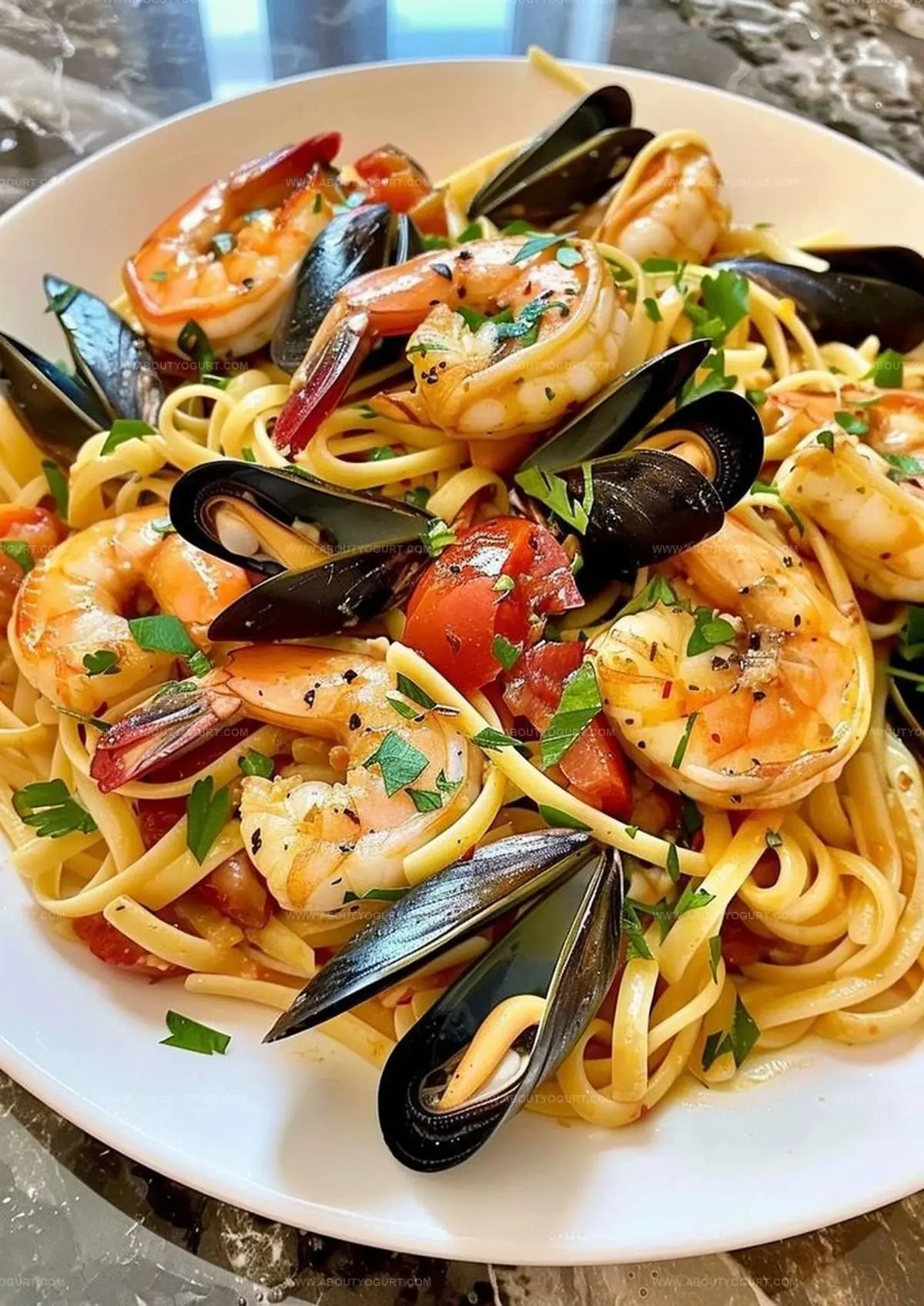

Seafood Linguine with Shrimp and Mussels
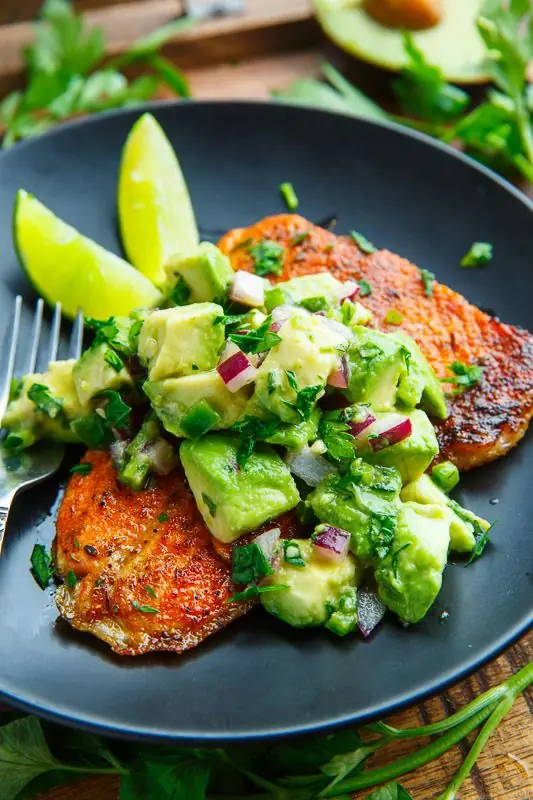

Pan-Seared Spiced Fish with Fresh Avocado Salsa

Did You Know Waking Up at 3 or 4 A.M. Could Be a Clear Warning Sign of Something Serious?

5 bad habits that increase the risk of str.oke at night

5 Groups of People Who Must Avoid Avocado — Even If They’re Craving It Like Crazy
Off The Record One Month Before A Heart Attack, Your Body Will Warn You Of These 7 Signs
Two it.chy body parts may signal liver can.cer - Many people mistakenly think it is an all.ergy
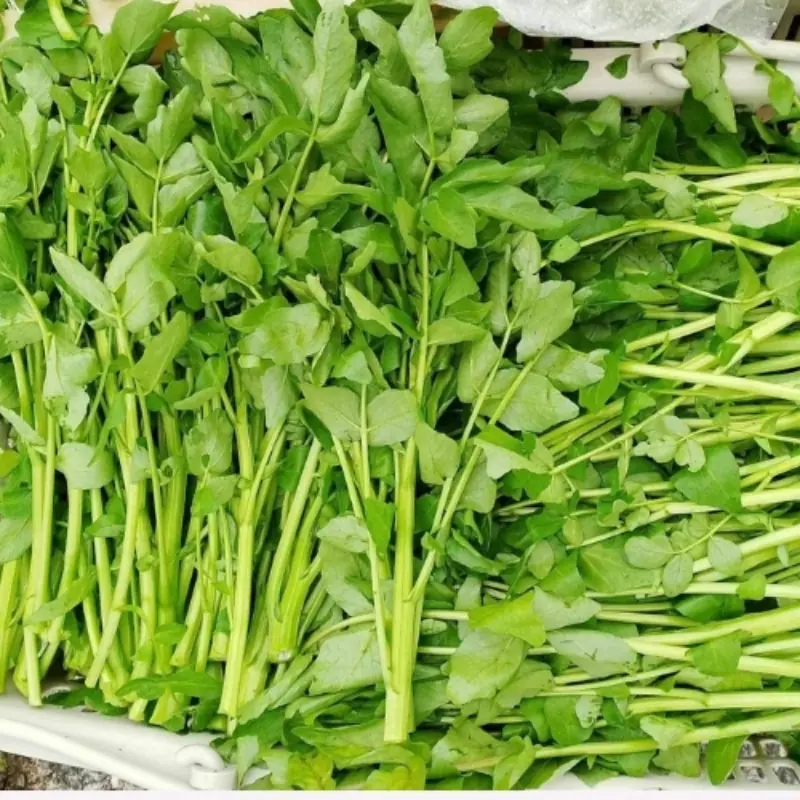

4 Vegetables Proven to Help Reduce Can.cer Risk
