
3 foods that may unlock your body’s longevity genes
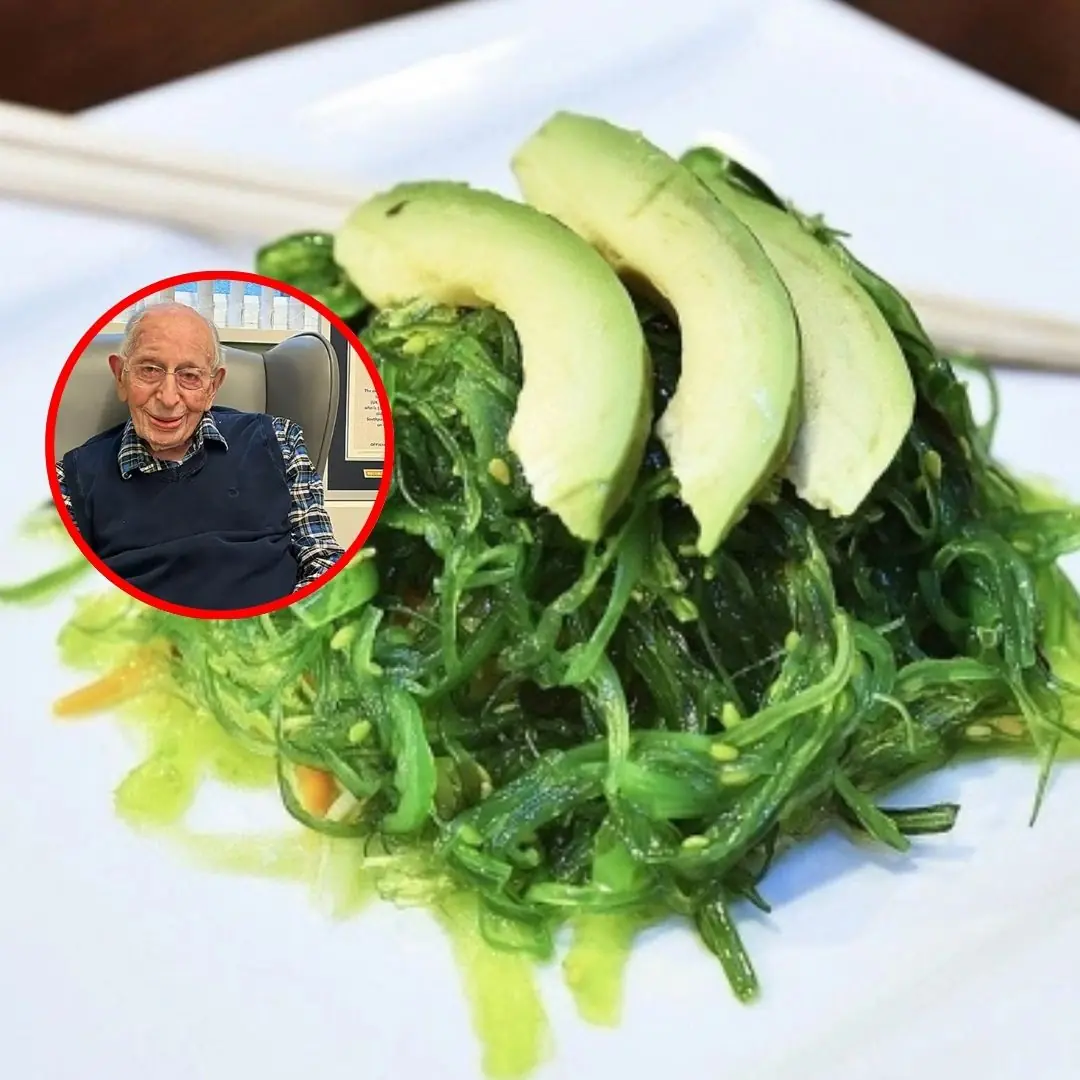

Experts point out that seaweed, algae, and bitter melon can activate genes related to longevity, serving as one of the secrets to the long lives of Okinawans.
At the end of February, the World Health Organization (WHO) predicted that there would be about 35 million new cancer cases by 2050, a 77% increase from the estimated 20 million cases in 2022. This means the global cancer burden will rise rapidly. Alongside screening and preventive treatment, Sanjay Gupta, Associate Professor of Neurosurgery at Emory University School of Medicine, emphasized that daily diet also plays a vital role in preventing this disease.
During his visit to the “Blue Zone” of Okinawa, where the highest number of centenarians live, he identified a method to support rejuvenation and stimulate the body’s “longevity genes.”
“Hidden in our DNA is a gene called FOXO3. It can delay the aging process but needs to be activated by the right foods,” he said.
Previous scientific reports have also found that the Okinawan diet helps reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease and inflammation.
According to Gupta, there are three types of foods that locals eat regularly, which may activate longevity genes:
Bitter Melon
According to Dr. Gupta, bitter melon has been used by Okinawans for centuries both as food and as a natural remedy for type 2 diabetes. It contains a phytonutrient called polypeptide-P, which can help lower blood sugar levels. Another compound, charantin, promotes glucose metabolism in the body.
Outside of Japan, Ayurveda (Hindu traditional medicine) and Traditional Chinese Medicine have long used bitter melon for its detoxifying and blood-cleansing effects. Its bitterness helps clear heat, cool the body, and is particularly beneficial for the liver, gallbladder, kidney stones, and water retention. Its detoxifying properties also positively affect the skin, reducing acne, eczema, and psoriasis.
Seaweed
In Japan, seaweed is an important part of the diet. It is rich in fiber, omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins A, C, E, and B, as well as abundant minerals such as magnesium, potassium, and zinc.
Growing scientific research shows that seaweed’s components and compounds provide various health benefits. Studies on mice have shown that adding seaweed to the diet improves blood cholesterol levels, even when consuming high-fat, high-cholesterol diets.
Other analyses indicate that seaweed can support weight loss and reduce blood pressure. Its high fiber content helps prevent colon cancer, type 2 diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular disease. Other compounds in seaweed offer strong antioxidant effects.
Algae
In addition to seaweed, other forms of algae are also an essential part of the Okinawan diet and may activate longevity genes. Green algae contain various bioactive components such as phycocyanin, carotenoids, fiber, and plant sterols, which help reduce total cholesterol in the intestines and downregulate fat-producing genes in the liver.
Green algae also reduce inflammation by suppressing the activity of a specific gene, thereby lowering the production of inflammatory cytokines. This plant inhibits lipid peroxidation, prevents free radical formation, and combats oxidative stress.
A 2021 study published in the U.S. National Library of Medicine found that consuming 1–8 grams of spirulina per day may help regulate both systolic and diastolic blood pressure, especially in people with high blood pressure.
Although more research is needed, some evidence suggests that algae may have anti-cancer properties. Animal studies indicate that algae can reduce tumor size in various types of cancer.
News in the same category


When a cat rubs against you - This is what it really means

While Silicon Valley Sleeps, Europe Is Rewriting the Rules of Tech

Some people are only now realizing what the “WC” sign stands for on washrooms

Feng Shui masters say these 4 apartment floors bring wealth and stability — are you living on one of them?

If AI Keeps Growing This Fast, Which Job Will Vanish First?

Hacks Everywhere: How the Age of Digital Shortcuts Is Rewriting Power, Privacy, and Survival
Europe’s Tech Awakening: How the EU Is Racing to Reclaim Its Digital Power

Here's why you should never sleep with a fan on at night
8 Foods You Should Not Combine With Chicken Meat — Everyone Should Know to Avoid Health Risks

A Builder’s Warning: Why You Shouldn’t Put a Bathroom Under the Stairs — Even With an Unlimited Budget

Air Fryers Are Convenient—but Never Use Them to Cook These Foods: The Complete List

What Happens to Your Body If You Eat 1 Clove of Garlic Every Day?

So this is what it does, here is the answer

People Who Eat Sweet Potatoes for Breakfast Daily Notice These Changes

Study reveals what really happens to your body if you go in sauna directly after working out

Why are the toilets on the train connected directly to the tracks?

A Flower Once Thought Useless Turns Out to Be a Fragrant, Delicious Dish—Now Going Viral
These are the consequences of wearing used…
If you often notice ringing in your ears, this might be a sign that you will suffer from...
News Post
Sudden confusion or difficulty speaking: when it’s more than just fatigue

Cherry Pistachio Cheesecake
Age 46-55 is 'high ri.sk period in life': 10 signs in people prone to str.o.ke, 'early de.a.th'
Unusual changes in the body warn that the kidneys are weakening. You should not be subjective
Vegetables listed as can:cer - causing that many people still eat, should be stopped immediately

Livestock and Veterinary Experts: 5 Ways to Identify Safe, High-Quality Pork and Distinguish It from Dise.ased or De.ad Pigs
Do Women Have Only 400 Eggs in a Lifetime? The Truth Behind the Claim “Whoever Runs Out of Eggs First Ages First”

Most people will go their entire life without ever knowing what the little arrow next to the gas gauge actually means

When a cat rubs against you - This is what it really means

While Silicon Valley Sleeps, Europe Is Rewriting the Rules of Tech

What happens to people who regularly eat sweet potatoes for breakfast over a long period of time?

The Health Hacks No One Told You About (But Your Body Has Been Begging For)

Banana Split Milkshake

What is the nutritional difference between black garlic and regular garlic?

What really happens when you sleep with socks on?

Euphorbia Hirta (Asthma-plant): Traditional Uses and Applications
4 red flags your brain is in trouble as scientists warn Alzheimer's starts decades before you realize

Some people are only now realizing what the “WC” sign stands for on washrooms
Beware of dia.betes if you frequently experience these 5 strange symptoms
