5 groups of people should limit shrimp intake

Shrimp is widely loved around the world for its sweet flavor, tender texture, and versatility in cooking. It is also considered a nutritious food, rich in protein, iodine, selenium, and omega-3 fatty acids. For many people, shrimp is a regular part of meals and special occasions alike.
However, doctors and nutrition experts caution that shrimp is not suitable for everyone. Despite its nutritional benefits, shrimp can pose health risks to certain groups of people. For these individuals, frequent or excessive consumption may worsen existing conditions or trigger serious reactions.
Below are five groups of people who should limit or avoid eating shrimp, even if they enjoy it.
1. People With Shellfish Allergies
One of the most important groups that should avoid shrimp entirely is people with shellfish allergies.
Shrimp is a common allergen, and reactions can range from mild to life-threatening. Symptoms may include:
-
Skin rashes, itching, or hives
-
Swelling of the lips, face, or throat
-
Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea
-
Difficulty breathing or wheezing
-
Anaphylaxis in severe cases
Even a small amount of shrimp can trigger a serious allergic reaction. Cooking does not destroy the allergenic proteins, so shrimp remains dangerous in all forms - boiled, fried, or grilled.
For people with known shellfish allergies, strict avoidance is essential.
2. People With High Cholesterol or Heart Disease
Shrimp is relatively low in fat, but it is high in dietary cholesterol. A 100-gram serving of shrimp can contain over 180 mg of cholesterol, which is close to the recommended daily limit for some individuals.
While dietary cholesterol does not affect everyone equally, people with:
-
High LDL (“bad”) cholesterol
-
Coronary artery disease
-
A history of heart attack or stroke
should be cautious. Frequent shrimp consumption, especially when cooked with butter, oil, or creamy sauces, may contribute to unhealthy cholesterol levels.
Doctors often recommend limiting shrimp intake or consuming it occasionally and pairing it with heart-healthy foods such as vegetables and whole grains.
3. People With Gout or High Uric Acid Levels
Shrimp contains purines, compounds that break down into uric acid in the body. High uric acid levels can trigger or worsen gout attacks.
For people with gout, eating shrimp may lead to:
-
Sudden joint pain
-
Swelling and redness, often in the toes or knees
-
Increased frequency of gout flare-ups
Individuals with a history of gout or hyperuricemia are generally advised to limit high-purine foods, including shrimp and other shellfish.
4. People With Kidney Disease
Shrimp is high in protein and contains minerals such as phosphorus and sodium, which can be problematic for people with impaired kidney function.
For individuals with chronic kidney disease:
-
Excess protein can strain the kidneys
-
High phosphorus levels may weaken bones
-
Sodium can worsen fluid retention and blood pressure
Additionally, shrimp may contain trace amounts of heavy metals depending on where it is sourced. Healthy kidneys can usually filter these substances, but damaged kidneys may struggle to do so.
Doctors often recommend limiting seafood intake and following a kidney-friendly diet under medical supervision.
5. People With Digestive Disorders or Weak Digestion
Shrimp can be difficult to digest for some individuals, especially when fried or heavily seasoned. People with digestive issues such as:
-
Chronic gastritis
-
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
-
Acid reflux or indigestion
may experience bloating, abdominal pain, or diarrhea after eating shrimp.
Shrimp is also considered a “cold” food in some traditional medicine systems, which may worsen digestive discomfort in sensitive individuals.
Eating shrimp in small amounts, well-cooked, and without heavy spices may reduce symptoms, but moderation is key.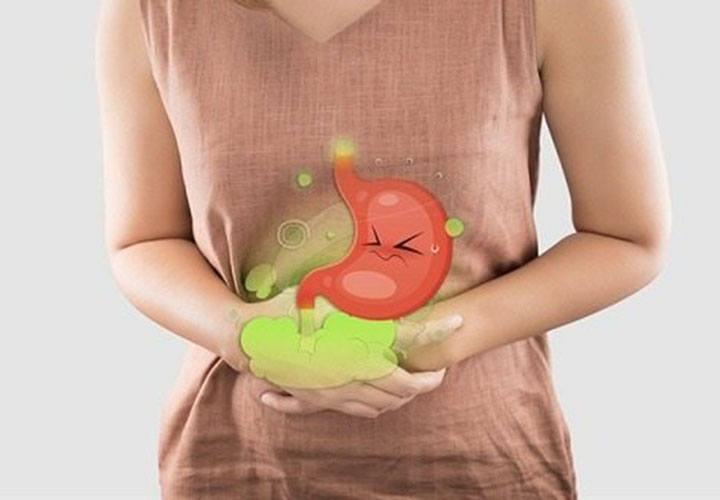
Additional Concerns About Shrimp Consumption
Food Safety and Contamination
Shrimp can carry bacteria, parasites, or antibiotic residues if not sourced or handled properly. Eating undercooked or contaminated shrimp increases the risk of food poisoning.
Cooking Methods Matter
Deep-frying shrimp or cooking it with excessive oil, salt, or butter can turn a healthy food into an unhealthy one—especially for people with metabolic or cardiovascular conditions.
How to Eat Shrimp More Safely (If You Are Not in a High-Risk Group)
If you do not fall into the groups above and choose to eat shrimp, consider these tips:
-
Limit portion sizes
-
Choose steaming, boiling, or grilling instead of frying
-
Avoid pairing shrimp with high-fat sauces
-
Buy shrimp from reputable sources
-
Ensure it is fully cooked
Final Thoughts
Shrimp can be a nutritious and enjoyable food, but it is not suitable for everyone. People with allergies, high cholesterol, gout, kidney disease, or digestive problems should be especially cautious.
Listening to your body, understanding your health conditions, and following medical advice are far more important than taste alone. When it comes to shrimp - or any food - moderation and personalization are key to long-term health.
Basic Steps to Take if You Have a Shrimp Allergy Reaction
A shrimp allergy can range from mild discomfort to a life-threatening emergency. Knowing how to respond quickly and appropriately can make a critical difference.
1. Stop Eating Shrimp Immediately
At the first sign of an allergic reaction, stop consuming shrimp or any food that may contain shellfish. Do not try to “wait it out” or continue eating.
Common early symptoms may include:
-
Itching or tingling in the mouth or throat
-
Skin redness, hives, or swelling
-
Nausea, stomach pain, or vomiting
2. Rinse the Mouth and Avoid Further Exposure
Gently rinse your mouth with clean water to remove any remaining shrimp proteins. Avoid touching your face, eyes, or lips, as allergens can be transferred through contact.
3. Take an Antihistamine for Mild Symptoms
For mild reactions such as itching, hives, or mild swelling, an over-the-counter antihistamine (such as cetirizine or loratadine) may help reduce symptoms.
Important note:
-
Antihistamines do not treat severe allergic reactions.
-
They should not delay emergency care if symptoms worsen.
4. Watch Closely for Worsening Symptoms
Allergic reactions can escalate quickly. Seek emergency medical help immediately if any of the following occur:
-
Difficulty breathing or wheezing
-
Swelling of the lips, tongue, or throat
-
Dizziness, fainting, or confusion
-
Rapid heartbeat
-
Severe vomiting or diarrhea
These symptoms may indicate anaphylaxis, a life-threatening condition that requires urgent treatment.
5. Use an Epinephrine Auto-Injector if Prescribed
If the person has a known shrimp or shellfish allergy and carries an epinephrine auto-injector (such as an EpiPen):
-
Use it immediately at the first sign of severe symptoms
-
Inject into the outer thigh, even through clothing if necessary
-
Call emergency services right away after use
Epinephrine is the only effective first-line treatment for anaphylaxis.
6. Seek Medical Evaluation After Any Reaction
Even if symptoms improve, medical evaluation is important. Some allergic reactions can return hours later (a biphasic reaction).
Doctors may:
-
Monitor breathing and blood pressure
-
Prescribe emergency medications
-
Recommend allergy testing or long-term management plans
How to Prevent Future Shrimp Allergy Reactions
-
Avoid shrimp and all shellfish completely if allergic
-
Read food labels carefully
-
Be cautious when eating at restaurants due to cross-contamination
-
Inform friends, family, and food handlers about the allergy
-
Carry an epinephrine auto-injector if prescribed
Final Reminder
A shrimp allergy should never be taken lightly. Early recognition, fast action, and proper medical care are essential. When in doubt, always choose safety and seek professional help.

News in the same category
8 Red Flags That Your Stomach Problem May Be Advanced — See a Doctor Early
These 10 Symptoms Could Mean Your Kidneys Are Failing—Act Now

What is the safest time to bathe to protect your health and reduce str.oke risk?

Drooling during sleep: A small sign that may point to bigger health issues

4 anti-aging dietary principles you should apply
Pan.creatic can.cer: 10 early warning signs you should never ignore

Doctors Reveal the Truth About Avocado That Most People Don’t Know
His whole body was itchy, he thought it was an allergy. But he was diagnosed with

Heart Surgeon Warns People Should Remove This One Thing From Their Life After Turning 40
Foods to be mindful of when living with hypo.thyroidism

4 types of people who should avoid eating cabbage

5 unusual foot symptoms that may indicate abnormal blo.od sugar levels
Sleeping Without a Blanket Feels Impossible for Many — Here’s Why

Those who love eating sweet potatoes must read this article, it will change your life! It's not too late to know now!
Persistent Cough, Lingering Flu Symptoms: Warning Signs of Lung Can.cer Often Mistaken for “Minor ill.nesses”

Leg pain, rheumatism, varicose veins, arthritis – a natural remedy with cloves and garlic that many people don't know about
Health Expert Reveals Warning Signs of Two Silent Foot Killers and How To Spot Them

Itching at night, woman goes to the doctor and learns she only has 8 months to live
News Post
Sheet Pan Gnocchi with Zucchini, Tomatoes, and Bell Peppers

Mediterranean Chickpea Salad with Feta

3 types of shirts you should never wear to a funeral

8 Red Flags That Your Stomach Problem May Be Advanced — See a Doctor Early

Creamy Crab and Shrimp Seafood Bisque

These 10 Symptoms Could Mean Your Kidneys Are Failing—Act Now

What is the safest time to bathe to protect your health and reduce str.oke risk?

Flight Attendant Reveals the Real Reason Cabin Crew Sit on Their Hands During Takeoff

Drooling during sleep: A small sign that may point to bigger health issues

4 anti-aging dietary principles you should apply

Roasted Beetroot and Avocado Salad with Feta

Pan.creatic can.cer: 10 early warning signs you should never ignore

Avocado Berry Salad with Nuts & Greens

Doctors Reveal the Truth About Avocado That Most People Don’t Know

Mediterranean Meatball Bowl with Roasted Potatoes & Tzatziki

Churro Caramel Crunch Cupcakes

Creamy Chicken Vegetable Soup

His whole body was itchy, he thought it was an allergy. But he was diagnosed with
