
The convenience is temporary — the problems are permanent
The convenience is temporary — the problems are permanent

Coconut water is often referred to as a “natural sports drink” thanks to its refreshing taste and naturally occurring electrolytes. Extracted from young green coconuts, coconut water has gained global popularity as a hydrating beverage and a healthier alternative to sugary soft drinks and some commercial sports drinks. But how accurate are the health claims surrounding coconut water?
Coconut water is the clear liquid found inside young coconuts, typically harvested when the coconut is around 6–7 months old. An average green coconut provides approximately half a cup to one cup of coconut water.
One cup (240 ml) of coconut water contains about:
Calories: ~60
Carbohydrates: ~15 g
Sugars: ~8 g
Potassium: ~15% of the recommended daily value (DV)
Magnesium: ~4% DV
Calcium: ~4% DV
Phosphorus: ~2% DV
Sodium: ~2% DV
Coconut water is about 94% water, contains very little fat, and provides a modest amount of natural sugars along with key minerals.

Thanks to its electrolyte content—particularly potassium, along with smaller amounts of sodium, magnesium, and calcium—coconut water can help replenish fluids lost through sweating. These electrolytes play essential roles in muscle contraction, nerve transmission, and maintaining proper fluid balance in the body.
While coconut water can be effective for light to moderate hydration, it contains less sodium than many commercial sports drinks. Therefore, during prolonged or extremely intense exercise, athletes may still require specialized electrolyte solutions.
Coconut water is rich in potassium, a mineral known to help regulate blood pressure. Potassium helps counteract the effects of excess sodium by promoting sodium excretion through urine and relaxing blood vessel walls. Regular potassium intake has been associated with improved blood pressure control and reduced cardiovascular risk.
Adequate fluid intake is crucial for preventing kidney stones, as it dilutes urine and reduces crystal formation. Some preliminary research suggests coconut water may help lower urinary crystal formation, although more large-scale human studies are needed to confirm this effect.
Small studies suggest that coconut water may help lower cholesterol and triglyceride levels in people with elevated blood lipids. By improving lipid profiles and supporting healthy blood pressure, coconut water may indirectly contribute to better cardiovascular health.
Coconut water helps maintain hydration, which is essential for healthy digestion and bowel function. While laboratory studies indicate possible anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties, strong clinical evidence in humans is still limited. Coconut water should be viewed as supportive rather than a treatment for digestive disorders.
Coconut water contains compounds called cytokinins, plant hormones involved in cell growth. While laboratory studies suggest they may have antioxidant or anti-aging properties, there is currently no strong clinical evidence proving that drinking coconut water significantly slows aging or dramatically improves skin elasticity in humans.
Coconut water is generally safe and beneficial for most people when consumed in moderation. However:
People with kidney disease should monitor potassium intake.
Excessive consumption may contribute unnecessary sugar and calories.
It should not be relied upon as a medical treatment or sole electrolyte source in extreme conditions.
Coconut water is a refreshing, nutrient-rich beverage that offers real hydration benefits and provides essential electrolytes, particularly potassium. It can support fluid balance, help maintain healthy blood pressure, and serve as a natural alternative to sugary drinks. However, some health claims—especially those related to anti-aging and disease treatment—are not yet supported by strong scientific evidence.
When enjoyed as part of a balanced diet, coconut water can be a healthy and enjoyable addition to daily hydration—but it is best viewed as a supportive wellness drink rather than a cure-all.

The convenience is temporary — the problems are permanent

What’s the ideal schedule for changing your underwear?

This common electric kettle habit may be driving up your power costs

Do You Nap During the Day? Here’s What You Should Know

10 Habits Often Seen as Rude That May Reflect Intelligence
Understanding Moles on the Lip: Possible Causes and Concerns

Once Ignored, Now Celebrated: The Wild-Growing Vegetable Being Called a “Miracle Herb” for Health

Cats are curious, independent creatures—and while that’s part of their charm, it can also be the source of stress when one suddenly disappears.

When a lizard visits your house that’s a sign...

She Was Just Peeling a Boiled Egg… Until She Saw What Was Hidden Inside

When Your Parent Shows These 4 Signs, Emotional Preparation Matters

Here’s What That Little Pocket in Women’s Underwear Is Actually For

Regardless of How Much You Earn, Get Rid of These 4 Things Without Delay

That tiny pocket on your jeans has a surprising history you probably never knew.

Keep these 3 mindsets, and success will follow

Not all garlic is safe to buy—learn which cloves you should avoid at the market today.

She Di:ed From a Stroke and Came Back: What She Saw Will Sho:ck You

The meaning of a ring worn on the right hand is not widely known

Most people THROW IT AWAY — but this tiny metal ring on sausages is actually saving your health!
Do you know why there’s a small scar on the upper left arm and what it means?
Sleeping With… Could Affect You More Than You Think
Lung cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths worldwide.
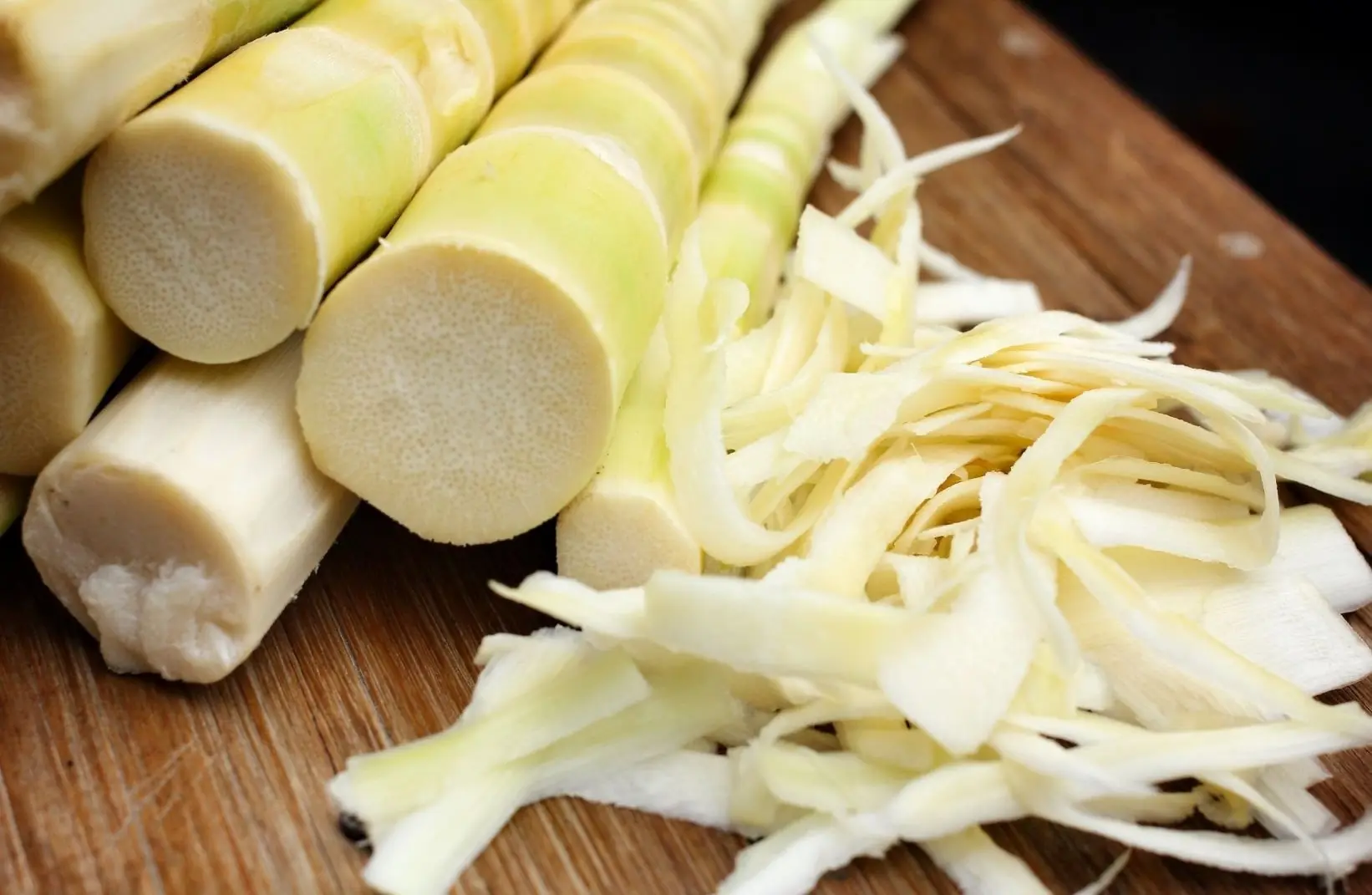

Are Bamboo Shoots Harmful in Large Amounts?
Itchy Ears? Beware of Juvenile Spring Eruption
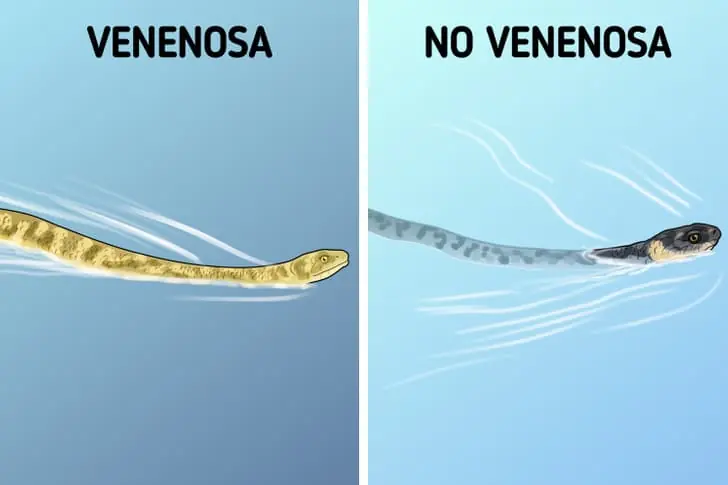
Simple ways to recognize venomous snakes and protect yourself in the wild
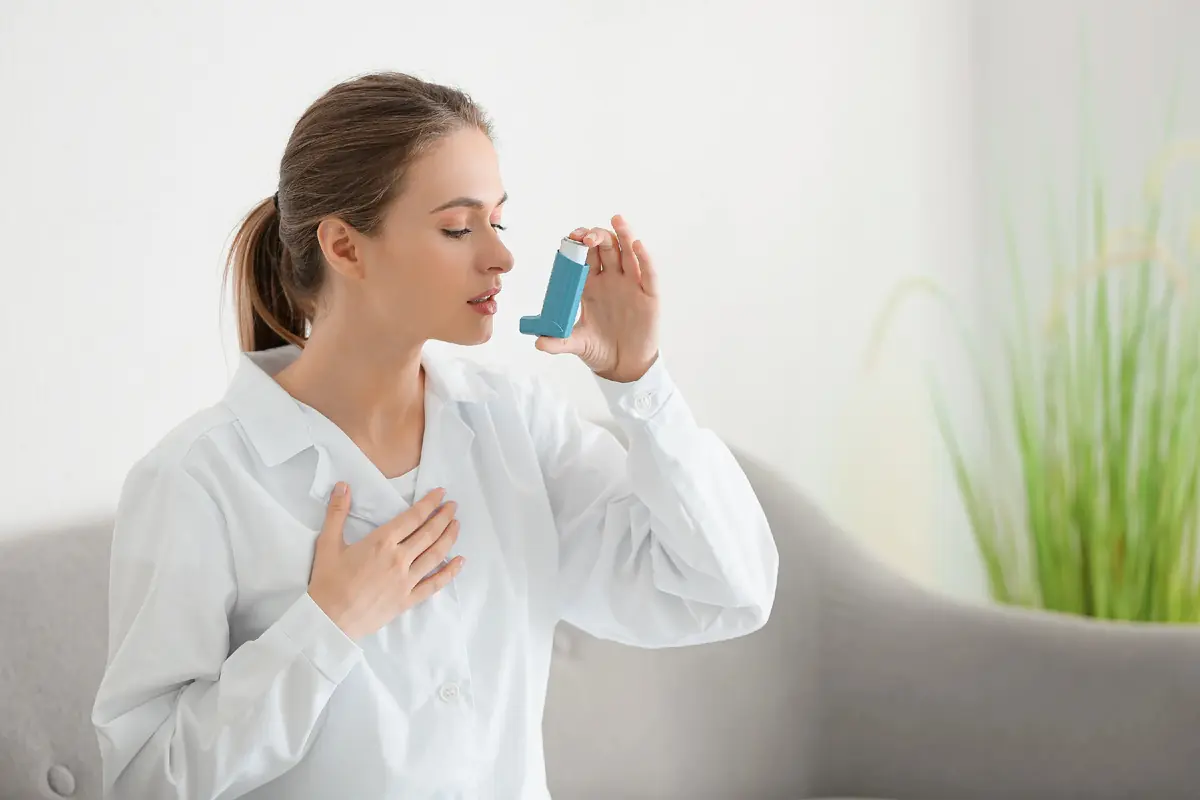

Serious Health Clues Hidden in Your Nasal Symptoms
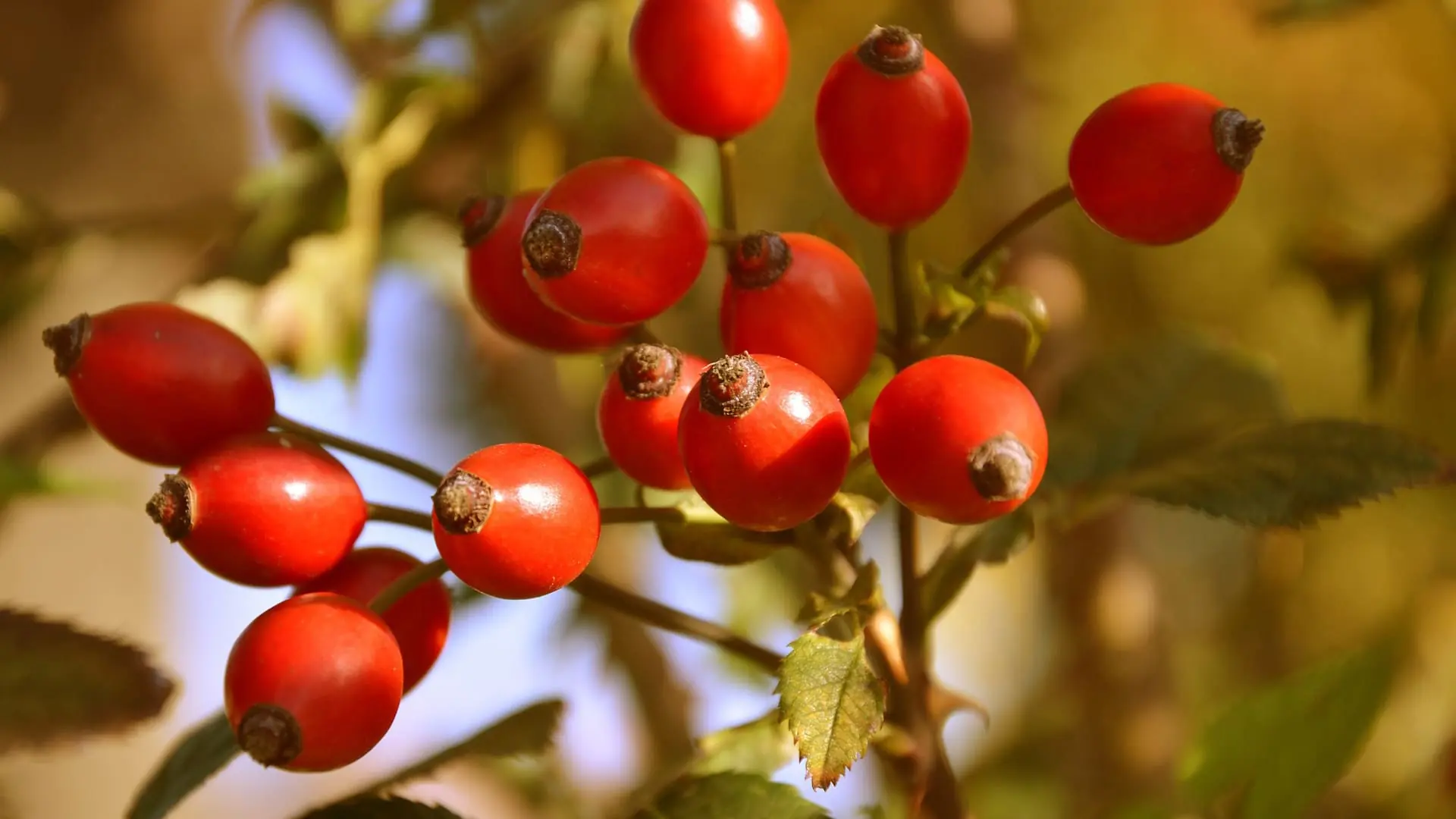

10 powerful health benefits of Dog Rose (Rosa canina) and the best ways to use it
Don’t ignore this unusual sign in your body - it may indicate late-stage nasopharyngeal can.cer

Is tilapia really good for you? Some facts might make you think twice
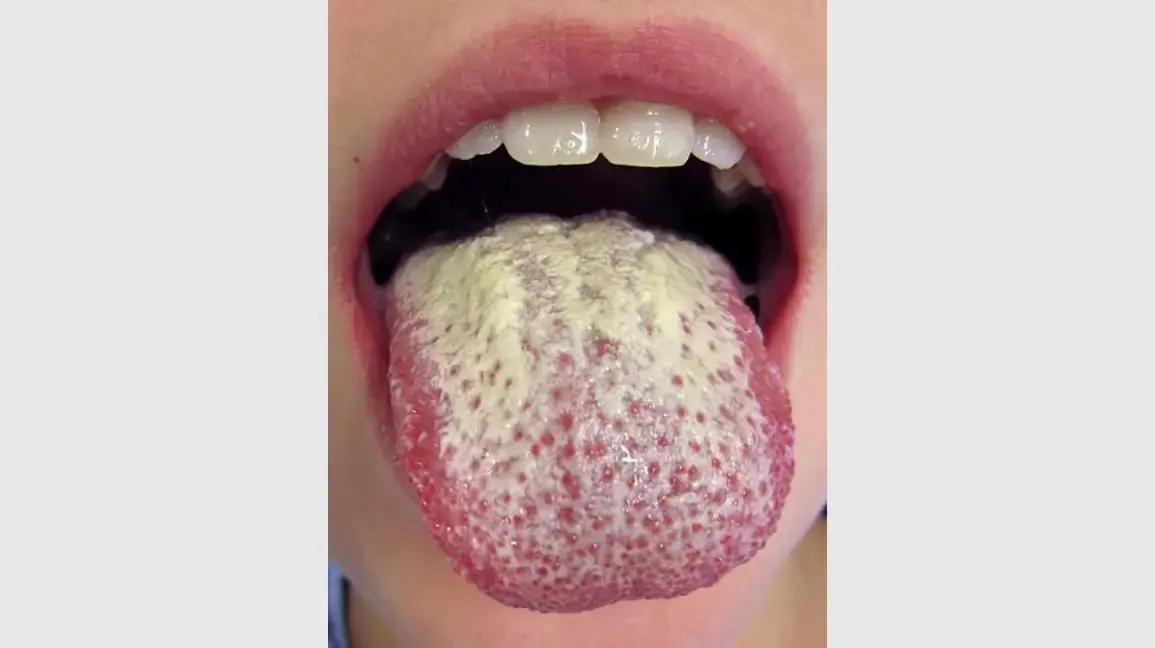
White Coating on Your Tongue? Here’s What Your Body Might Be Telling You

3 overlooked spousal habits that may put wives at greater risk for cer.vical can.cer - awareness matters

The 3-Hour Rule Before Bed: A Simple Habit for Better Blood Pressure and Blood Sugar

These 5 strange signs could be warning signals of dia.betes - don’t ignore them

Why People in Japan Sleep on the Floor and 5 Reasons to Give It a Try
7 Important Signs Your Body Is Crying Out for Help

Taro: The Underrated Superfood That Could Transform Your Energy, Digestion, and Overall Wellness
At just 20 years old, Linh Nguyen (name changed), a young and passionate teacher at a local elementary school, passed away from liver cancer — a disease typically associated with older individuals or those with long-term health issues.

Cancer is one of the leading causes of death worldwide, but the good news is that certain foods contain powerful compounds that may help prevent and even fight cancer.

Magnesium is an essential mineral in the human body, playing a critical role in over 300 enzymatic processes.

Three Morning Habits Young People Often Ignore That Can Seriously Dam:age Their Kidneys — Quit These Now