
Why don't Americans eat pork?
We all know that food consumption habits vary greatly among countries.
Snakes are often misunderstood creatures. While they play an essential role in maintaining balance in ecosystems by controlling rodent and
pest populations, the mere sight of a snake can trigger fear and panic in many people. This reaction is understandable - some snakes are
venomous and can pose serious risks to human health if bitten.
However, the truth is that the majority of snakes are non-venomous and pose little to no threat to humans. The real danger often comes
not from the snake itself, but from misidentification, panic, and improper reactions. Learning how to tell the difference between poisonous
(venomous) and non-poisonous snakes can help you stay calm, make safer decisions, and avoid unnecessary harm to both yourself and the
animal.
This article explores the key physical and behavioral differences between venomous and non-venomous snakes, along with practical advice on
what to do if you encounter one.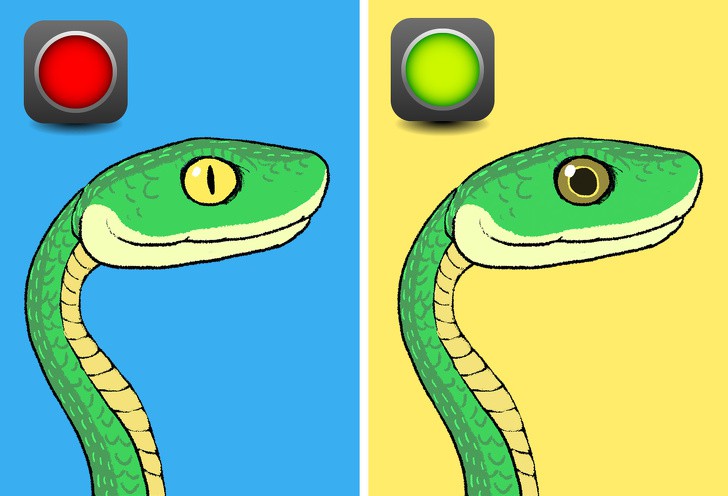
Although no single feature can identify every snake with absolute certainty, several physical traits can provide helpful clues when viewed
together.
Venomous snakes:
Many venomous snakes - especially pit vipers such as rattlesnakes, copperheads, and water moccasins - have a distinctly triangular or arrow-
shaped head. This shape is caused by large venom glands located behind the eyes, making the head appear wider than the neck.
Non-venomous snakes:
Most non-poisonous snakes have rounded or oval-shaped heads that blend smoothly into the neck. There is usually no dramatic widening
behind the eyes.
⚠️ Important note: Some non-venomous snakes can flatten their heads when threatened, temporarily mimicking this triangular appearance.
Venomous snakes:
Many venomous species, particularly pit vipers, have vertical, slit-like pupils similar to a cat’s eyes. This feature helps them hunt effectively in
low-light conditions.
Non-venomous snakes:
Most non-poisonous snakes have round pupils. However, this rule is not universal - some harmless snakes may also have slit-like pupils.
Because pupil shape can be difficult to observe safely, it should never be used as the sole identifying feature.
Venomous snakes:
Some venomous snakes have keeled scales - scales with a raised ridge down the center - giving their skin a rough, matte texture.
Non-venomous snakes:
Non-venomous snakes often have smooth, shiny scales that give their bodies a sleek appearance.
Again, this is a guideline rather than a guarantee, as there are exceptions on both sides.
Venomous snakes:
Many venomous snakes display distinctive patterns or bold coloration. For example:
Coral snakes have bright red, yellow, and black bands
Rattlesnakes and copperheads often have camouflage patterns that blend into leaves, rocks, or dirt
These colors may serve as warning signals or help with camouflage.
Non-venomous snakes:
Non-poisonous snakes may also have patterns, but they are often less vivid or dramatic. Some harmless species even mimic the appearance of
venomous snakes as a defense mechanism..jpg)
Venomous snakes:
Rattlesnakes are easily identified by the rattle at the end of their tail, which produces a distinctive sound when shaken. This rattle serves as a
warning, not an attack signal.
Non-venomous snakes:
Some harmless snakes will vibrate their tails in dry leaves or grass to imitate the sound of a rattlesnake, but they do not have an actual rattle.
Never rely on sound alone to identify a snake.
Behavior can provide additional clues about whether a snake is dangerous.
Venomous snakes:
Venomous snakes may coil their bodies, raise their heads, hiss loudly, or strike if they feel threatened or cornered. These behaviors are
defensive - not aggressive. Most venomous snakes prefer to avoid humans entirely.
Non-venomous snakes:
Non-poisonous snakes are generally shy and will try to flee as soon as they sense danger. If escape is impossible, they may bluff by puffing up
their bodies, striking without venom, or vibrating their tails.
Venomous snakes:
Venomous species rely on venom to immobilize or kill prey. Many use specialized heat-sensing organs to detect warm-blooded animals and
deliver venom through fangs.
Non-venomous snakes:
Non-poisonous snakes typically kill prey by constriction - wrapping around it and squeezing until it suffocates. While their bites can be
painful, they are not medically dangerous.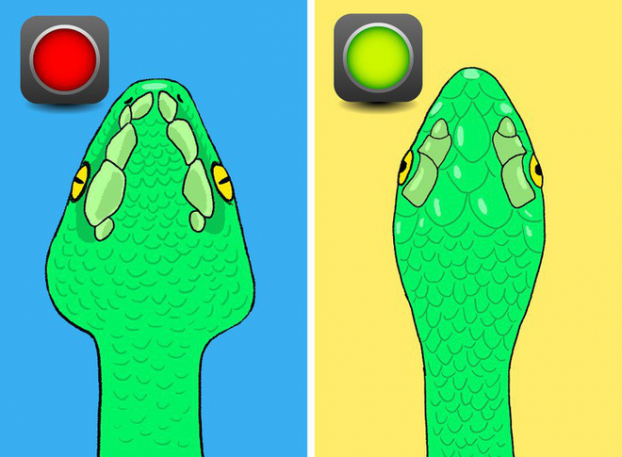
Regardless of whether a snake is venomous or not, the safest response is always the same.
Do not panic, run, or attempt to touch the snake. Slowly back away and give it plenty of space.
Quick motions can startle a snake and trigger defensive behavior.
If the snake is moving away or remaining still, let it be. Most snakes will retreat if given the opportunity.
If a snake enters your home or a public area, contact wildlife control or local authorities. Do not attempt to remove it yourself.
Seek medical attention immediately - even if you believe the snake is non-venomous. Prompt treatment can prevent complications.
One of the best ways to stay safe is to learn which snake species live in your area. Local wildlife agencies often provide guides that show:
Which snakes are venomous
Where they are commonly found
How to avoid encounters
Knowledge reduces fear and helps you respond appropriately.
Being able to recognize the differences between venomous and non-venomous snakes is a valuable skill, especially for those who live, work,
or travel in snake-prone areas. By understanding physical traits, behavior patterns, and safe response strategies, you can protect yourself while
respecting wildlife.
Remember: most snakes do not want to harm humans. They bite only when threatened or startled. Staying calm, observant, and informed is
the best way to stay safe.
This article is for educational purposes only. If a snake bite occurs, always seek immediate medical care, regardless of the suspected species.

We all know that food consumption habits vary greatly among countries.

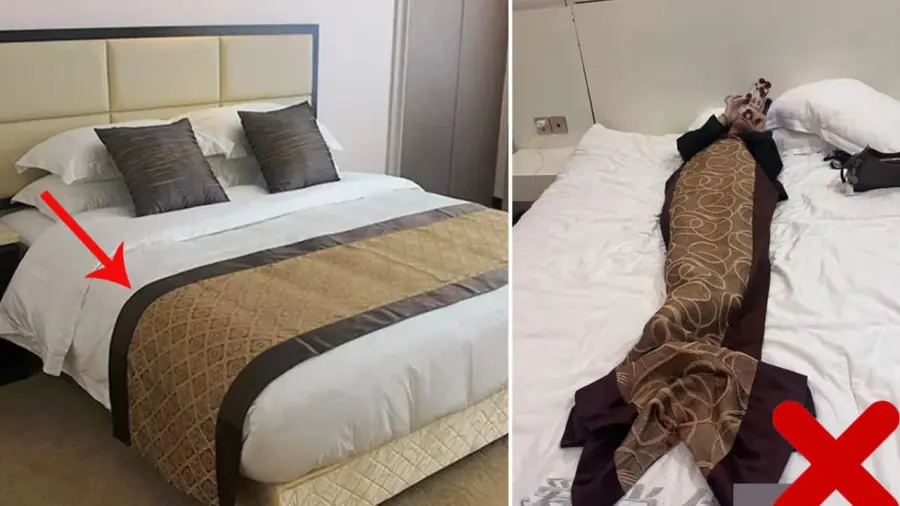
Typically, hotel beds come with at least four pillows

Plants that should not be planted because they attract snakes into the house, including very familiar types
Your feet might not be the first place you think of when you hear “heart health”

3 quick and reliable methods to safely defrost fish and get it perfectly ready for cooking
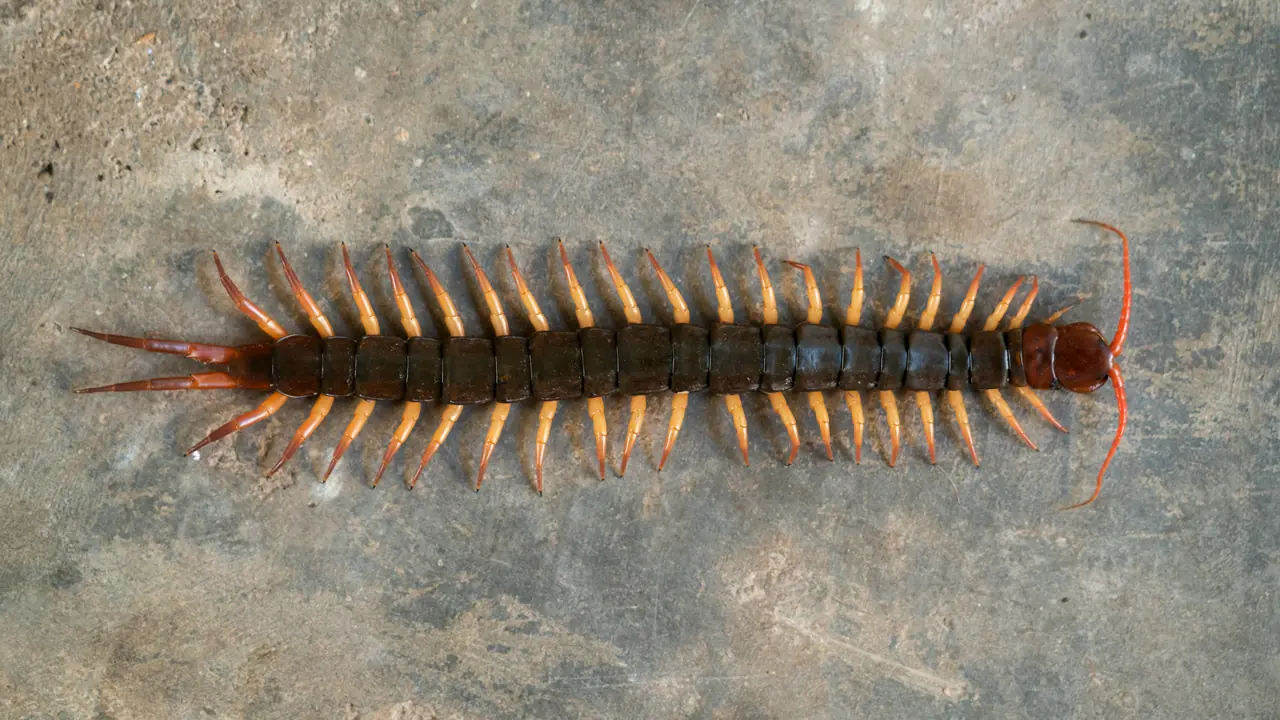

Why you shouldn’t rush to ki.ll millipedes when you find them inside your home?
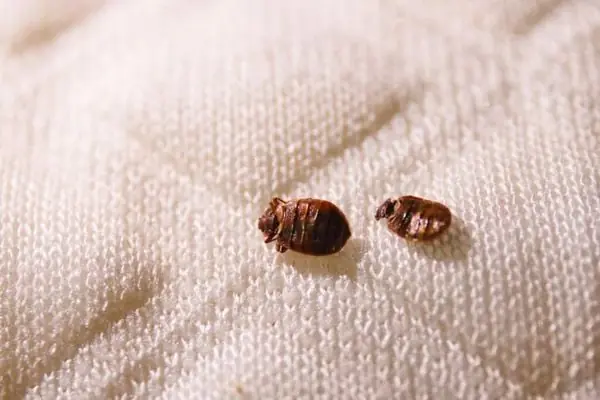

Natural ways to eliminate bed bugs: Proven home solutions
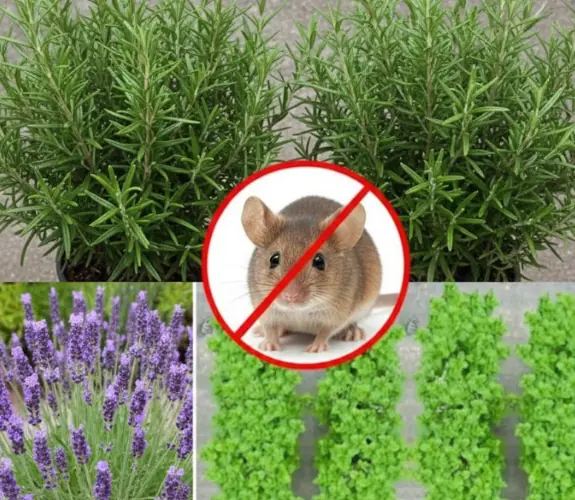

Best plants to grow for repelling mice from the house effectively

After a period of use, showerheads often get clogged due to mineral deposits sticking inside, causing uneven water flow.

Here’s a surprisingly simple household trick to sharpen your old, dull scissors without any special tools.
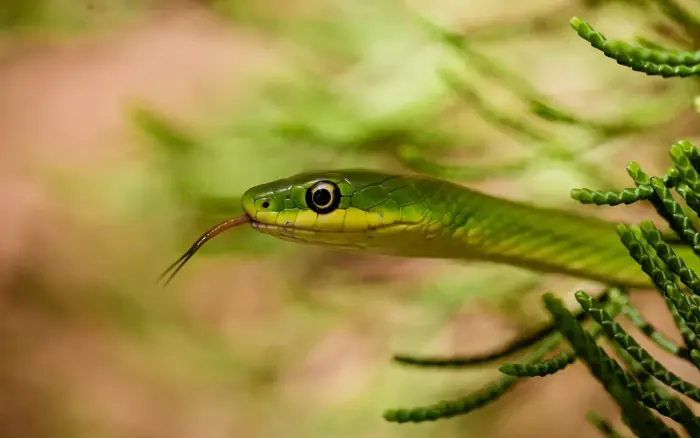

These 5 plants in your garden could make it more appealing to snakes

A simple Japanese food hack keeps leftover rice soft, fresh, and tasty.

5 powerful plants that help fight formaldehyde and purify indoor air
Your phone’s volume buttons do more than you realize: 6 hidden tricks

4 great reasons to place an onion in the corner of your room
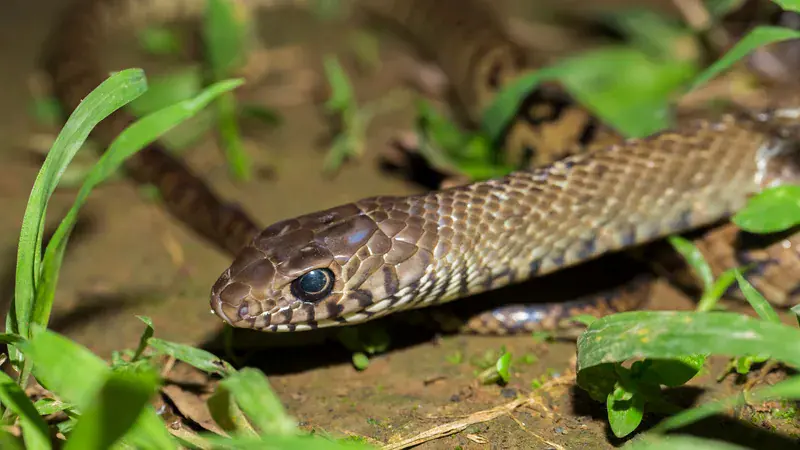

7 smells snakes can’t stand that help keep them away from your home
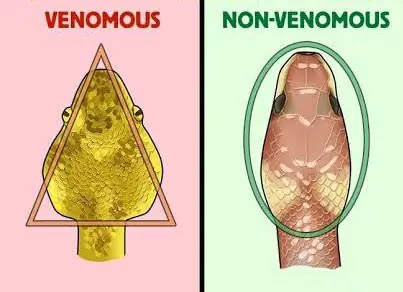
If a Snake Bites You, These First Actions Could Save Your Life

Just one careless step can cause the filling to collapse, distort the shape, and reduce its ability to retain heat.

Noisy, shaking washer? Try these quick fixes before calling a technician
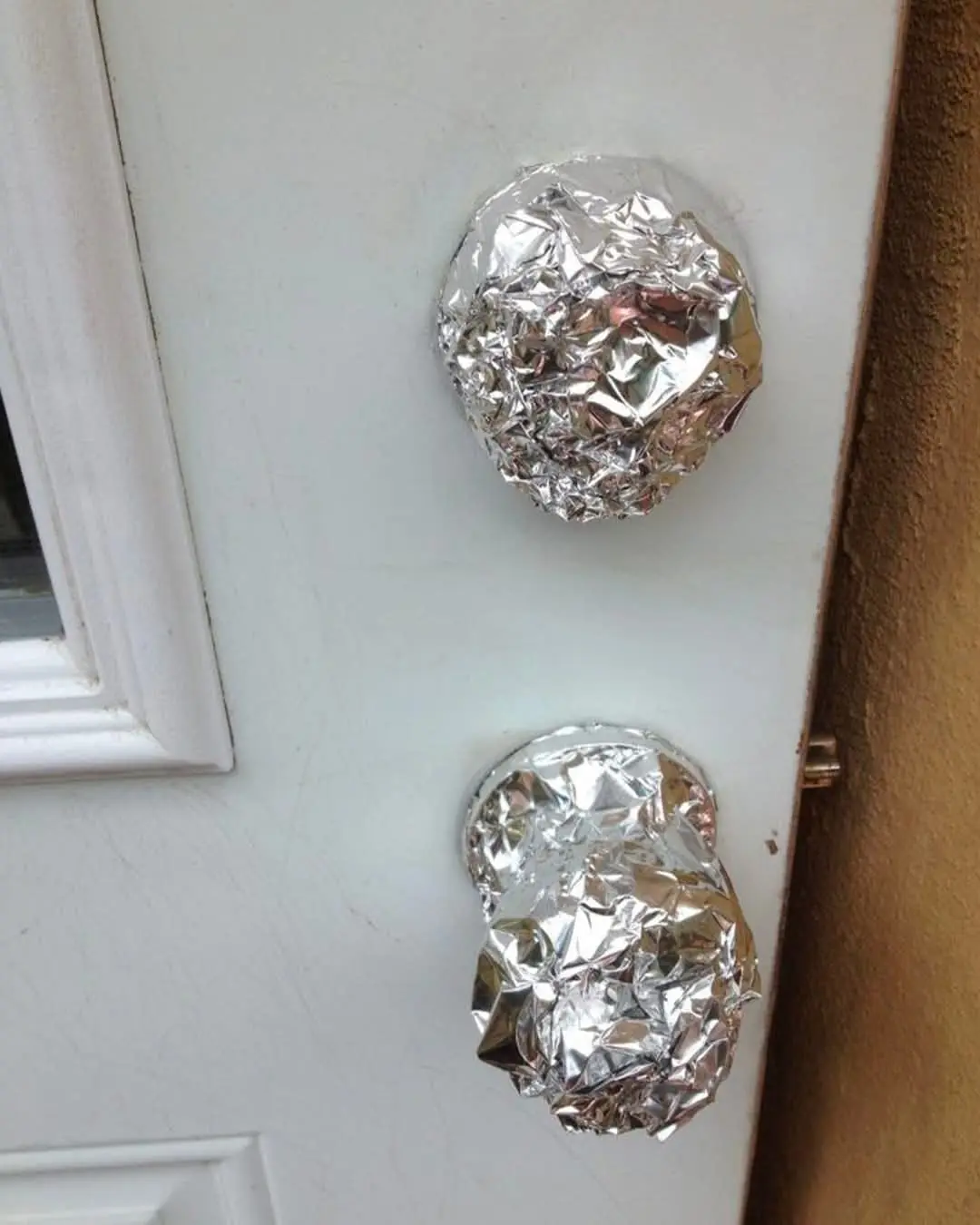

Wrap Your Door Handle in Aluminum Foil Before Bed — The Unexpected Security Hack That Works


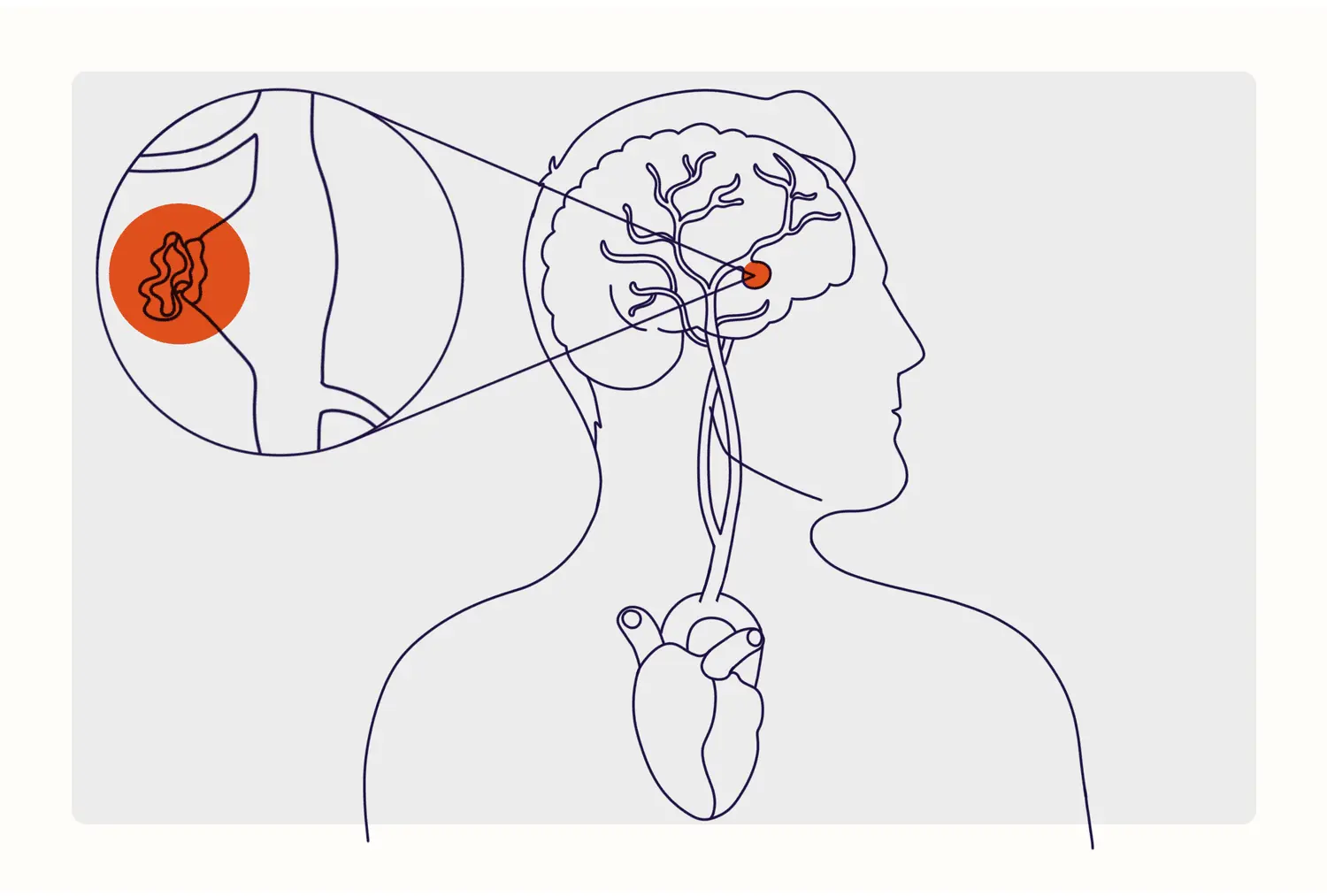
Warning Signs of an Aneurysm: Don’t Ignore These Life - Threa:tening Symptoms

Wearing Socks to Bed? You'll Be Surprised What Happens

Doctors consider serious red flags
A man in his 40s di.ed of a stroke after doing just one thing to “warm up” immediately after waking.

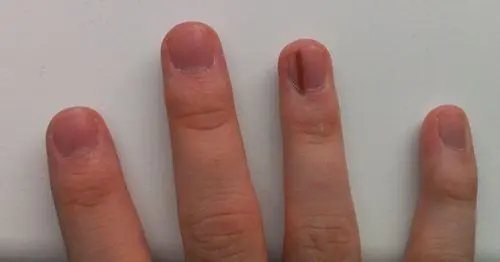
Doctors Warn: 3 Nail Symptoms That May Indicate Underlying Health Issues

Doctors were confused when a strange growth was found in a 9-month-old ba.by’s mouth
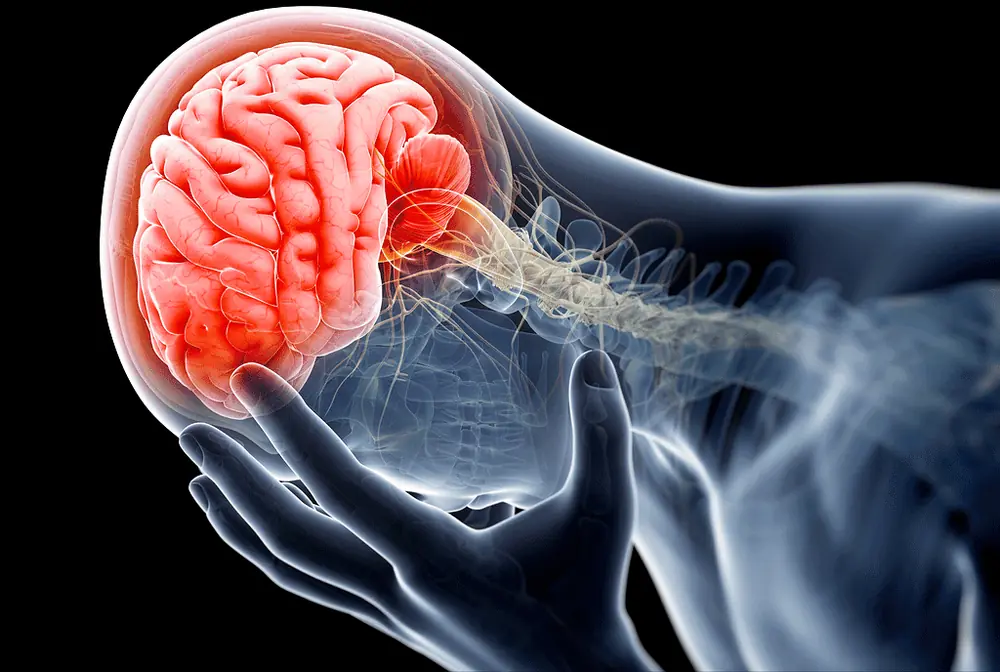
5 critical periods when the risk of brain hemo.rrhage increases
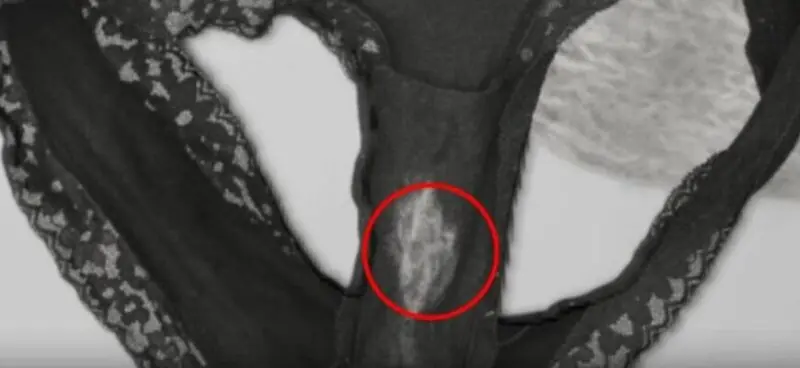
Warning: A Bleach - Like Stain in Your Underwear May Be Trying to Tell You Something
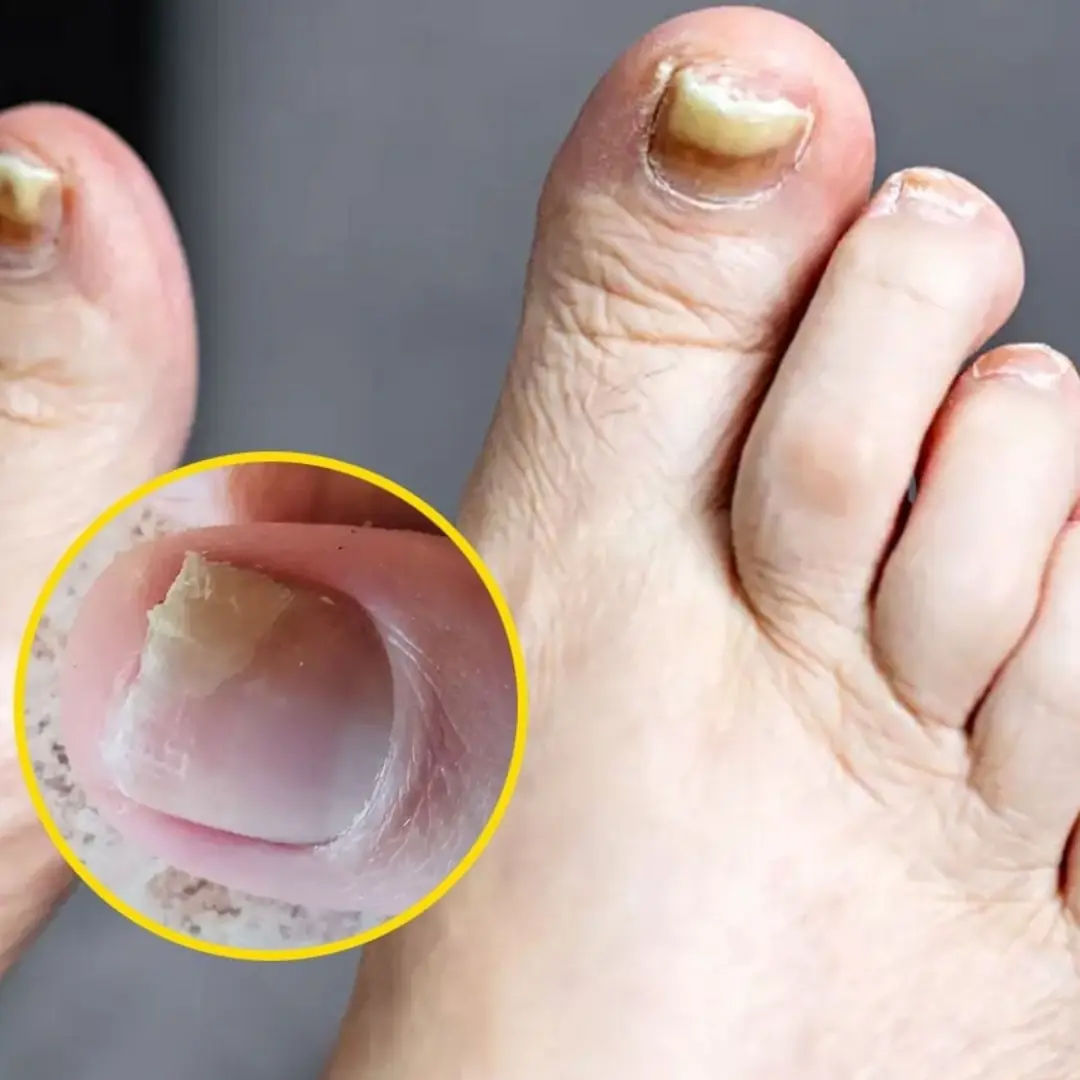
Two Warning Signs Of Silent Kil:ler That You Might Spot In Your Feet
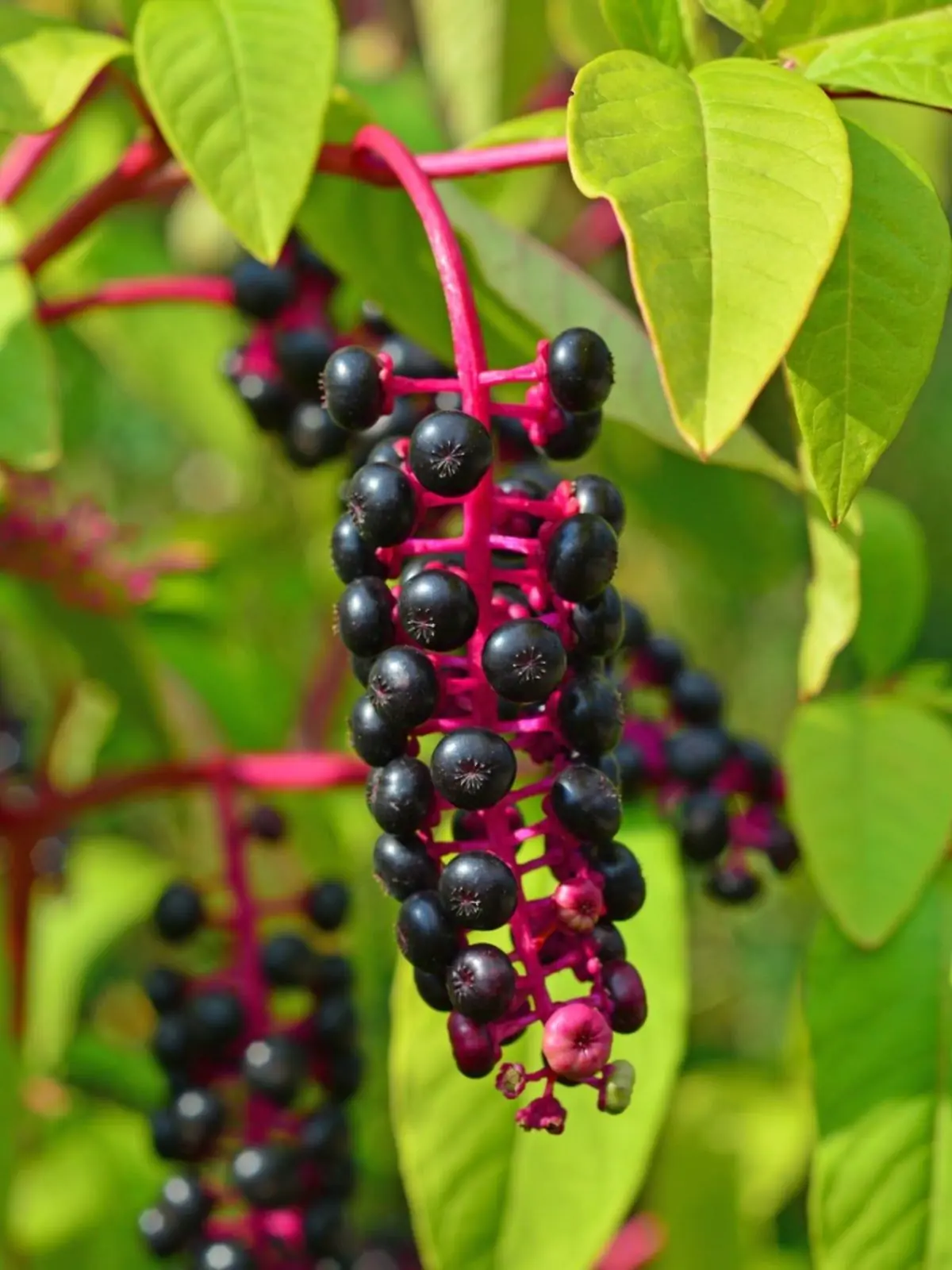

Pokeweed (Phytolacca americana): Beautiful to Look At, Dan.gerous to Touch
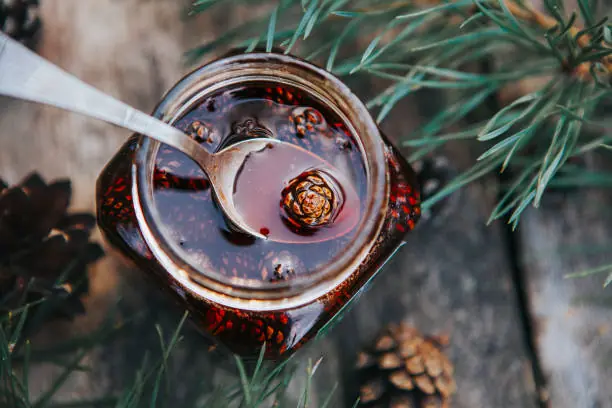

Discover Pine Cone Syrup: Benefits, Easy Recipe, and Creative Everyday Uses
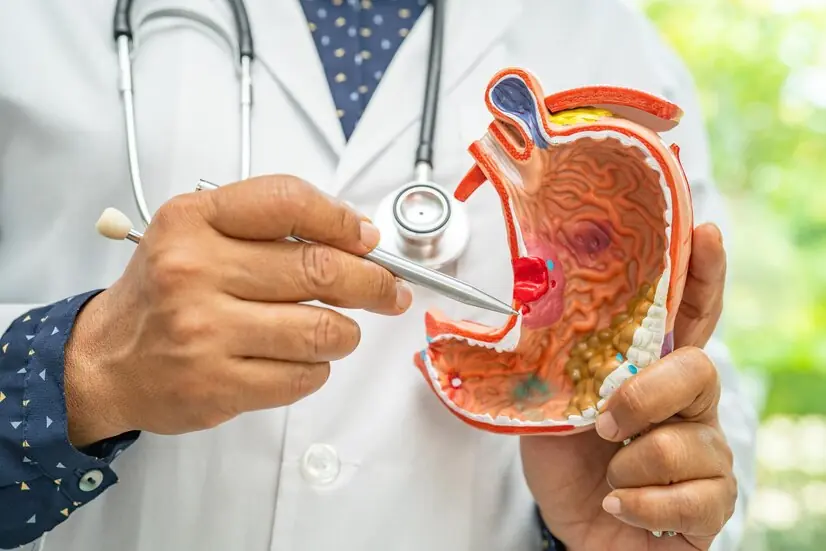
Woman Di:es of Stomach Can:cer; Doctor Reveals 3 Bedtime Habits That Silent Harmed Her Health
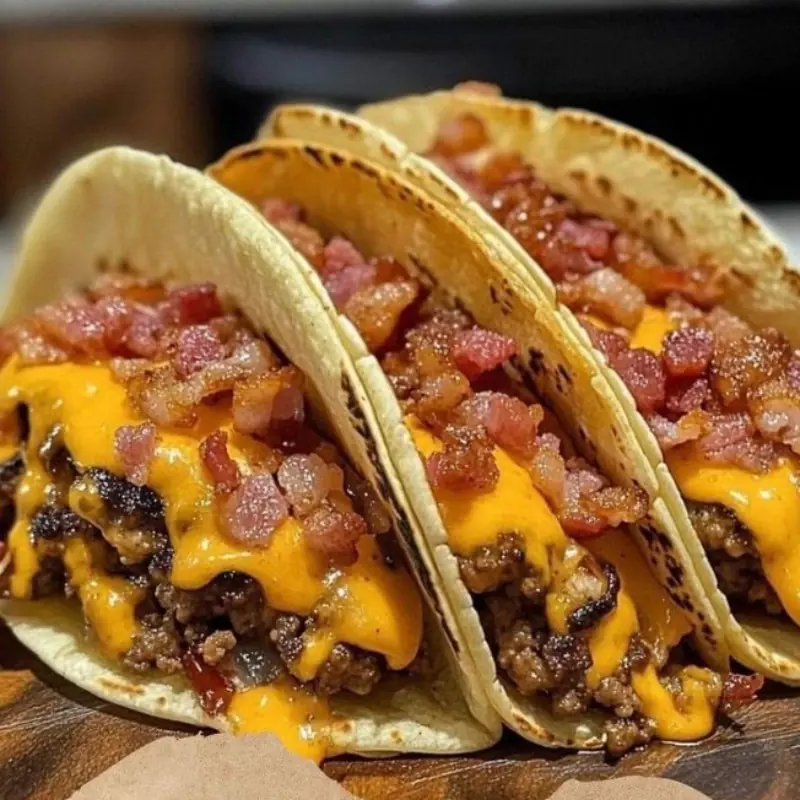

A crave-worthy fusion that combines tacos with classic cheeseburgers.
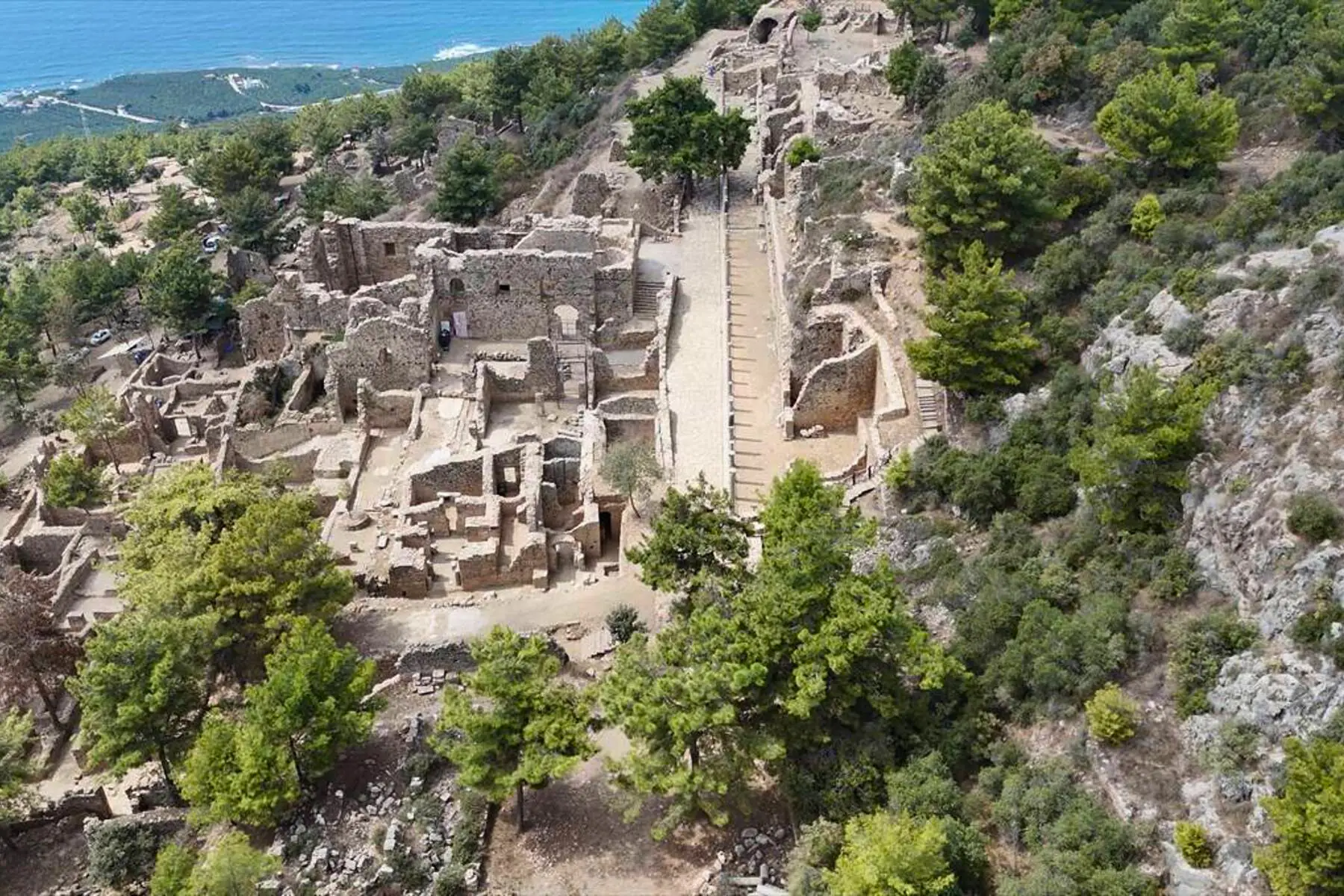

Researchers say the findings indicate Syedra was not only a regional producer but one of the Mediterranean’s key suppliers in antiquity, challenging earlier assumptions about the city’s economic role.

We all know that food consumption habits vary greatly among countries.