4 Types of Fish That Are Prone to Heavy Metal Contamination — Even Sellers Rarely Eat Them
4 Types of Fish That Are Prone to Heavy Metal Contamination — Even Sellers Rarely Eat Them
Some fish species, due to their habitats or biological traits, can accumulate heavy metals beyond safe limits. Long-term consumption may harm the nervous system, kidneys, and cardiovascular health.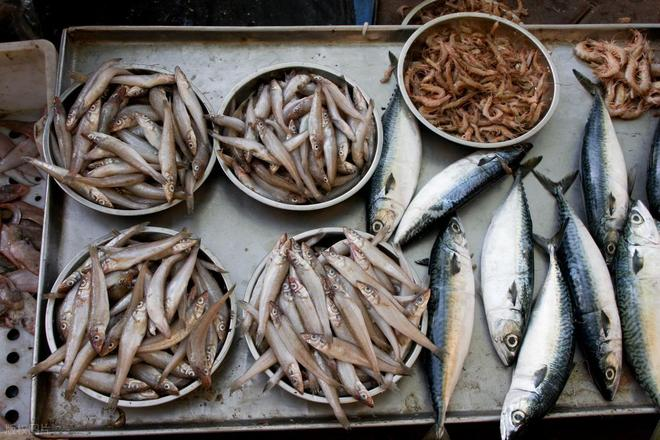
On cold winter days, a steaming bowl of fish soup can feel comforting and nourishing for the whole family. However, not all fish are suitable for frequent consumption in winter. Certain species are more likely to accumulate excessive heavy metals because of where they live or how they feed. If eaten regularly over time, they can pose serious health risks.
Based on recommendations from fisheries experts and real-world market inspections, here are four groups of fish that require special caution when buying in winter, helping consumers enjoy their meals while protecting their health.
1. Fish That Live in Muddy Environments (Eels and Catfish)
Eels are freshwater fish with strong survivability, commonly found in stagnant ponds, ditches, and muddy rice fields. As scavengers, they feed on decomposing organic matter and insect larvae, making them prone to accumulating lead, mercury, and other heavy metals.
Studies show that wild eels contain 3–5 times higher levels of heavy metals than farmed eels, and parasite infection rates can exceed 60%. If not thoroughly cooked, parasites such as tapeworms may infect humans.
Catfish—often labeled “garbage-eating fish”—are also controversial. They can survive in heavily polluted waters, even near industrial wastewater outlets, feeding on carcasses and algae. This makes catfish a hotspot for heavy metals and pathogens.
Market inspections in parts of China in 2024 found that 30% of catfish samples exceeded mercury limits, with some containing cadmium levels up to eight times higher than safety standards. If catfish appear covered in cloudy slime or have soft, mushy flesh, they should be avoided.
2. Fish That Have Been Dead Too Long
Although low winter temperatures slow decomposition, fish that have been dead for more than six hours still pose significant risks. After death, proteins break down into histamine, which can cause nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. At the same time, cell breakdown makes heavy metals easier for the human body to absorb.
A fish vendor admitted:
“Dead fish sell for only about one-third the price of live fish, but their organs have already started to spoil. Even we sellers don’t dare eat them.”
How to tell fresh fish from dead fish: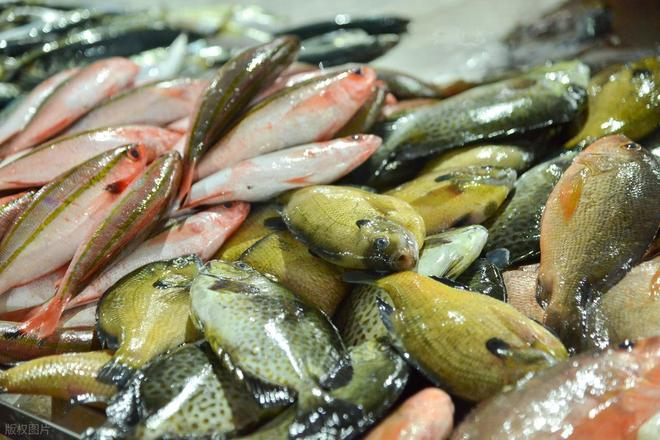
-
Gills: Fresh fish have bright red gills; dead fish have pale or dark brown gills.
-
Flesh: Fresh fish is firm and springs back when pressed; spoiled fish leaves an indentation.
-
Smell: Fresh fish smells mildly fishy; spoiled fish has a sour or foul odor.
3. Poorly Preserved Marine Fish
Hairtail (cutlassfish) is popular in winter but difficult to preserve properly. High-quality fish are flash-frozen at –18°C, with shiny bodies and tightly attached scales. Low-quality fish are often thawed and refrozen multiple times, causing scales to fall off and flesh to become soft.
More concerning, some sellers soak fish in industrial preservatives to mask spoilage.
How to choose safe hairtail fish:
-
Scales: Fresh fish have tightly attached scales that are hard to remove.
-
Eyes: Clear, bulging eyes indicate freshness; sunken or cloudy eyes suggest poor quality.
-
Belly: The flesh should be firm and odorless; grayish flesh or sliminess is a red flag.
4. Fish From Polluted Waters
Filter-feeding fish such as silver carp and bighead carp feed on plankton, making them more likely to accumulate heavy metals. Fish from polluted waters often have an unusually strong fishy smell that is hard to remove, even after thorough cooking.
In 2025, a Chinese environmental organization found that silver carp from rivers near industrial zones contained lead levels 4.2 times higher than national safety standards.
Safer Alternatives
-
Choose fish farmed in controlled environments, such as tilapia or farmed sea bass using recirculating systems, which can have over 70% lower heavy metal levels than wild fish.
-
Opt for smaller marine fish with lower mercury levels, such as salmon and sardines; avoid large predatory fish like tuna and swordfish.
-
When cooking, add garlic or onions rich in sulfur compounds to help support heavy metal detoxification.
-
After meals, consume vitamin C–rich fruits like kiwi or vegetables such as broccoli to enhance the liver’s detoxifying capacity.
Eat Fish Wisely for Both Taste and Safety
-
Adults should consume no more than 500 grams of fish per week; pregnant women and children should limit intake to half that amount.
-
Avoid eating fish heads, skin, and internal organs, where heavy metals can accumulate at 3–5 times higher levels than in muscle meat.
-
Prefer steaming or making soup to preserve nutrients and eliminate parasites; limit frying or high-temperature grilling.
Eating fish can be healthy—but only when chosen and prepared wisely.
News in the same category


Electrical devices to unplug during storms, thunder, and lightning

The Military Sleep Technique That Can Help You Fall Asleep in 2 Minutes

Why shouldn't you set the air conditioner to 26°C at night?

9 out of 10 people store onions incorrectly: Here's why you shouldn't keep them in the fridge

Smart travel tip: Why you should toss a water bottle under your hotel bed?

Don't throw away your yellowed white shirts - try this soaking method to make them bright and as good as new

Easy lemon storage hacks that keep them fresh for a long time
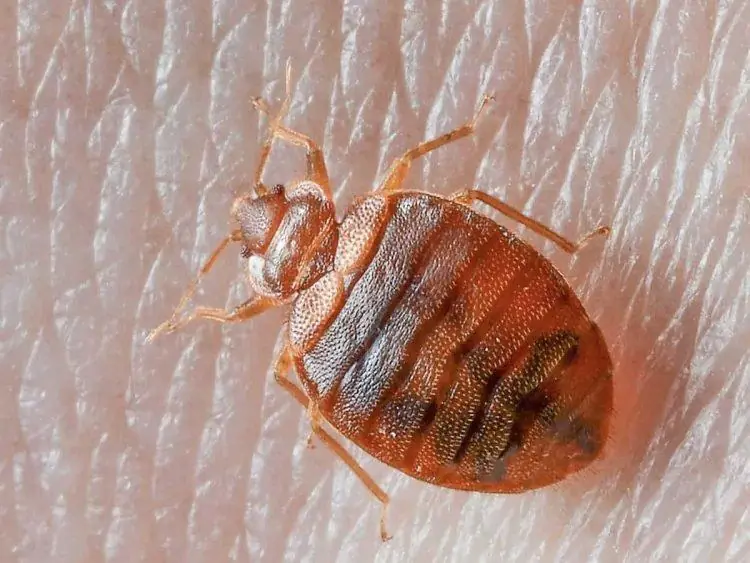

Natural Pest Control: Using Diatomaceous Earth and Cloves Against Bed Bugs and More
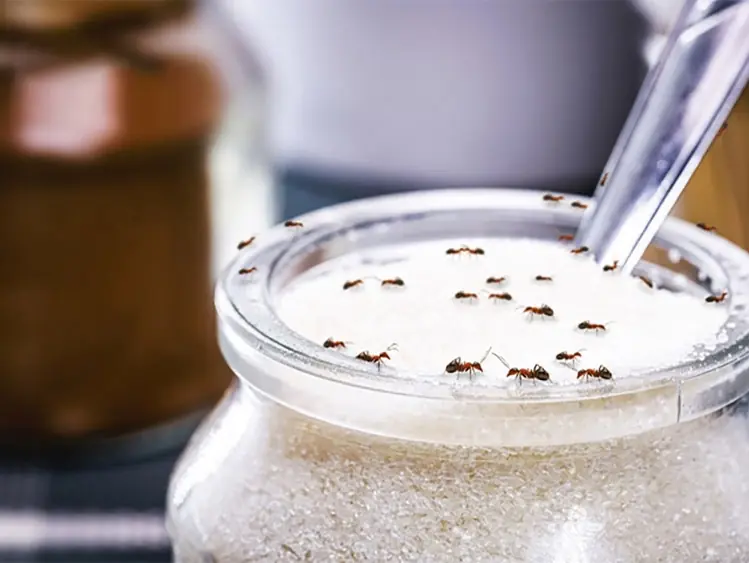

Tips to Quickly Get Ants Out of Sugar Jars and Keep Them Away for Good
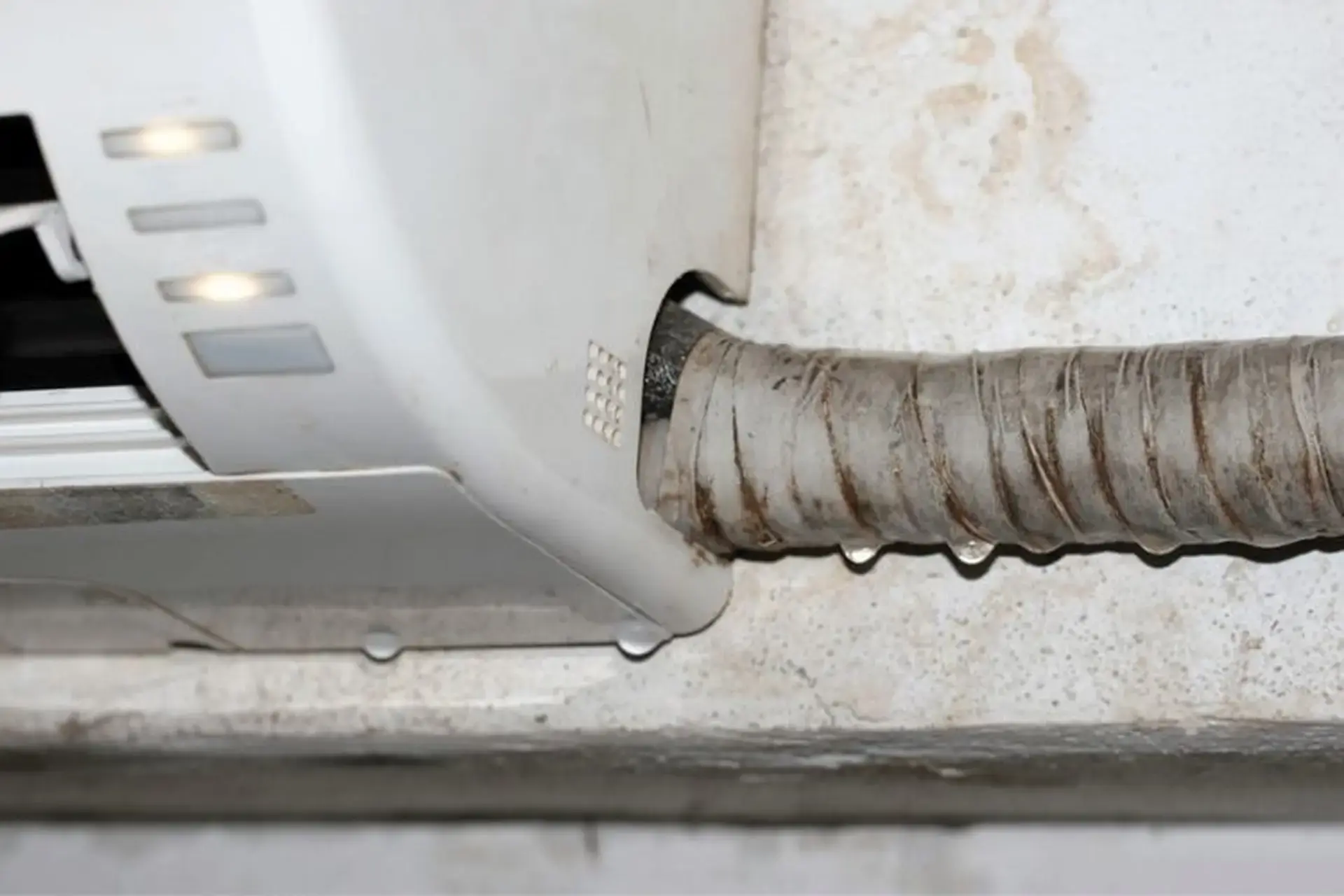

Common causes of water leaks from air conditioners and how to fix them.

Keep Ginger Fresh and Intact for a Long Time With This Simple Trick
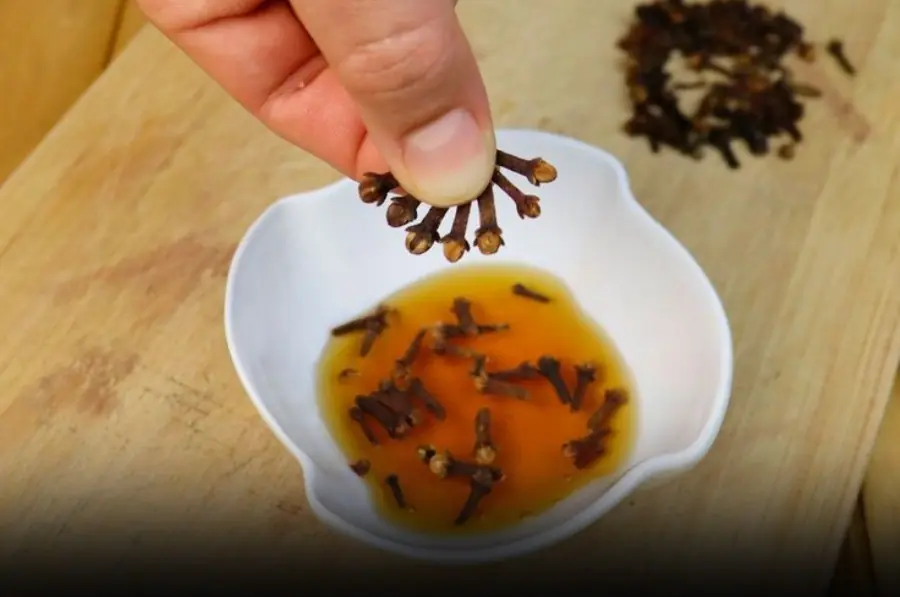

Mix cloves, honey, and cinnamon and you will thank me! This is my grandmother's secret...

Experts Warn: Never Unplug These 7 Household Devices — You Won’t Save Money, and It Could Cause Even More Harm

A 3-Year-Old Boy Nearly Blinded by 502 Super Glue
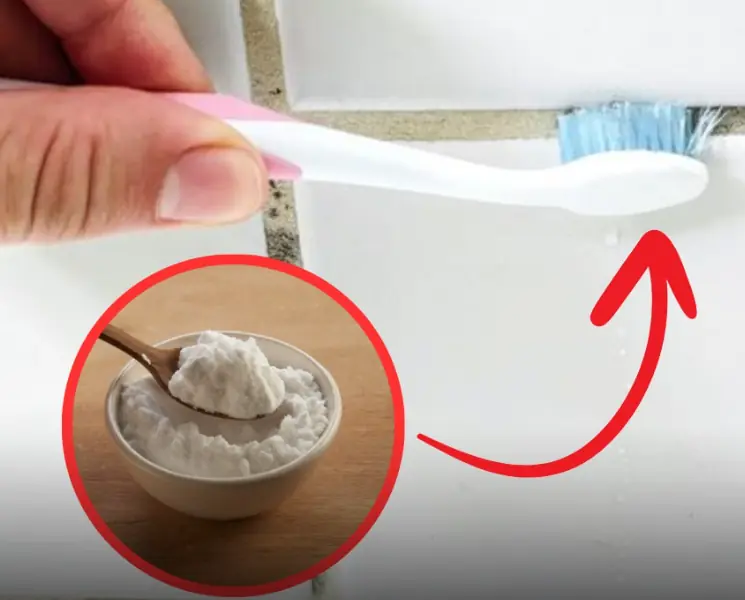

Simple hack to remove mold from bathroom grout using just 2 common ingredients - Better than bleach!

Smart people unplug the TV when checking into a hotel - Knowing why you will do it immediately
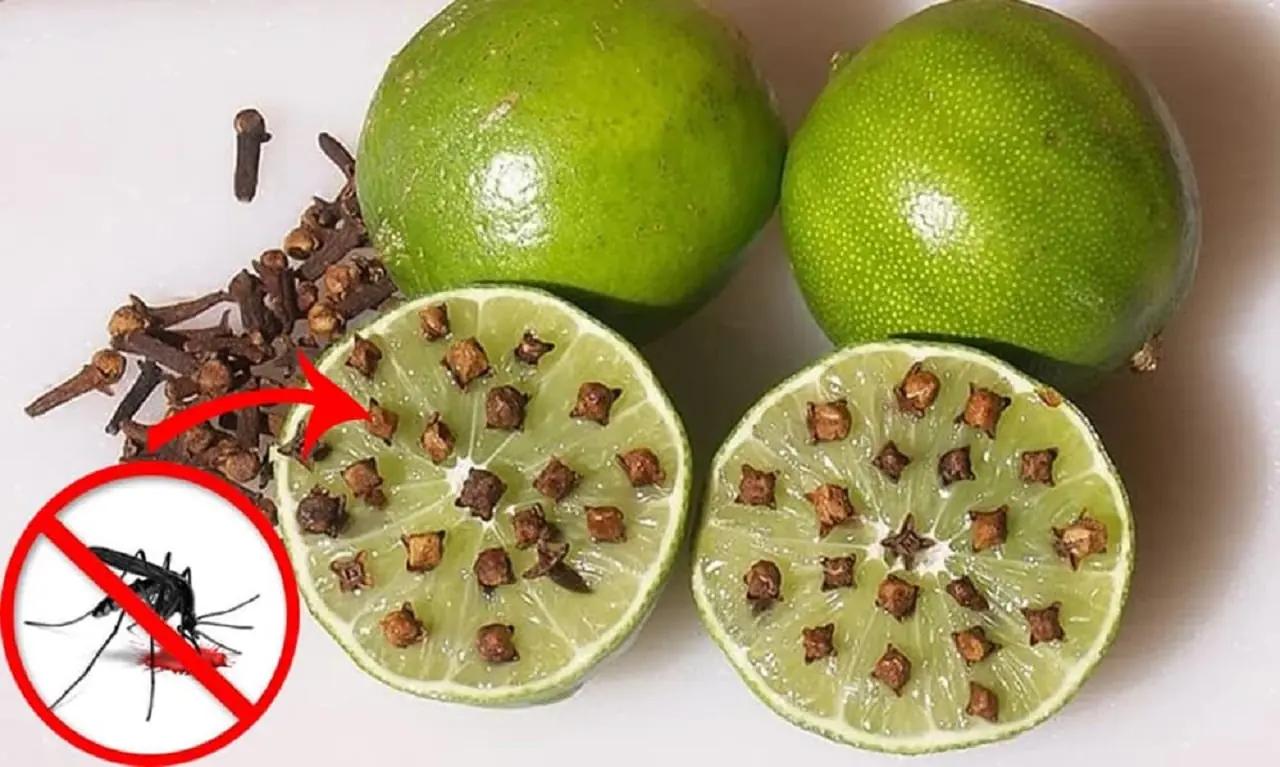

Don’t Throw Away Lemon Peels: Smart, Natural Ways to Clean and Freshen Your Home
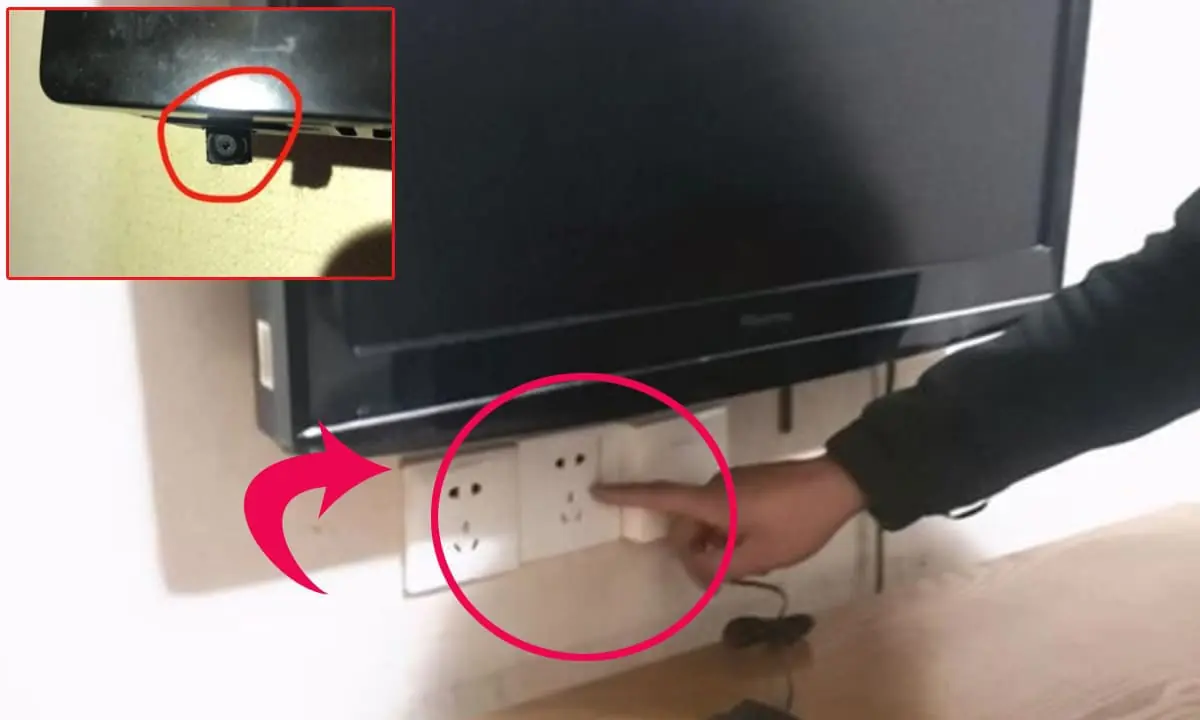

Why smart travelers always unplug the hotel TV when they arrive?
News Post

4 anti-aging dietary principles you should apply

Roasted Beetroot and Avocado Salad with Feta
Pan.creatic can.cer: 10 early warning signs you should never ignore

Avocado Berry Salad with Nuts & Greens

Doctors Reveal the Truth About Avocado That Most People Don’t Know

Mediterranean Meatball Bowl with Roasted Potatoes & Tzatziki

Churro Caramel Crunch Cupcakes

Creamy Chicken Vegetable Soup
His whole body was itchy, he thought it was an allergy. But he was diagnosed with

Heart Surgeon Warns People Should Remove This One Thing From Their Life After Turning 40
Foods to be mindful of when living with hypo.thyroidism

4 types of people who should avoid eating cabbage

5 unusual foot symptoms that may indicate abnormal blo.od sugar levels
Sleeping Without a Blanket Feels Impossible for Many — Here’s Why

Those who love eating sweet potatoes must read this article, it will change your life! It's not too late to know now!
Persistent Cough, Lingering Flu Symptoms: Warning Signs of Lung Can.cer Often Mistaken for “Minor ill.nesses”

Leg pain, rheumatism, varicose veins, arthritis – a natural remedy with cloves and garlic that many people don't know about
Health Expert Reveals Warning Signs of Two Silent Foot Killers and How To Spot Them

Itching at night, woman goes to the doctor and learns she only has 8 months to live