
Why keeping garlic near your bed might have unexpected advantages?
The surprising benefits of placing garlic at the head of your bed
Why Couples Who Argue Often Age Faster — Science Explains
Arguments are often dismissed as a normal part of long-term relationships. Many couples believe that as long as conflicts don’t lead to separation, the emotional damage is minimal. Science, however, paints a far less comforting picture. A growing body of research suggests that couples who argue frequently — especially in hostile or unresolved ways — may actually age faster at a biological level, increasing their risk of chronic illness and premature aging.
This isn’t about occasional disagreements. It’s about repeated conflict that triggers stress responses in the body over months or years. According to scientists, the body does not distinguish between emotional threats and physical ones. When conflict becomes routine, the nervous system stays on high alert — and that state comes at a cost.
When couples argue, the brain perceives danger. The hypothalamus signals the adrenal glands to release stress hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline. In small doses, these hormones are helpful. They sharpen focus and prepare the body to respond. But when arguments are frequent, cortisol levels remain elevated far longer than nature intended.
Studies from institutions such as the University of California and Ohio State University have shown that couples who engage in hostile arguments have higher baseline cortisol levels even outside of conflicts. Over time, chronically elevated cortisol accelerates cellular aging, disrupts sleep, impairs memory, and weakens the immune system.
In simple terms: arguing doesn’t just ruin your mood — it keeps your body in survival mode.
One of the strongest pieces of evidence linking conflict to accelerated aging comes from research on telomeres. Telomeres are protective caps at the ends of chromosomes that shorten as cells divide. Shorter telomeres are associated with aging, inflammation, cardiovascular disease, and reduced lifespan.
Research published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences found that individuals in high-conflict relationships tend to have significantly shorter telomeres compared to those in supportive partnerships. In some cases, the biological age difference equated to several years — even when the couples were the same chronological age.
The takeaway is unsettling: emotional stress from relationships can physically age cells faster than time alone.

Another mechanism behind accelerated aging is chronic inflammation. During repeated arguments, the immune system releases inflammatory molecules such as cytokines. While these substances help fight infection, constant activation leads to tissue damage over time.
Researchers have observed that couples who argue aggressively heal more slowly from wounds and show higher markers of systemic inflammation. This inflammation is linked to conditions commonly associated with aging, including arthritis, heart disease, diabetes, and cognitive decline.
What’s alarming is that many couples feel “used to” their arguments and underestimate their physiological impact. The body, however, never adapts — it continues paying the price.
Frequent conflict also disrupts sleep, one of the most critical processes for cellular repair and brain health. Studies show that couples who argue before bed experience poorer sleep quality, more nighttime awakenings, and shorter REM cycles.
Poor sleep amplifies stress hormones, impairs emotional regulation, and accelerates aging-related processes such as memory loss and metabolic dysfunction. This creates a vicious cycle: arguments damage sleep, poor sleep increases irritability, and irritability fuels more arguments.
Over time, this loop silently accelerates both physical and cognitive aging.
Interestingly, research suggests that relationship stress may affect men and women differently. Men in high-conflict marriages show higher risks of cardiovascular disease, while women tend to exhibit stronger immune suppression and inflammatory responses.
However, both sexes experience increased aging-related risks when emotional conflict is persistent and unresolved. The common factor is not gender, but emotional safety — or the lack of it.
Importantly, scientists emphasize that disagreement itself is not the problem. Couples who communicate openly, resolve conflicts respectfully, and feel emotionally secure do not show the same biological damage.
What accelerates aging is hostility, contempt, stonewalling, and unresolved tension. Studies from the Gottman Institute reveal that couples who express criticism or defensiveness during arguments are far more likely to experience long-term health decline than those who argue calmly and repair emotionally afterward.
In other words, the body responds not to disagreement, but to emotional threat.
The science is clear, but it is not hopeless. Research also shows that improving communication, reducing emotional hostility, and fostering emotional safety can lower cortisol levels, reduce inflammation, and even slow telomere shortening.
Couples who learn to argue less destructively don’t just protect their relationships — they protect their health and longevity.
In the end, the question is no longer whether arguing affects your relationship. Science has answered something far more unsettling: repeated emotional conflict may be quietly stealing years from your life.

The surprising benefits of placing garlic at the head of your bed

Why many Indians eat with their right hand, even if their dominant hand is the left

The truth about why hotel receptionists may refuse rooms late at night

The convenience is temporary — the problems are permanent

What’s the ideal schedule for changing your underwear?

This common electric kettle habit may be driving up your power costs

Do You Nap During the Day? Here’s What You Should Know

10 Habits Often Seen as Rude That May Reflect Intelligence
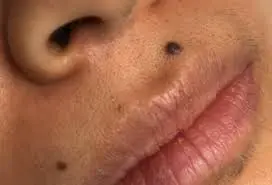
Understanding Moles on the Lip: Possible Causes and Concerns

Once Ignored, Now Celebrated: The Wild-Growing Vegetable Being Called a “Miracle Herb” for Health

Cats are curious, independent creatures—and while that’s part of their charm, it can also be the source of stress when one suddenly disappears.

When a lizard visits your house that’s a sign...

She Was Just Peeling a Boiled Egg… Until She Saw What Was Hidden Inside

When Your Parent Shows These 4 Signs, Emotional Preparation Matters

Here’s What That Little Pocket in Women’s Underwear Is Actually For

Regardless of How Much You Earn, Get Rid of These 4 Things Without Delay
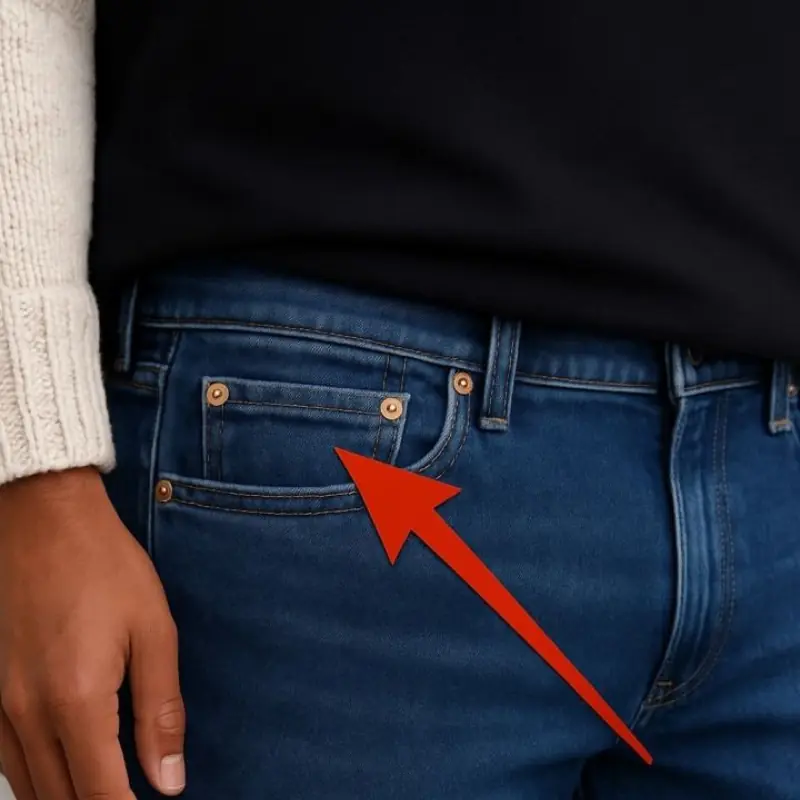

That tiny pocket on your jeans has a surprising history you probably never knew.

Keep these 3 mindsets, and success will follow
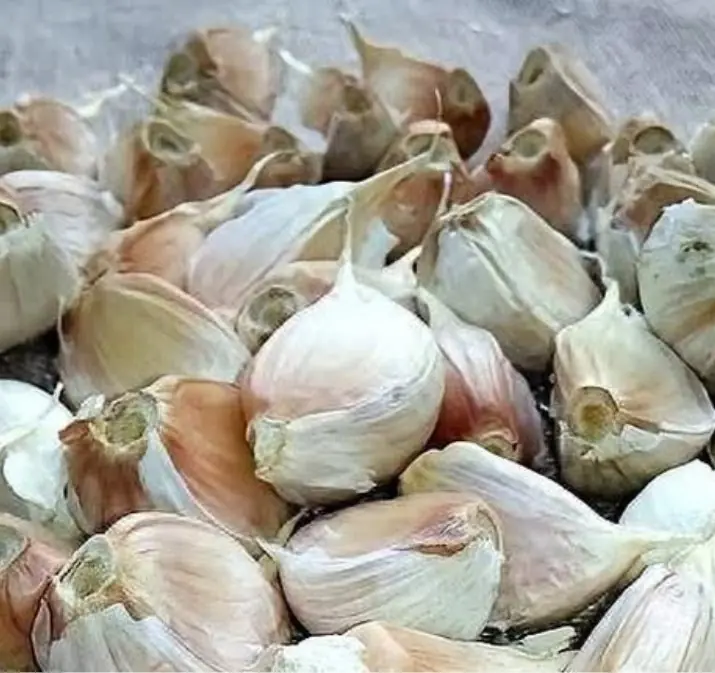

Not all garlic is safe to buy—learn which cloves you should avoid at the market today.

She Di:ed From a Stroke and Came Back: What She Saw Will Sho:ck You
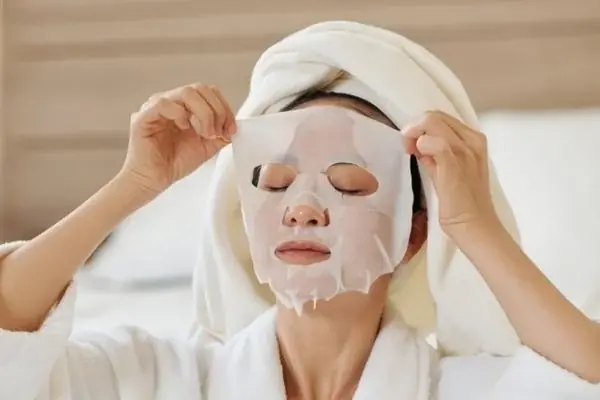

7 face mask mistakes that may be ruining your skincare results
Warning signs your body may show when potassium levels are low

What to do with sprouting potatoes instead of throwing them away?

The surprising benefits of placing garlic at the head of your bed

Why many Indians eat with their right hand, even if their dominant hand is the left
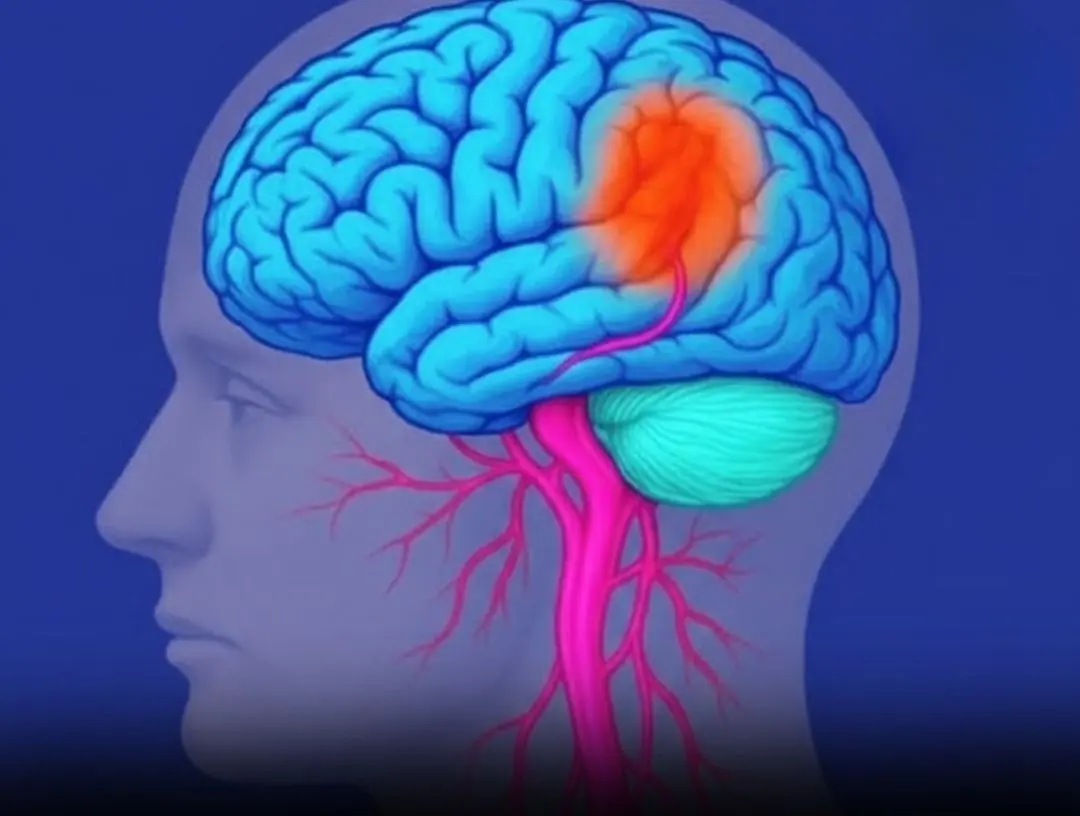
These Signs Can Appear a Month Earlier
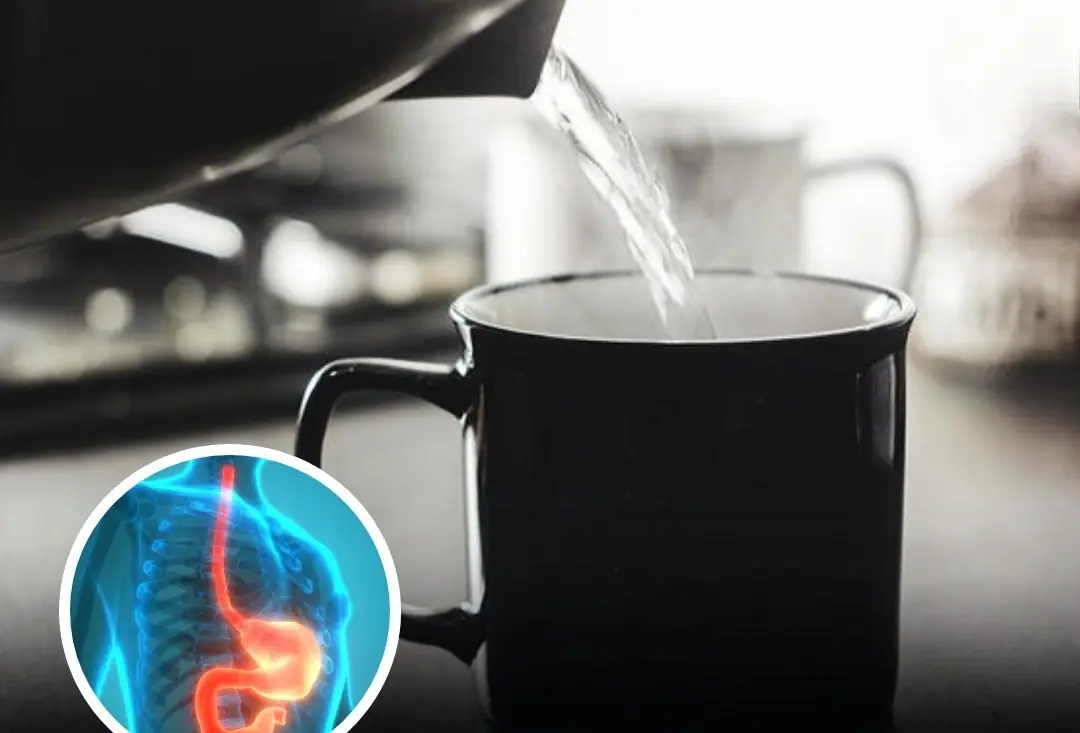

What Happens When You Drink Warm Water After Waking Up? Foods You Should Avoid on an Empty Stomach
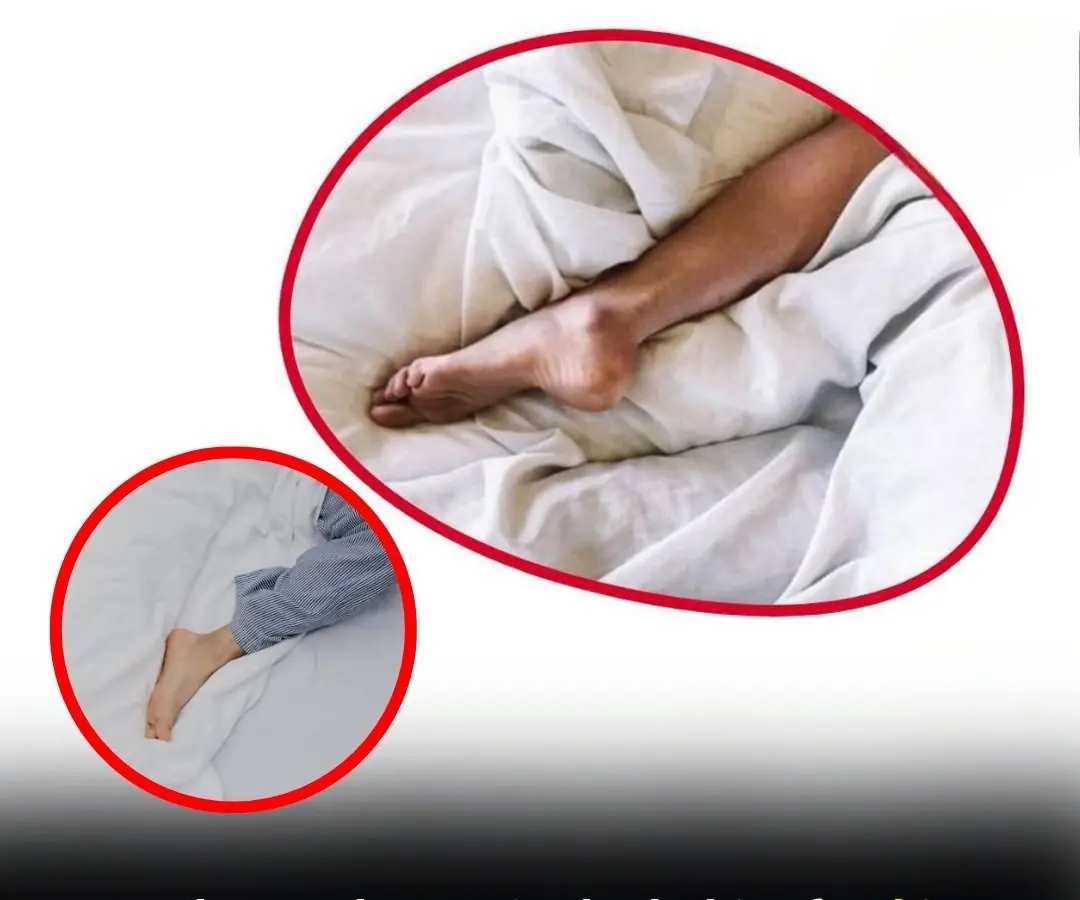
For those who find comfort in sleeping with one leg peeking out from beneath the covers
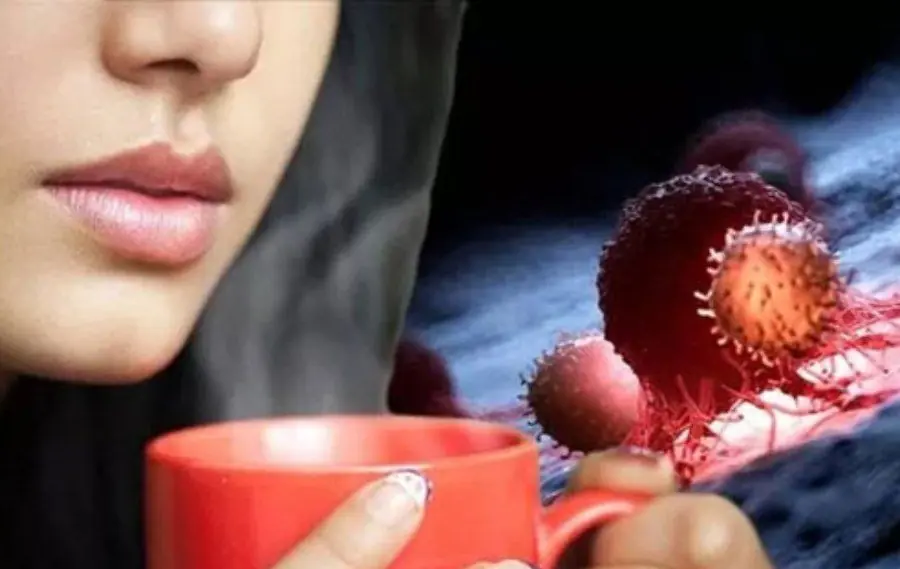

One daily drink many people love is being linked to a sharply higher cancer risk — doctors are urging caution
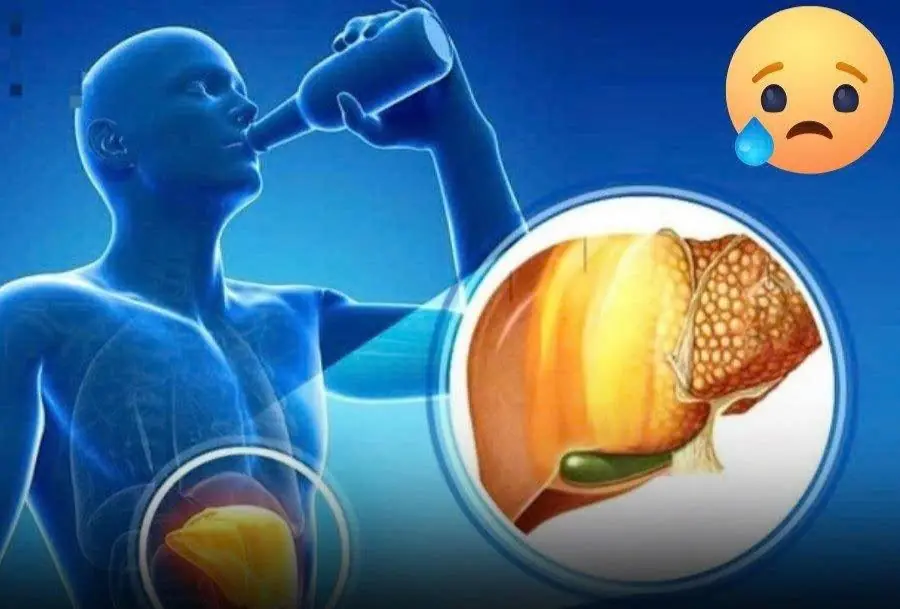
Many people still have the habit of drinking these beverages daily without knowing their ha.rmful effects
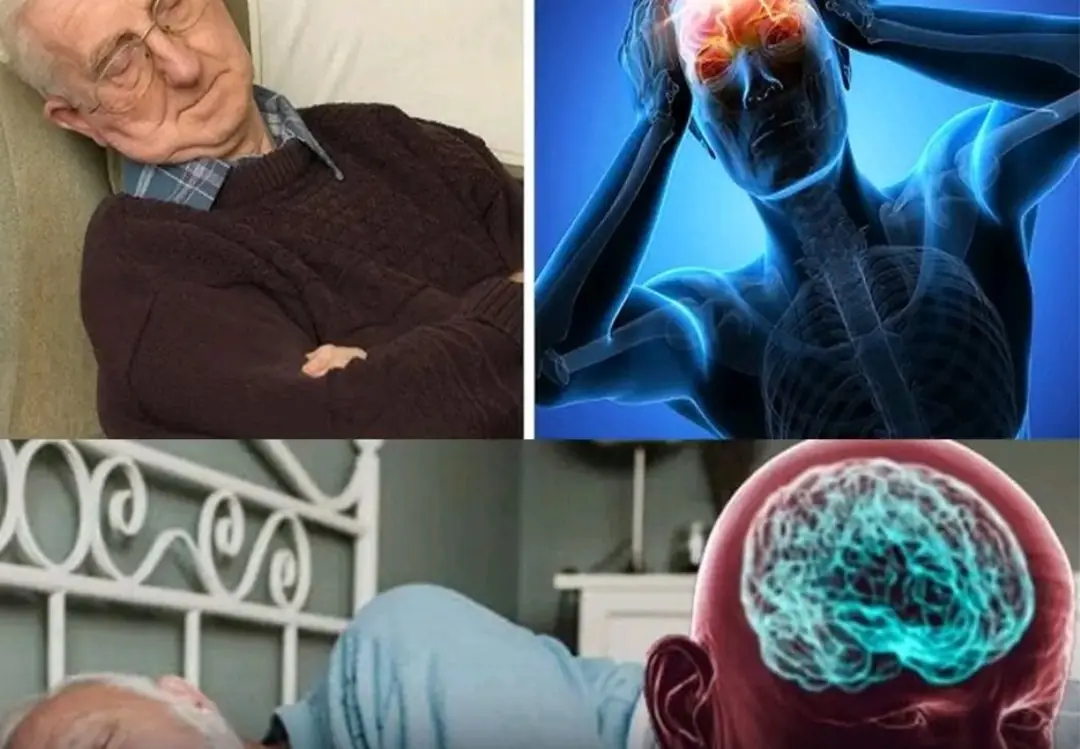
10 Early Dementia Signs Your Brain Is Warning You About
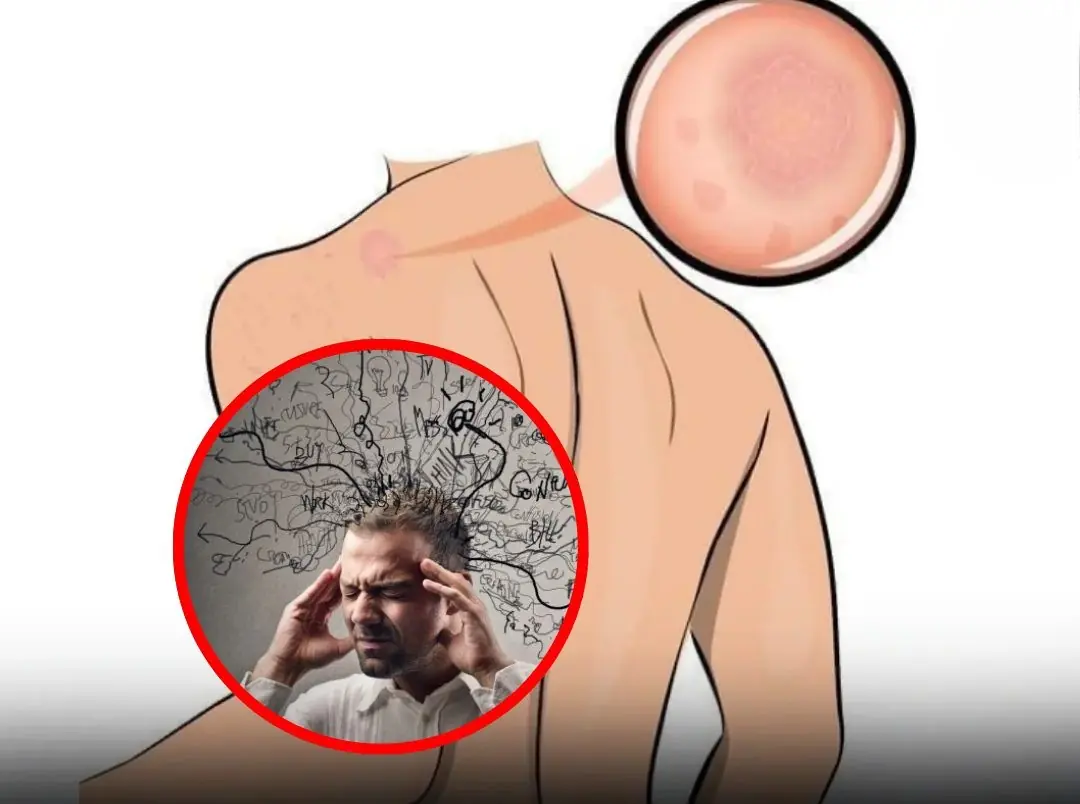
7 Warning Signals Your Body Sends When Stress Is Taking Over
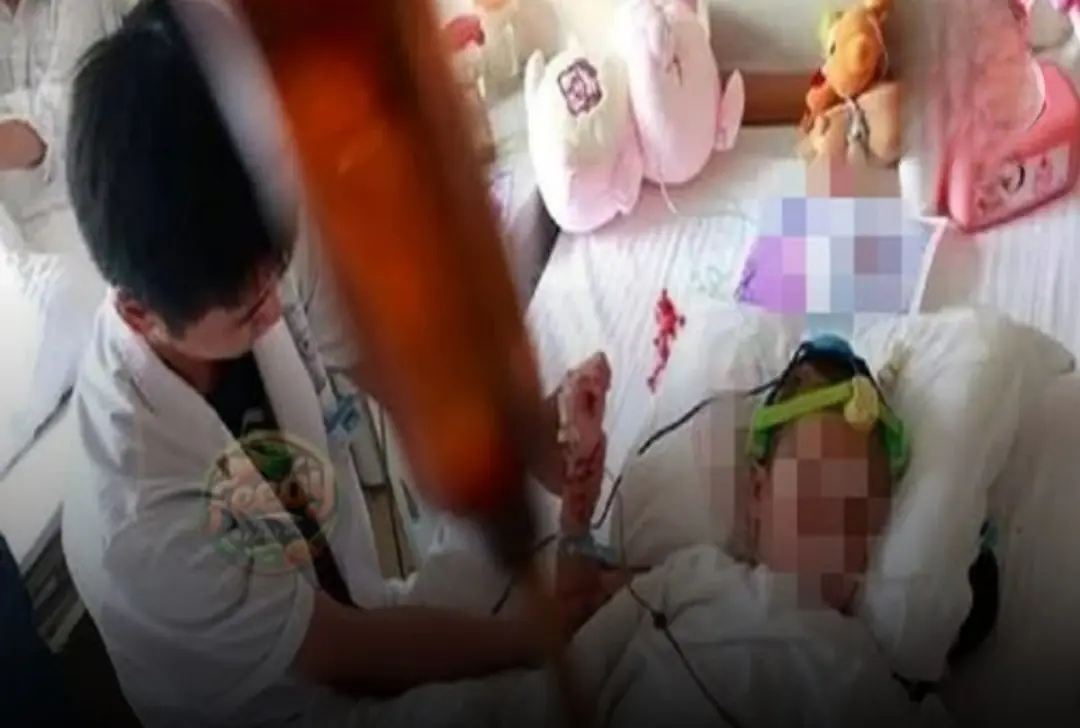
5-year-old girl with late-stage can.cer — a wake-up call for parents
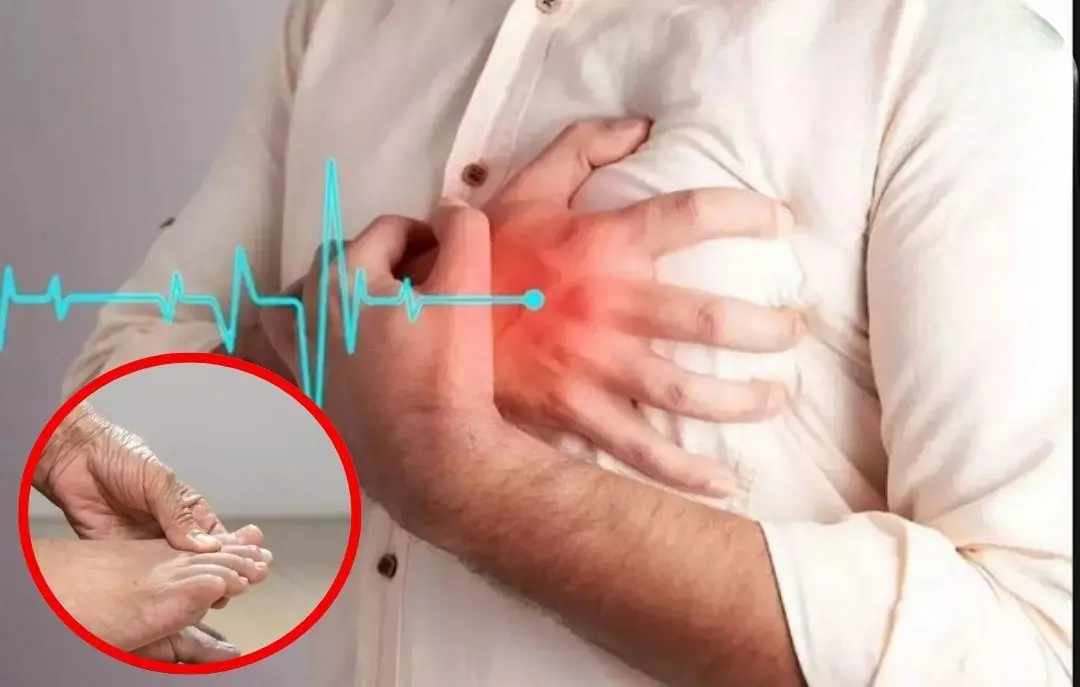
3 warning signs of an imminent heart at.tack - Never ignore these symptoms
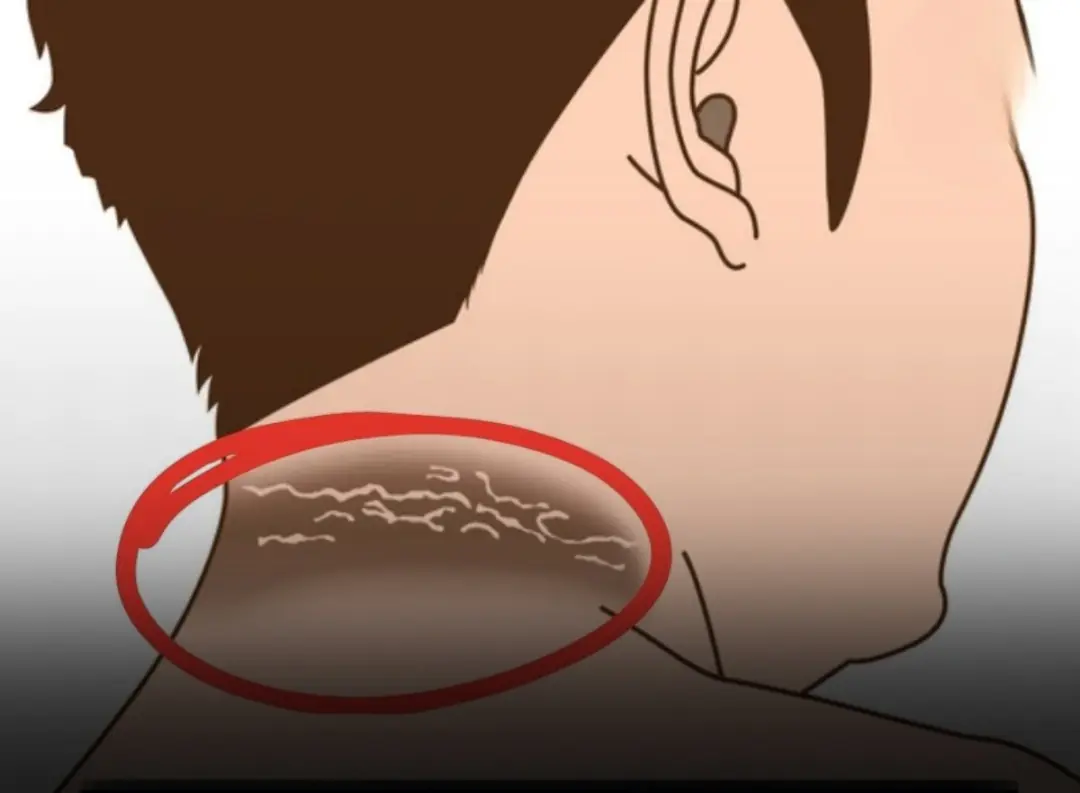
These 12 skin changes might look harmless — but they could be early clues of hidden diabetes...
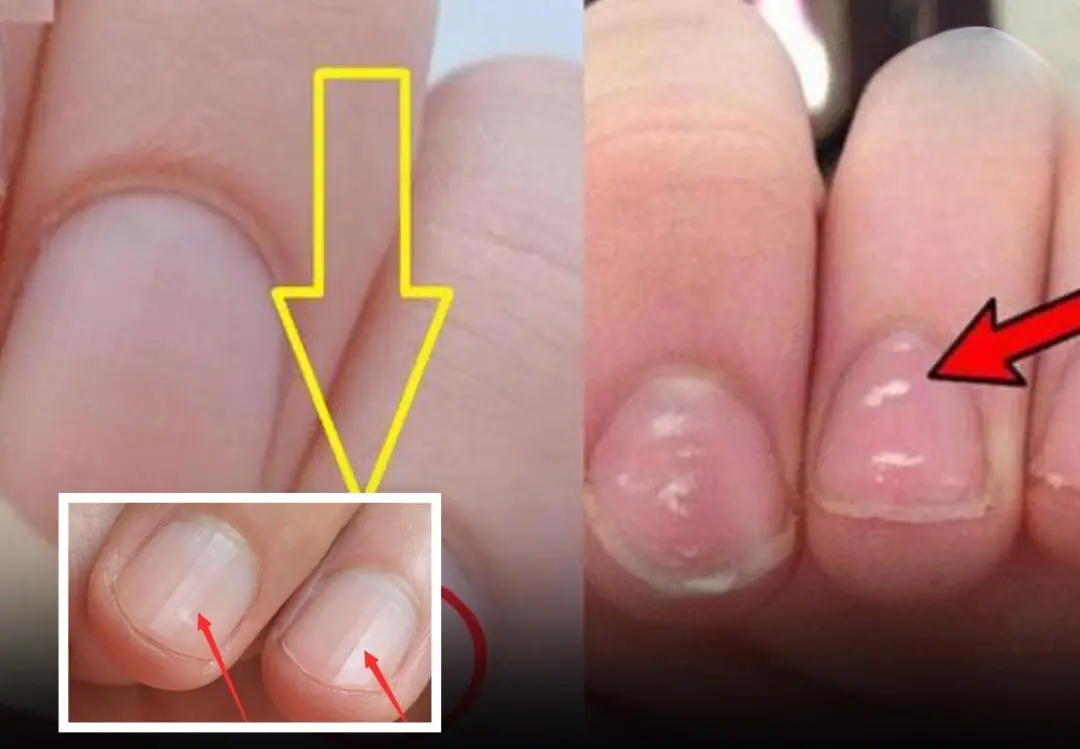
Your Nails Might Be Warning You: 3 Health Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore
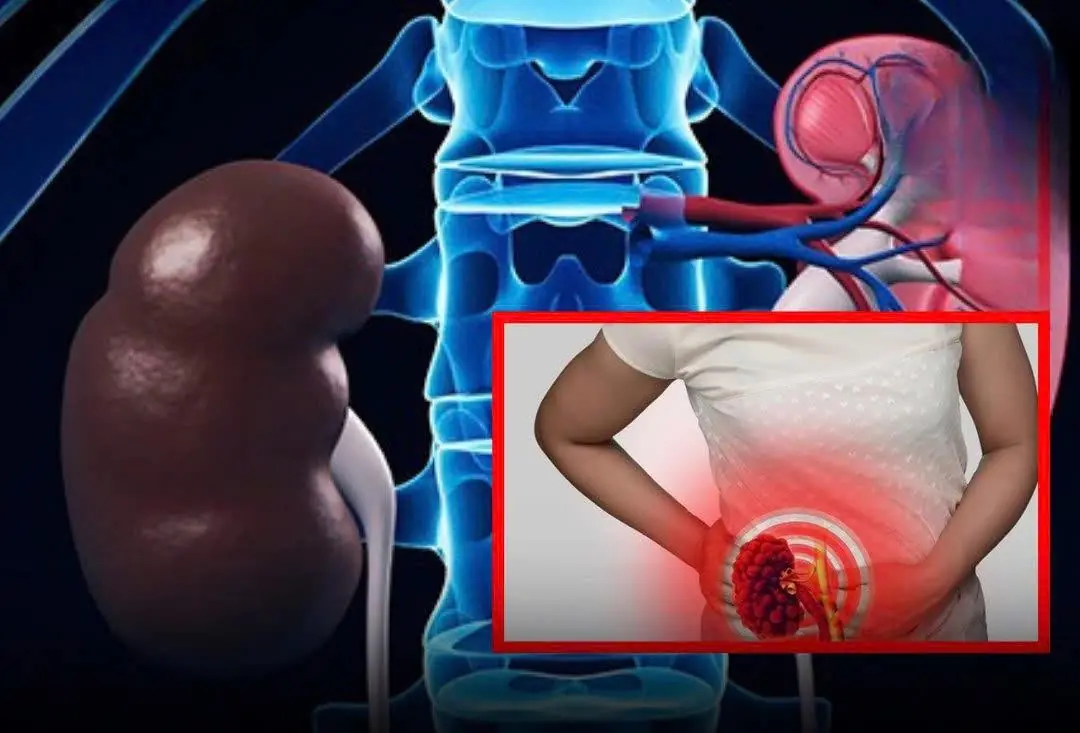
7 Signs Your Kidneys Are Working Well — Check Yourself
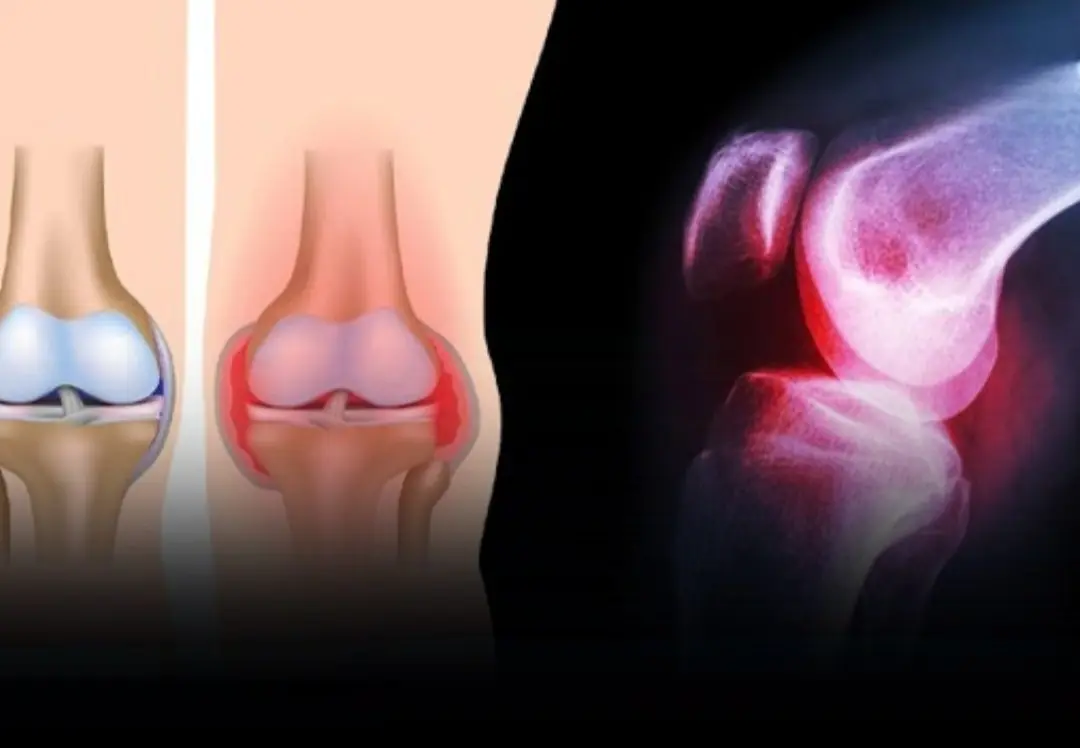
Warning: These 6 Foods Can Quietly Drain Calcium From Your Body — The More You Eat, the Weaker Your Bones Become
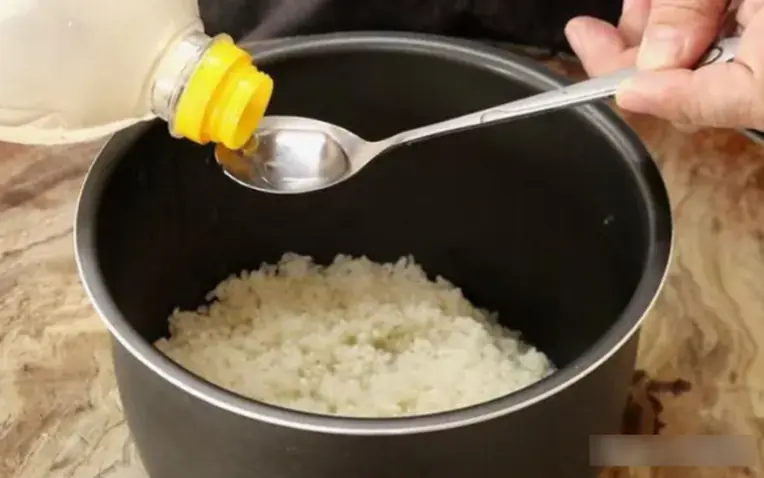

Easy ways to cook flavorful rice and keep it fresh longer
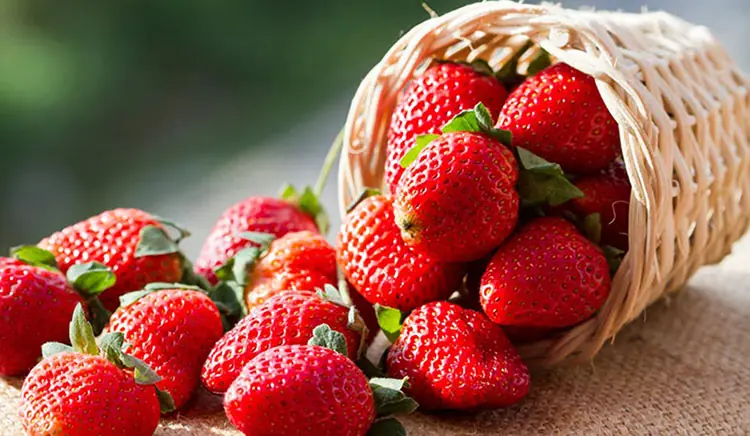

Can Strawberries Help Lower Blood Pressure? Here’s the Science