
10 Social Habits Commonly Misunderstood as Rude but Associated with Intelligence
10 Habits Often Seen as Rude That May Reflect Intelligence
If you have ever tracked a flight on a map, you may have noticed something strange: instead of flying straight from departure to destination, airplanes often follow curved or arched paths. This raises a natural question - if the shortest distance between two points is a straight line, wouldn’t flying straight save fuel, time, and money?
The answer is more complex than it appears. In reality, airplanes already fly the most efficient routes possible. The curved paths you see are not wasteful detours but carefully calculated routes based on Earth’s shape, atmospheric conditions, safety considerations, and air traffic management. Understanding how aviation works helps explain why “straight” is not always the shortest - or smartest - way to fly.
Most flight tracking maps use a flat, two-dimensional projection of Earth. On these maps, straight lines appear shorter, while curved lines seem longer. However, Earth is not flat - it is a sphere. When distances are calculated on a spherical surface, the shortest path between two points is not a straight line on a flat map.
This misunderstanding is one of the main reasons flight routes look inefficient when, in fact, they are highly optimized.
A Great Circle Route is the shortest distance between two points on the surface of a sphere. Airlines rely on these routes to minimize travel distance, fuel consumption, and flight time.
When a great circle route is projected onto a flat map, it often appears curved, especially on long-haul flights crossing continents or oceans.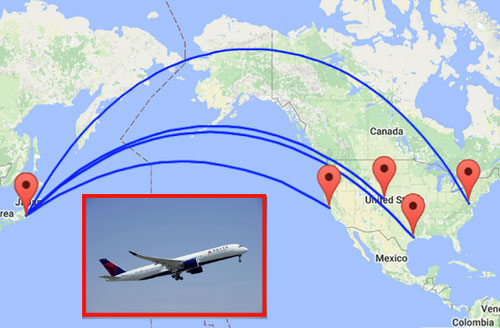
Earth slightly bulges at the equator due to rotation, making polar routes shorter for long-distance travel. That is why flights between North America and Asia often pass over:
Alaska
Northern Canada
Greenland
Siberia
Although this looks like a detour on a flat map, it is actually the shortest and most fuel-efficient path.
Example:
A flight from New York to Tokyo looks curved but saves hundreds of kilometers compared to an equatorial route.
Jet streams are narrow bands of extremely fast-moving air located at high altitudes. They can reach speeds of 300–400 km/h (190–250 mph) and play a crucial role in flight planning.
Flying with a jet stream reduces travel time and fuel consumption
Flying against a jet stream increases drag and fuel use
Airlines carefully plan routes to take advantage of tailwinds while avoiding strong headwinds. This means planes may deliberately fly a longer distance if it results in less resistance and lower fuel burn overall.
Eastbound flights across the Atlantic are often much faster than westbound flights because they ride powerful jet streams. In some cases, flights arrive over an hour earlier than scheduled.
Weather is a major factor in determining flight paths. Pilots and dispatchers constantly monitor:
Storm systems
Thunderclouds
Turbulence zones
Icing conditions
Flying straight through severe weather can be dangerous and uncomfortable, even if it appears shorter.
Air over oceans tends to be more stable than air over land because water retains heat better. Land heats unevenly, causing rising warm air that leads to turbulence.
As a result, flight routes are often designed to:
Reduce turbulence
Improve passenger comfort
Minimize structural stress on the aircraft
Safety always takes priority over distance.
Airplanes cannot fly freely anywhere in the sky. Certain airspaces are restricted due to:
Military activity
Political conflicts
Sensitive national borders
High traffic congestion
Flights must navigate around these zones, sometimes creating curved paths that appear indirect but are legally and operationally necessary.
Busy air corridors require precise coordination to prevent collisions. Air traffic controllers assign routes and altitudes to maintain safe separation between aircraft.
This means that even if a straight path exists, it may not be available at that time.
The current longest commercial non-stop flight operates between Singapore and Newark, New Jersey, covering more than 16,700 kilometers (10,400 miles) in approximately 18 hours and 45 minutes.
This route relies heavily on:
Great circle navigation
Jet stream optimization
Advanced fuel management
Without curved routing and wind optimization, such long-distance flights would be far less efficient - or impossible.
Passengers often feel anxious when a plane suddenly ascends after beginning its descent. According to aviation expert and pilot Patrick Smith, this maneuver is called a go-around and is a normal safety procedure - not an emergency.
Runway Obstruction
Another aircraft or vehicle may still be on the runway.
Sudden Weather Changes
Poor visibility, wind shear, or unstable conditions may make landing unsafe.
Unstable Approach
If the aircraft is not properly aligned or configured, pilots will abort the landing.
Go-arounds are trained procedures designed to ensure maximum safety.
Movies often exaggerate cabin pressure loss as explosive and catastrophic. In reality, such events are extremely rare.
Cabin pressure loss usually occurs gradually, not explosively
Oxygen masks deploy automatically
Pilots descend to a safe altitude where oxygen is not required
Ear discomfort
Mild dizziness
Occasional nosebleeds
Pilots and crew are extensively trained to handle these situations calmly and efficiently.
Airplanes do not fly straight lines because straight lines on flat maps are misleading. Instead, they fly:
The shortest distance on a spherical Earth
Routes optimized for wind and fuel efficiency
Paths designed to avoid danger and turbulence
Courses that comply with international airspace rules
What looks curved to passengers is actually the most efficient, safest, and fastest route available.
The next time you watch a flight path arc across the globe, remember - you are already traveling the smartest way possible.

10 Habits Often Seen as Rude That May Reflect Intelligence
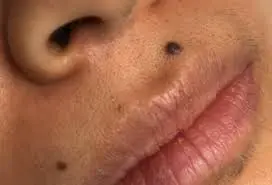
Understanding Moles on the Lip: Possible Causes and Concerns

Once Ignored, Now Celebrated: The Wild-Growing Vegetable Being Called a “Miracle Herb” for Health

Cats are curious, independent creatures—and while that’s part of their charm, it can also be the source of stress when one suddenly disappears.

When a lizard visits your house that’s a sign...
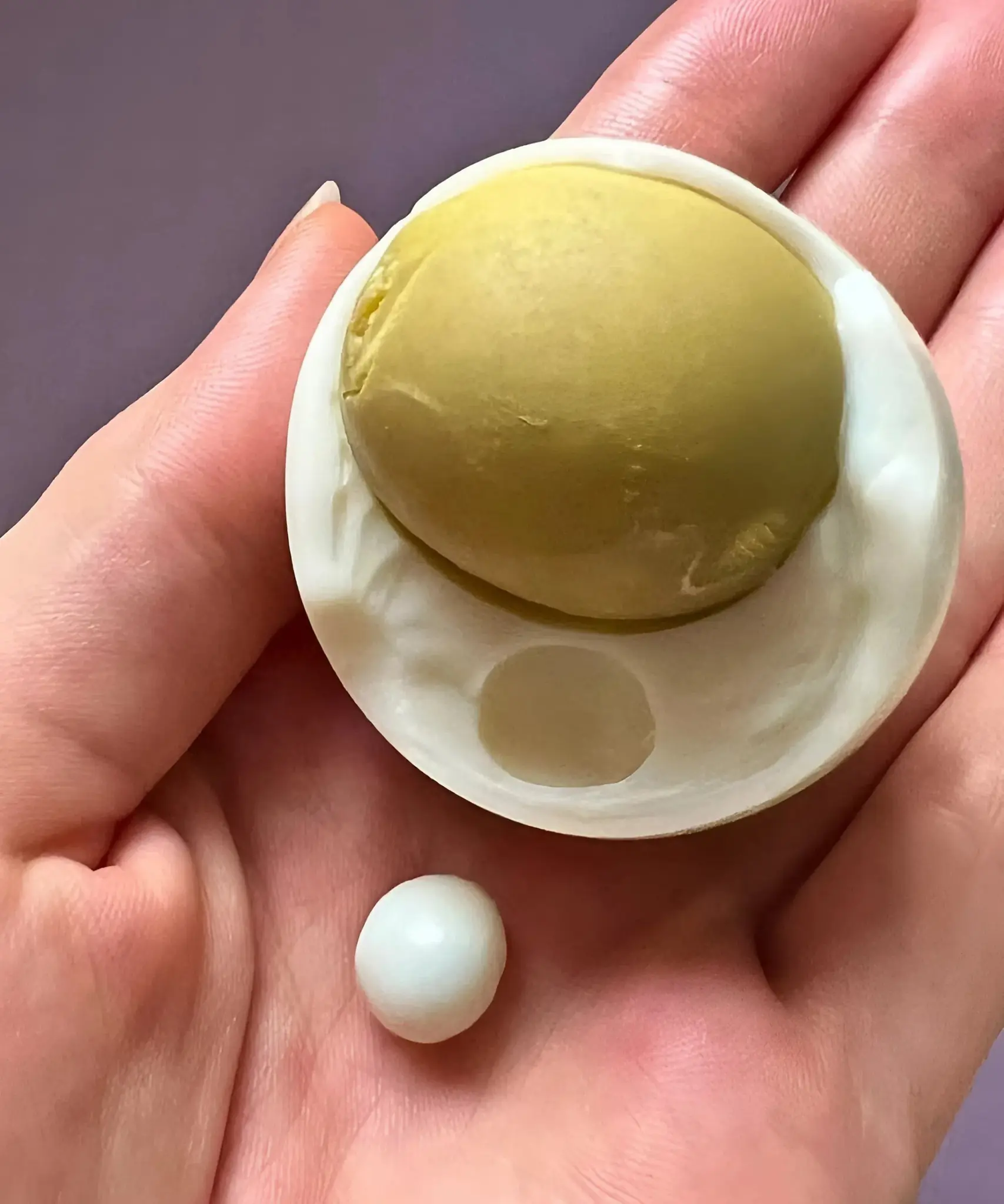

She Was Just Peeling a Boiled Egg… Until She Saw What Was Hidden Inside
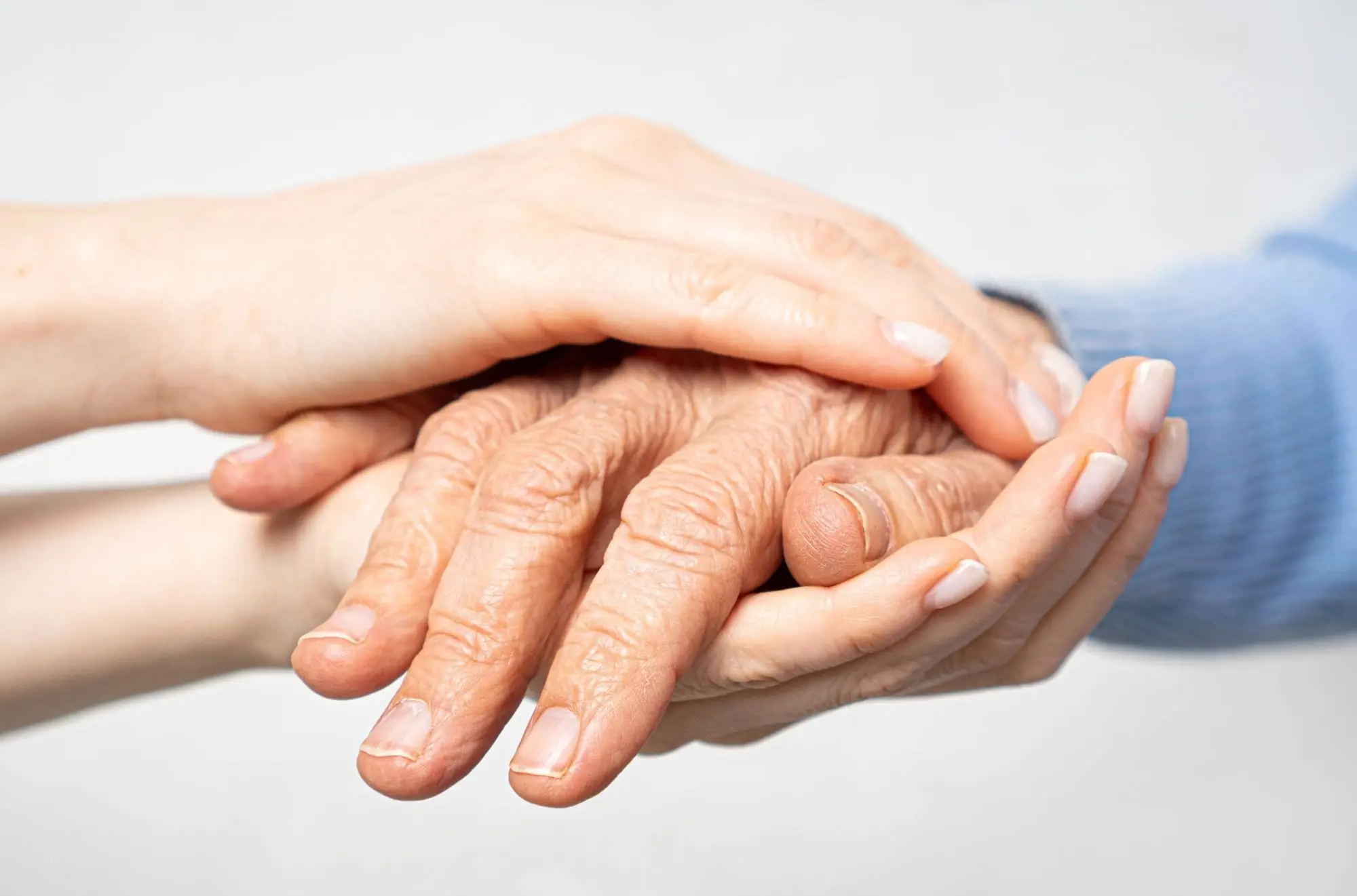

When Your Parent Shows These 4 Signs, Emotional Preparation Matters
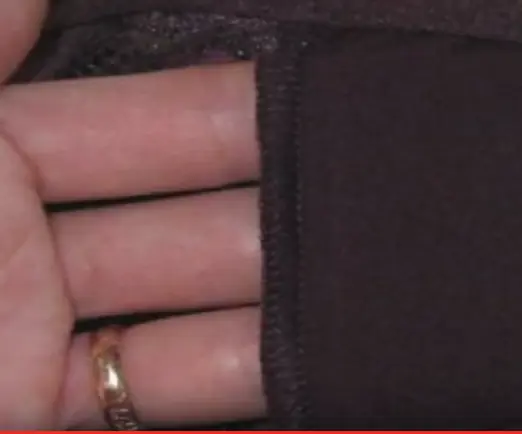

Here’s What That Little Pocket in Women’s Underwear Is Actually For

Regardless of How Much You Earn, Get Rid of These 4 Things Without Delay
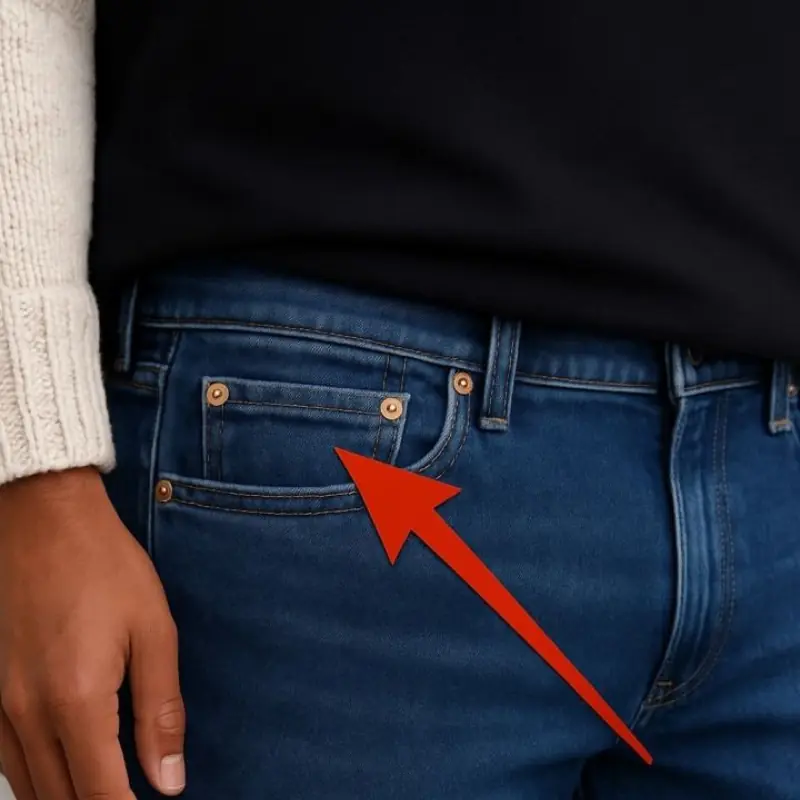

That tiny pocket on your jeans has a surprising history you probably never knew.

Keep these 3 mindsets, and success will follow

Not all garlic is safe to buy—learn which cloves you should avoid at the market today.

She Di:ed From a Stroke and Came Back: What She Saw Will Sho:ck You

The meaning of a ring worn on the right hand is not widely known

Most people THROW IT AWAY — but this tiny metal ring on sausages is actually saving your health!
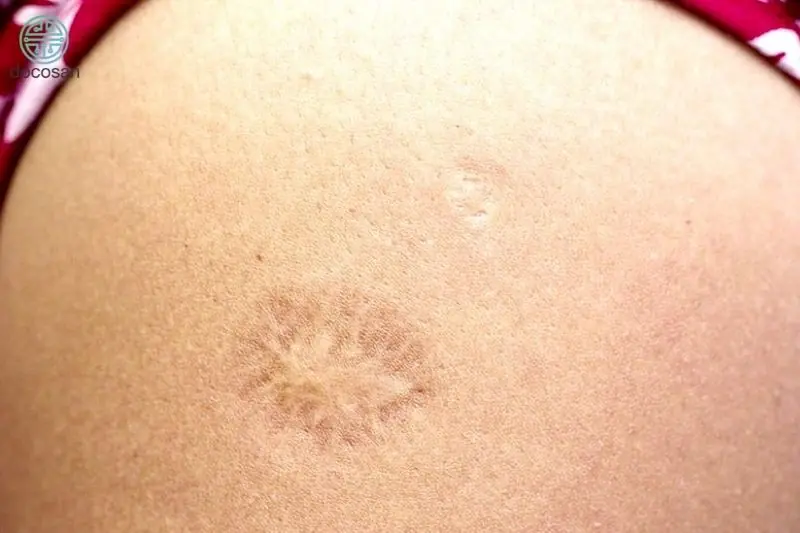
Do you know why there’s a small scar on the upper left arm and what it means?

Using an electric kettle daily? Here are 4 errors you should watch out for

If a millipede crawls indoors, don’t eliminate it immediately

If You Don’t Unplug These 5 Electrical Devices at Home, Your Electricity Bill Could Skyrocket!
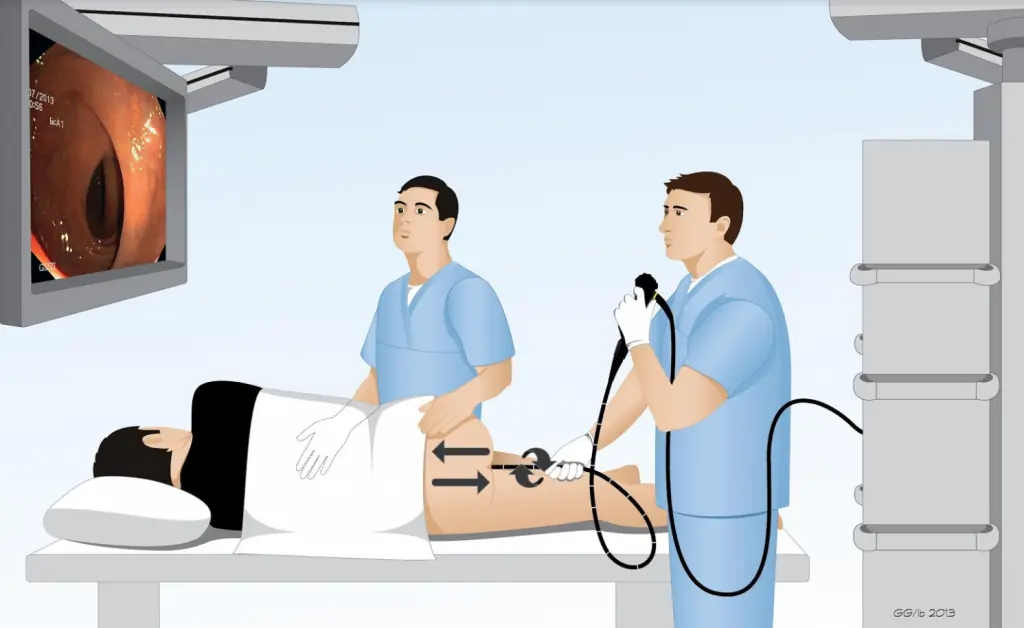
There’s one critical thing to clarify before your colonoscopy - don’t skip it
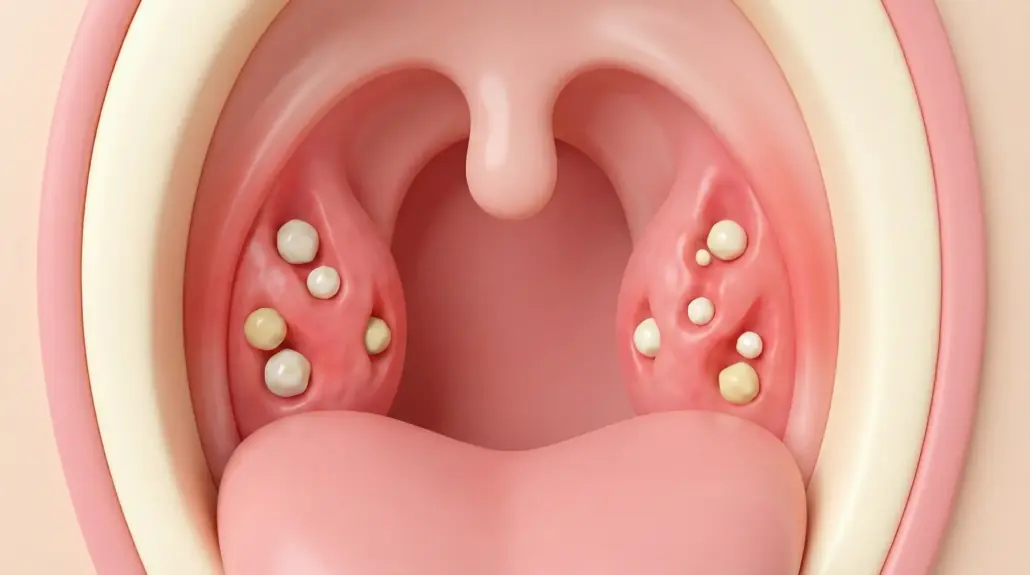
The Truth Behind Those Smelly “White Stones” in Your Mouth
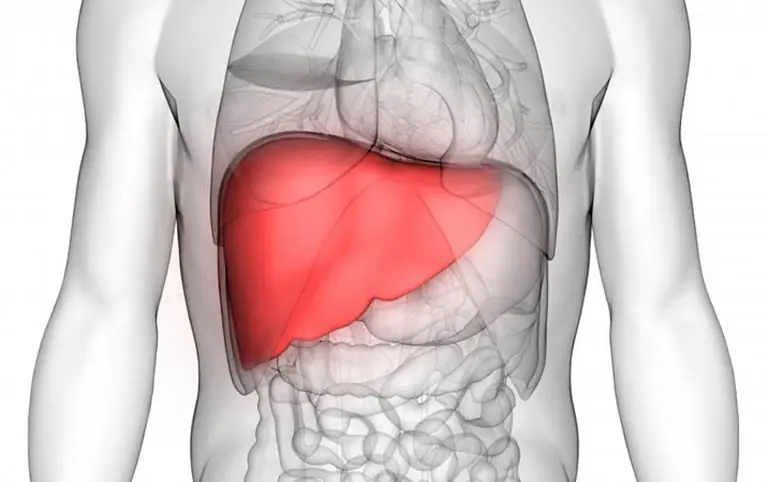
5 red flags that could signal advanced liver dis.ease

The top five golden foods that support a strong, healthy heart

Want a sharper memory? Adding an egg to your day might be a smart move

Medical Experts Share Insights on the Impact of Eating Okra

Waking Up With These 3 Nighttime Signs? Experts Say It’s Time for a Medical Checkup
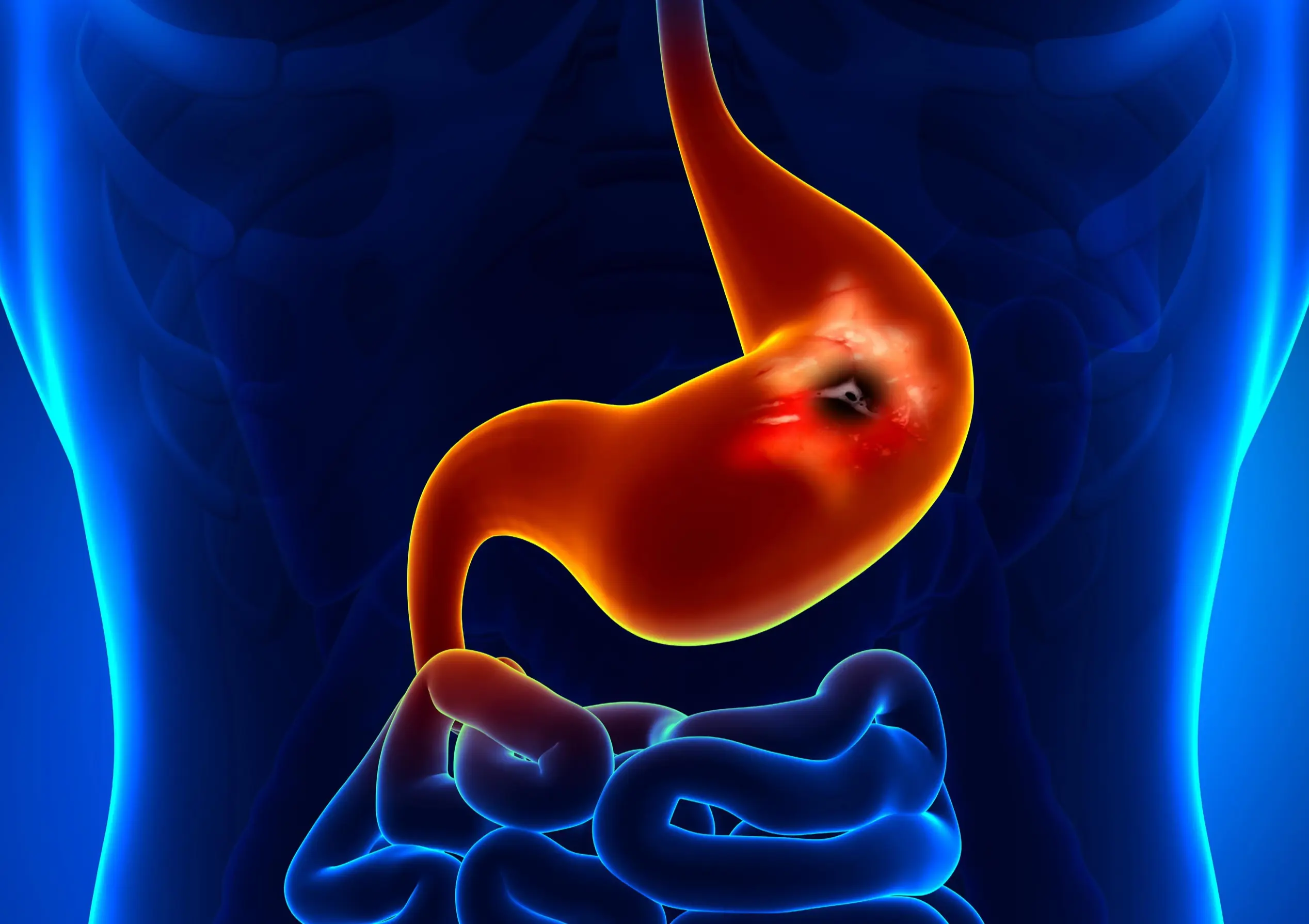
6 Subtle Symptoms of Stomach Cancer to Watch for Early

Think Pumpkin Seeds Are Always Healthy? Think Again

Do You Nap During the Day? Here’s What You Should Know
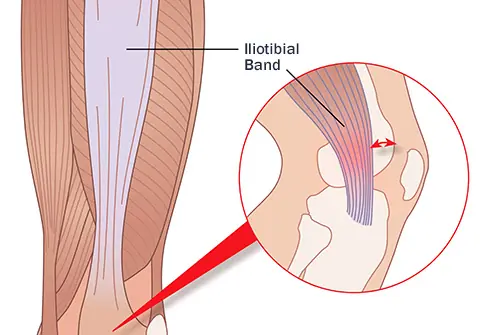
Posterior Knee Pain: When It May Indicate a Serious Condition

8 Landscaping Choices That May Encourage Snakes to Hide Nearby

The Truth About Tilapia: Is It as Healthy as You Think?

10 Habits Often Seen as Rude That May Reflect Intelligence
Are These Chicken Parts Safe to Eat? What Experts Say

Frequent Ringing in the Ears? Here’s What It Could Indicate

Understanding Moles on the Lip: Possible Causes and Concerns
Got a Large Spot on Your Skin? Here’s What You Should Know
Seeing Strange Bruises on Your Body? Read This First
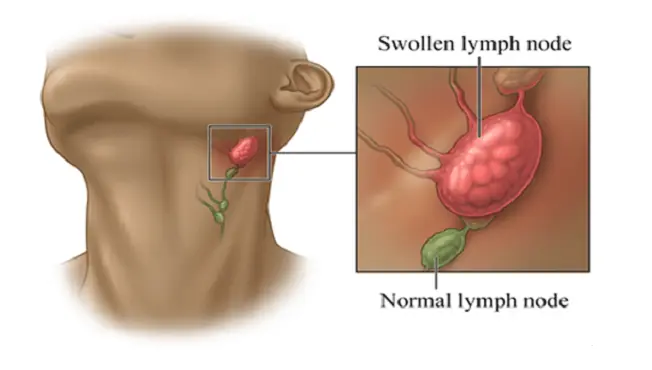
Clinical Red Flags for Swollen Lymph Nodes in the Neck